Final Study Guide
advertisement
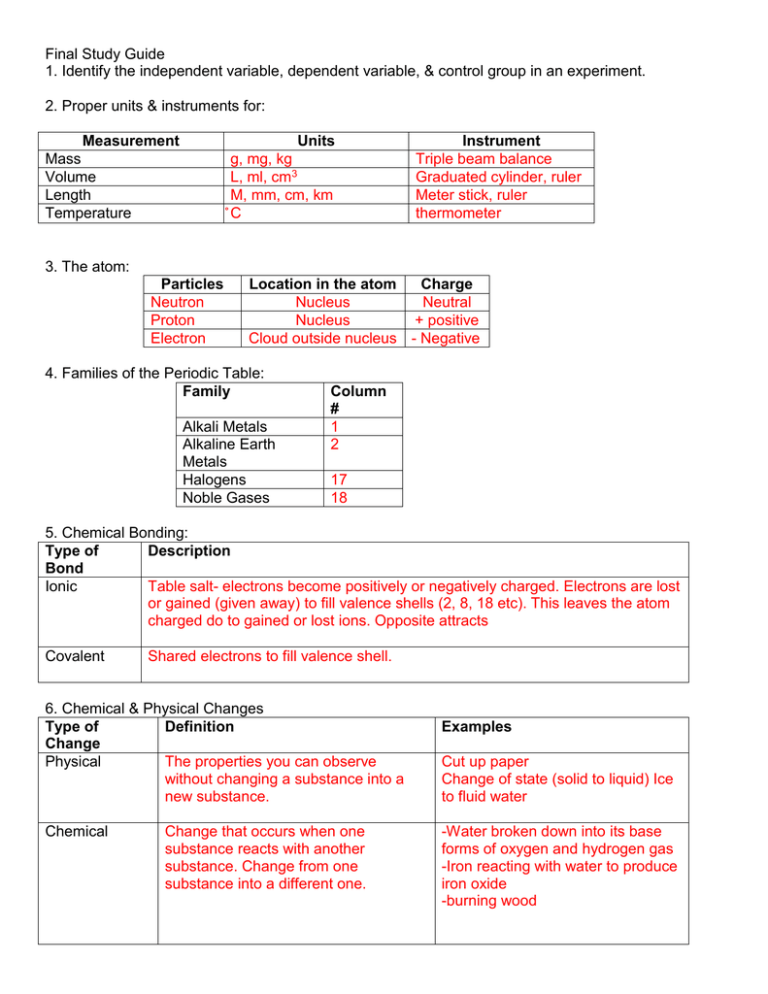
Final Study Guide 1. Identify the independent variable, dependent variable, & control group in an experiment. 2. Proper units & instruments for: Measurement Mass Volume Length Temperature Units g, mg, kg L, ml, cm3 M, mm, cm, km ̊ C Instrument Triple beam balance Graduated cylinder, ruler Meter stick, ruler thermometer 3. The atom: Particles Neutron Proton Electron Location in the atom Charge Nucleus Neutral Nucleus + positive Cloud outside nucleus - Negative 4. Families of the Periodic Table: Family Alkali Metals Alkaline Earth Metals Halogens Noble Gases Column # 1 2 17 18 5. Chemical Bonding: Type of Description Bond Ionic Table salt- electrons become positively or negatively charged. Electrons are lost or gained (given away) to fill valence shells (2, 8, 18 etc). This leaves the atom charged do to gained or lost ions. Opposite attracts Covalent Shared electrons to fill valence shell. 6. Chemical & Physical Changes Type of Definition Change Physical The properties you can observe without changing a substance into a new substance. Chemical Change that occurs when one substance reacts with another substance. Change from one substance into a different one. Examples Cut up paper Change of state (solid to liquid) Ice to fluid water -Water broken down into its base forms of oxygen and hydrogen gas -Iron reacting with water to produce iron oxide -burning wood 7. What are the 5 traits that define a mineral? -naturally occurring -inorganic -definite chemical composition -crystalline -solid 8. Mineral Physical Properties: Property Definition Luster The way a mineral reflects light Streak Hardness Cleavage Fracture Example Shiny, metallic, dull, pearly, silky, glassy, opaque, etc Powder left behind Gold= yellow, pyrite=greenish blue Graphite=grey How easily the mineral can be scratched Diamond=10 Talc=1 Minerals break along smooth flat Mica surfaces Minerals break uneven rough or jagged edges quartz 9. How does the Law of Conservation of Mass apply to the Rock Cycle? Rocks cannot be created or destroyed. They can just change into other types of rocks or become magma-The rock cycle 10. Rock Types: Type Definition Igneous Formed from magma that cools and hardens. Metamorphic Rocks that have changed because of temperature and pressure or the presence of hot watery fluids Sedimentary When sediments are pressed together and cemented or minerals form from solution. 11. Which layer of soil must be present for grass to grow? Topsoil Classification Groups Intrusive Extrusive Foliated-mineral grain parallel layers (slate) NonfoliatedDetrital- made from broken fragments (sandstone) Chemical-dissolved minerals from soln. (limestone rock salt) Organic=chalk and coal 12. Weathering & Erosion: Definition Erosion Process that wears away surface materials and moves them to another place Mechanical Physical process that breaks rocks Weathering apart Chemical Weathering Chemical rxn that dissolve minerals in rocks and changes them into another substance Examples Gravity, water, glaciers, wind Ice wedging, plant roots, animals Carbonic acid-water reacts w/ CO2 Caves form when calcite dissolves 13. What is an ice age? Period of widespread glaciation 14. What factors will affect the amount of runoff in an area? Amount of rain and length of time it falls, steepness or slope of the land, amount of vegetation 15. How is a cave formed? Groundwater dissolves limestone 16. Volcanoes: Volcano Type Shield Description Quiet eruptions of basaltic lava spread in flat layers-Hawaii, Olympus Mons (Mars) Cinder cone Explosive eruptions, tephra dropped, steep sided, loosely packed(Paricutin the Mexico cornfield volcano) Composite Varied between quiet (dormant) and violently explosive, alternating layers, found mostly where plates converge- Pelée, Vesuvius, Pinatubo, Mt. St. Helens Super volcano A kind of composite volcano with longer periods of dormancy and much bigger explosions, world-wide consequences when an eruption occurs – (Yellowstone, Toba) 17. What is metamorphism? Change in a rock due primarily to heat and pressure. 18. What is the Theory of Plate Tectonics? The Earth’s crust and part of the upper mantle are broken into sections. Plates move on plastic-like layers of mantle. 19. What evidence is used to support the Theory of plate Tectonics? Continental drift, seafloor spreading, fossil clues, rock clues, magnetic clues, puzzle-like fit of the continents. 