Document 16608125
advertisement

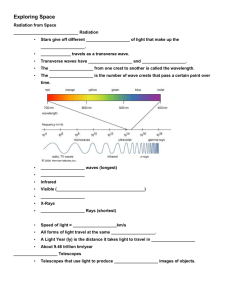
Ch 22 Exploring Space Radiation from Space Photons of light travel in waves just 380 to 750 nanometers (millionths of a millimeter) long. Electromagnetic Radiation • Stars give off different wavelengths of light that make up the spectrum. • Light travels as a transverse wave. Light is the fastest thing in the Universe, traveling at 299,792,458 meters per second. Light rays always travel in straight lines. • Transverse waves have crests and troughs. • The distance from one crest to another is called the wavelength. • The frequency is the number of wave crests that pass a certain point over time. crest wavelength trough The longest light waves you can see are red, and the shortest are violet • Radio waves (longest) • • • • • • Microwaves Infrared Visible (R.O.Y.G.B.I.V.) Ultraviolet X-Rays Gamma Rays (shortest) Light rays change direction as they pass from one material to another. This is called refraction • Speed of light ≈ 300,000 km/s • All forms of light travel at the same speed. • A Light Year (ly) is the distance it takes light to travel in one year. • About 9.46 trillion km/year According to Einstein's theory of special relativity objects gain mass as they speed up, and that speeding up requires energy. The more mass, the more energy is required. By the time an object reached the speed of light, Einstein calculated, its mass would be infinite, and so would the amount of energy required to increase its speed. To go beyond the infinite is impossible. Optical Telescopes • Telescopes that use light to produce magnified images of objects. Galileo had to leave the university because he ran out of money but his brilliant treatises on physical laws earned him a series of teaching posts at Italian universities Refracting Telescopes Refraction is the bending of light as it passes through different materials. A convex lens is used to bend the light and is magnified. Galileo built the 1st refractor. One day in 1608 a Dutch spectacle maker named Lippershey held a lens in each hand and peered through both at once, accidentally discovering that 2 lenses placed in line would magnify an image. He mounted a lens at each end of a tube and invented the telescope. Refraction & Refracting Telescopes Reflecting Telescopes Telescopes that use concave mirrors to reflect the light from an object to a focal point. All things being equal, the telescope that is easiest to set up is the one that'll get used by amateur astronomers. Forget about magnification when buying a telescope. The size of the lens or mirror is WAYYYYY more important! Hubble Space Telescope Launched in 1990 Placed in high Earth orbit, free of atmospheric distortion. You are not going to see anything remotely like what you see on the NASA websites or on calendars and posters through a telescope at home. Those images were taken by multi-million dollar spacecraft that were processed by a team of scientists whose job is to make pretty pictures. With the exception of the planets and the Orion Nebula, you're going to see a smudge of light through even the largest amateur telescopes. Radio Telescopes Used to map the Universe Detects objects Search for signs of intelligent life on other planets Early Space Missions To leave orbit, spacecraft must move faster than 11 km/s Newton’s Laws of Motion Law of Inertia An object in motion will stay in motion, an object at rest will stay at rest. An outside force will change the inertia. Inertia Law of Acceleration (Force) An accelerated mass creates force. F = ma Newton (N) = kg • m/s2 a Law of Action/Reaction For every action (force), there is an equal action in the opposite direction. Reaction Action Rocketry Solid Fueled Rockets Solid fueled rockets were invented by the Chinese. Difficult to control Liquid Fueled Rockets Dr. Robert Goddard successfully launched the first liquid fueled rocket in 1926. Rocketry is based on Newton’s 3rd Law of Motion Action Reaction • Notable Rockets: German V-2 Rocket of WWII USA Saturn V Rocket for the Moon missions. Only one Gemini capsule was given a name , the first capsule was called Molly Brown by Astronaut Gus Grissom. Apollo Artificial Satellites • Satellites are objects that orbit around another large object. • Sputnik I was the 1st satellite to orbit Earth (Russia, 1957) • Hundreds of satellites orbit the Earth today (weather, GPS, communications, etc.) • Satellites maintain their orbit as a result of gravity & inertia counteracting each other. • “Falling around Earth” Inertia Resulting Orbit Gravity Space Probes • Satellites with instruments that travel away from the Earth. • Some orbit distant objects while others land on surfaces. Galileo studied Europa (one of 61 moons of Jupiter), Europa may have an ocean and heat under it’s ice. Maybe life! • Notable Space Probes: Mars: • Vikings I & II (1974) • Mariner Program (Mercury, Venus also) • Mars Pathfinder w/ rover (1998) • Spirit & Opportunity (2004) Venus: • Venera program (1960s-1970s) • Magellan Program Outer Planets & Objects • Voyagers I & II • Galileo (Jupiter) • Cassini-Huygens (Saturn & Titan) • New Horizons (Pluto) • Stardust probe (comet) • NEAR-Shoemaker (asteroids) Manned Space Missions Yuri Gagarin was the first person in space! Alan Shepard was the first American in space. Neil Armstrong was the first person on the moon. Who was second? Space Shuttle Program • A set of reusable, Earth orbiting spacecrafts by NASA. • First launch in 1981 (Columbia) • Other space shuttles include: Challenger Discovery Atlantis Endeavour Challenger Disaster Shuttle blew apart 73 seconds into its mission. (January 1986) Columbia Disaster Shuttle broke apart during re-entry to the Earth’s atmosphere 16 minutes before landing (February 2003) • The shuttles will be decommissioned in 2010 to prepare for missions to the moon. • (Endeavour was originally scheduled to be decommissioned in 2010 after 18 years of service, but on July 1, 2010, NASA released a statement saying the shuttle Endeavour mission was rescheduled for February 27, 2011, instead of late November, 2010.)[ Space Stations U.S. Skylab (1973-1979) U.S. only solo attempt at building a space station. Study the effects of living & working in space. Crashed into the Indian Ocean in 1979 Mir (1986-2001) Russia’s 7th space station Only supposed to last 5 years. De-orbited in 2001 into the Pacific Ocean International Space Station (ISS) Construction began in space in 1998 16 countries involved Support 7 crew members for 3-6 months when finished.