UNITED REGIONAL WORKSHOP ON CENSUS CARTOGRAPHY AND
advertisement

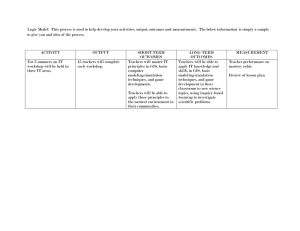
CARICOM UNITED NATIONS REGIONAL WORKSHOP ON CENSUS CARTOGRAPHY AND MANAGEMENT : CENSUS MANAMGENT AND PLANNING WITH THE USE OF GIS Port of Spain 22-26 Oct 2007 OVERVIEW OF PRESENTATION • Introduction • What is GIS and the Benefits • Census Management and Planning with the use of GIS in 2000 Round • Country Experience • Major Challenges • Recommendation for the way forward • Conclusion INTRODUCTION • The Caribbean Community (CARICOM) comprises 15 Member States and 5 Associate Members • The countries of the Caribbean Community (CARICOM) have a long history of conducting population censuses • Appreciable • regional collaboration and coordination in conducting population censuses have existed over the years. What is GIS Geographic Information System or GIS is a collection of computer hardware, software, geographic data and personnel assembled to capture, store, retrieve, update, manipulate, analyse and display geographically referenced information. How is it applied • Cartographic segmenting activities are developed within census preparatory tasks and consist of executing a set of different field and office tasks, directed towards dividing the territory of each district of the country into work areas (Enumeration Districts) which shall be assigned to various census officials (Enumerators and Supervisors) during the Survey stage. What are the benefits The data integration functions provided by GIS, for example linking of information from many different subject matters have led to a wider use of statistical information in the Caribbean region. What are the benefits • Cartographic presentation of census results using GIS provides a powerful means for visualizing the results of census. • Maps are integral part of policy analysis in the public and private sectors in the region. What are the benefits • In addition to enabling more efficient production of enumerator maps and thematic maps of census results, Geographic Information System (GIS) now plays a key role in census data analysis and dissemination Census Management and Planning with the use of GIS in 2000 Round In the framework of the preparatory tasks of the 2000 Round of Censuses, some Member States and Associate Member States in The Caribbean Region embarked on developing digital mapping and applying Geographic Information System (GIS). Management and Planning with the use of GIS 2000 Round During the 2000 Round of censuses GIS was new in the region and not all Member States had the technology The extent to which Member States used GIS in the 2000 Round of Censuses differ from country to country but mostly centred on work load allocation. Management and Planning with the use of GIS in 2000 Round Effort were made by Member States to ensure that common GIS technology were used The main software used is ArcGIS. COUNTRY EXPERIENCE • Group 1: St Lucia, Trinidad & Tobago - GIS for Mapping, workload allocation, analysis and dissemination and has functional Cartographic Unit. In addition, St Lucia will use GPS technology in 2010 Round. • Group 2 Anguilla, Cayman Islands, OECS, Jamaica and Bermuda - GIS for mapping • Group 3 – Introductory to GIS: Guyana, Suriname, Bahamas, - Introduced to GIS and will be used in 2010 Round Major Challenges Arising out of the experience of the 2000 Round of Censuses on the use of GIS were the following challenges: • Acquisition Cost – Funding of Equipment and software • Availability of Technical Expertise • Retention of Qualified Staff to manage Project • Rapid Change of Technology Recommendation for the way forward The Caribbean Community and the Member and Associate Member States hope to improve and consolidate on the support and cooperation for the forth coming 2010 Round. Recommendation for the way forward Successful implementation of GIS for management and planning of 2010 Round of Censuses requires the following: • A detailed assessment of the status and need for assistance of Member States; • Strengthening of the regional coordination mechanism; • Providing advisory and technical support; Recommendation for the way forward Training in vital areas (and updated versions) in the use of GIS. Tertiary Institutions in the region to expand Geography/Cartography programs to include GIS to train more persons to better respond to market and labour requirements in the region Procuring of key equipment and software for use by Member and Associate Member States. conclusion Note the benefits and successful application of GIS in some Member States; Note the challenges arising from the 2000 Round of Censuses. A more improved, sustained and aggressive efforts on the application of GIS in the Region in the 2010 Round. CARICOM THANK YOU THE END