20. Plate Boundaries: Boundary Definition Transform Sliding past each other (North American plate and the Pacific plate around California) Divergent Plates moving apart. (seafloor spreading) Convergent Plates moving together. Builds mountains. (Himalayas) Subduction zones. (Andes Mountains at the Nazca and South American plate) Diagram 21. What may have caused the extinction of the dinosaurs? Comet or asteroid colliding with the Earth. This would create a massive, world-wide dust cloud that would block sunlight leading to a breakdown in the food chain. 22. What conditions will increase the possibility of something becoming fossilized? Buried quickly, have hard parts (shell, bones, teeth); make sure scavengers don’t eat the carcass. 23. What is the Principle of Superposition? In undisturbed layers of rocks the oldest rocks are on the bottom, becoming progressively younger as you go to the top. 24. What is half-life & how can it be calculated? The time it takes for half of the atoms in the isotope to decay. 25. Where are the focus& epicenter located during an earthquake? Focus-point of the earthquake where the energy is released Epicenter- point directly above the focus on the Earth’s surface 26. During which era & period did the largest extinction in Earth’s history occur? Paleozoic Era, Permian Period, Table p 393 27. Which type of seismic wave will reach a seismograph first? Second? Primary waves arrive first, secondary waves arrive second, L waves last (most destructive) 28. Laws of Motion Law Definition (1st) Law of Every object in a state of uniform motion Inertia tends to remain in that state of motion unless an external force is applied to it. Example In a car crash, you can fly through the windshield if you don’t use seatbelts (2nd) Law of Acceleration The relationship between an object's mass m, its acceleration a, and the applied force F is F = ma. Acceleration and force are vectors (as indicated by their symbols being displayed in slant bold font); in this law the direction of the force vector is the same as the direction of the acceleration vector. i.e. the heavier on object is, the more force required to move it Pushing a car requires more force to push it 10 meters than an empty shopping cart requires (3rd) Law of Action/Reaction For every action there is an equal and opposite reaction. Rocket launch, when you push on a table, it pushes you back 29. What causes the Earth to experience seasons? Tilt of the Earth’s axis – hemispheres tilted towards sun=summer 30. What causes the phases of the Moon? The relative position of the sun, Earth, and moon. New Moon-Moon is between the sun and the Earth (up during the day) so it isn’t visible at night 31. What shape is the Earth’s orbit around the Sun & where is the Sun positioned? Elliptical- Sun a little towards one end (ovoid shape) 32. What is the difference between the Terrestrial planets & the Jovian planets? Terrestrial planets- closer to the sun, rocky in nature, solid Jovian planets- Farther from the sun, gas giants 33. Hertzsrung – Russell Diagram: Where are the brightest & hottest stars found on the diagram? Top right i.e. Betelgeuse Where are the dimmest & coolest stars found on the diagram? Bottom right What are most of the stars in the Universe classified as? Main sequence 34. At which point during stellar evolution does a star become stable? When it enters the main sequence 35. What wavelength of light does the Ozone layer protect us from? Ultraviolet (UV) 36. What two major gases make up the Earth’s atmosphere & what are their percentages? O2=21% N=78% 37. What gas is said to cause the greenhouse effect? CO2 38. What causes low air pressure? High air pressure? Warm air-low Cold air-high 39. What causes air to move from one place to another? Rotation of the Earth, uneven heating of the Earth, and differences in air pressure 40. Fronts: Front Description Warm Warm air rises up over cold dense air Cold Cold air goes below warm air and pushes it up Stationary Cold front next to warm front Dry Line boundary that separates a moist air mass from a dry air mass Type of Weather Light rain Thunderstorm Rain Wind and rain for several days Big differences in dew point temperature Big storms 41. How do you use a psychrometer? Wet bulb/dry bulb- spin for 1 ½ minutes then record temperature. Find the relative humidity and dew point on a table.




