Nominative and Genitive Cases
advertisement

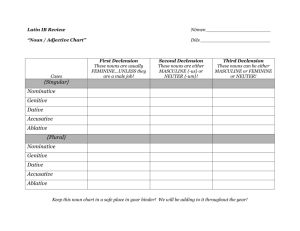
Nominative and Genitive Cases I. Nominative Case A. Subject__________________________________________________________ B. Predicate Nominative _______________________________________________ C. After verbs of electing or creating: Caesar has been elected consul._______________________________________ Augustus is chosen emperor.__________________________________________ II. Genitive Case A. Possession 1. Julia's house is nearest to the Forum.___________________________________ 2. Flavia's hair is very pretty.____________________________________________ 3. The name of the dictator is long._______________________________________ B. Description 1. The emperor is a man of great virtue.___________________________________ 2. The professor was a man of great knowledge._____________________________ C. Genitive with Adjectives. 1. Hercules was skilled in fighting.________________________________________. 2. The man was desirous of money._______________________________________ 3. Mary was full of grace._______________________________________________ 4. The student was mindful of the laws.____________________________________ Reason: peritus, cupidus, plenus, memor, particeps, avidus, conscius D. Genitive of the Whole/Partitive Genitive 1. There is enough water in the jar._______________________________________ 2. There is no wine on the table. ________________________________________ 3. We walked two miles.________________________________________________ cf. We walked a mile._________________________________________________ 4. They saw three thousand soldiers.______________________________________ cf. They saw a thousand soldiers.________________________________________ Reason: satis, nihil, more than one thousand Exceptions: With cardinal numbers, ex, de, pauci, and quidam use the ablative case instead (Ablative of Separation). one of(from) the soldiers__________________________________________________ a few of the men ______________________________cf. a few men_______________ certain ones of the students________________________________________________ Nominative and Genitive Cases E. Objective Genitive 1. The love of money is the root of evil._____________________________________ 2. the love of your country___________ 3. the love of your mother_____________ F. Genitive of Definite Measurement 1. a ten-foot wall ________________________________________ 2. a three-hour test________________________________________ G. Genitive of Indefinite Value 1. It is worthless.________________________________________ 2. It is of such great importance._________________________ 3. It is worthwhile._______________________________________ Reason: magni, tanti, parvi H. Genitive after Verbs of Remembering and Forgetting Reason: memini, obliviscor 1. Forget murder and fire. _______________________________________________ 2. Do you remember his name?____________________________________________ N.B. With words denoting things, the accusative case may be used instead. To remember the past. Praeterita meminisse. I forgot that. _________________ I. Genitive with Verbs of Judicial Action. I condemn myself of inactivity and negligence.________________________________ J. Genitive with Impersonal Verb. Follow this pattern: Accusative of the person who feels and the genitive of the person to whom the feeling is directed. 1. I pity the sailor._______________________________= It pities me of the sailor. 2. The children tire me._____________________________________ 3. I am ashamed of his deed.____________________________ Reason: miseret=___________ taedet=______________, piget=___________ paenitet=__________, pudet=_______________ Nominative and Genitive Cases 1. (Italia, Italiae, Italiam) est mea patria. _____________________ 2. Caesar (dictator, dictatoris, dictatorem) creatus est. _____________________ 3. Mucius appellatus est (Scaevola, Scaevolae,Scaevolam) ________________ 4. Populus Fabium (dictator, dictatoris, dictatorem) creavit. _____________________ 5. Nomen (mater, matris, matri) Gracchorum erat Cornelia. _____________________ 6. Catilina cupidus (imperium, imperi, imperio) erat. ________________ 7. Cicero erat vir magnae (virtus, virtutis, virtute). _____________________ 8. Non est satis (aqua, aquae, aquam) in flumine. _____________________ 9. Ambulavimus mille (passus, passuum, passibus). _____________________ 10. Cucurrimus sex milia (passus, passuum, passibus). _____________________ 11. Pauci ex (viri, viris, viros) discesserunt. _____________________ 12. Duo ex (amici, amicos, amicis) eum servaverunt. _____________________ 13. Amor (mater, matris, matri) est fortis. 14. four-foot wall murus quattuor (pedibus, pedes, pedum) ________________ _____________________ 15. It is worthless. Est (parvum, parvi, parvo). _____________________ 16. Obliviscere (timor, timorem, timoris). _____________________ 17. Oblita est (multi, multa, multis). ________________ 18. Miseret me (puer, pueri, puerum) _____________________ 19. Paenitet me (factum, facti, facto). _____________________ 20. Croesus erat clarus (rex, regis, regi) _____________________ 21. Tullia facta est (regina, reginae, reginam). _____________________ 22. Nomen (dictator, dictatoris, dictatori) erat Cincinnatus. ________________ 23. Imperator erat vir (sapientia, sapientiae, sapientiam). _____________________ 24. Maria erat femina plena (gratia, gratiae, gratiam). _____________________ 25. Sempronia erat memor (caedis, caedi, caedem). _____________________ 26. Erat nihil (loquendi, loquendo, loquendum) in classe. _____________________ 27. Sallustius erat peritus (scribendi,scribendo, scribendum) _____________________ 28. Unus ex (milites, militum, militibus) mortuus est. _____________________ 29. Piget nos (liberi, liberorum, liberis) 30. Amor (pecunia, pecuniae, pecuniam) est malus. ________________ _____________________