EEE 302 Electrical Networks II Dr. Keith E. Holbert Summer 2001
advertisement

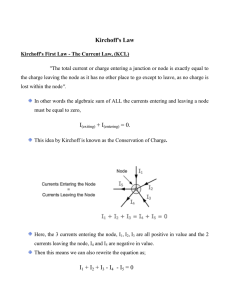
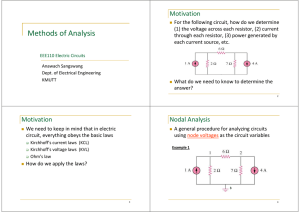
EEE 302 Electrical Networks II Dr. Keith E. Holbert Summer 2001 Lecture 2 1 Circuit Analysis Techniques • • • • While Obeying Passive Sign Convention Ohm’s Law; KCL; KVL Voltage and Current Division Series/Parallel Impedance combinations Z series Z1 Z 2 Z N Z j 1 1 1 1 1 Z par Z1 Z 2 ZM Zi Lecture 2 2 Kirchoff’s Current Law (KCL) i1(t) i5(t) i2(t) i4(t) i3(t) The sum of currents entering the node is zero: n i (t ) 0 j 1 j Analogy: mass flow at pipe junction Lecture 2 3 Kirchoff’s Voltage Law (KVL) + + v(t)1 v(t)2 - + v(t)3 - - • The sum of voltages around a loop is zero: n v j 1 j (t ) 0 • Analogy: pressure drop thru pipe loop Lecture 2 4 In General: Voltage Division Consider N impedances in series: Zi VZ i VS k Z j Source voltage(s) are divided between the resistors in direct proportion to their resistances Lecture 2 5 In General: Current Division Consider N impedances in parallel: I Z j I Sk 1 Z par Z par Zj 1 1 1 1 Z1 Z 2 ZN Zi Special Case (2 resistors in parallel) I Z1 Z2 IS Z1 Z 2 Lecture 2 6 Class Example • Extension Exercise E8.12 Lecture 2 7 Steps of Nodal Analysis 1. Choose a reference node. 2. Assign node voltages to the other nodes. 3. Apply KCL to each node other than the reference node; express currents in terms of node voltages. 4. Solve the resulting system of linear equations. Lecture 2 8 Class Example • Extension Exercise E8.13 Lecture 2 9 Steps of Mesh/Loop Analysis 1. Identify mesh (loops). 2. Assign a current to each mesh. 3. Apply KVL around each loop to get an equation in terms of the loop currents. 4. Solve the resulting system of linear equations. Lecture 2 10 Class Example • Extension Exercise E8.14 Lecture 2 11 Nodal and Loop Analyses Nodal Analysis Recipe 1&2) Identify and label N nodal voltages plus the ground node (V=0) 3) Apply KCL at N nodes (supernode makes constraint eq.) 4) Solve for the nodal voltages Loop Analysis Recipe 1&2) Identify and label N mesh currents 3) Apply KVL at the N meshes 4) Solve for the mesh currents Lecture 2 12