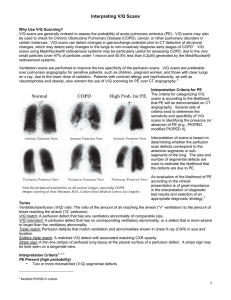
Electrical Impedance Tomography for Assessing Ventilation/Perfusion Mismatch for Pulmonary Embolism Detection without
advertisement

Electrical Impedance Tomography for Assessing Ventilation/Perfusion Mismatch for Pulmonary Embolism Detection without Interruption in Respiration D T Nguyen1, A Thiagalingam2 , A Bhaskaran2, M A Barry2, J Pouliopoulous2, C Jin1 and A McEwan1 1 School of Electrical and Information Engineering, The University of Sydney, New South Wales, Australia 2 Department of Cardiology, Westmead Hospital, New South Wales, Australia Outline • • • • • • Motivations Overview Materials and Methods Results Discussion Future works Motivation • Pulmonary perfusion is important: – Pulmonary embolism (PE) • together with VTE: fifth most cause of death in Australia – Pulmonary Artery Hypertension, etc. • Electrical Impedance Tomography of the lung: – Highly valuable tool for ventilation monitoring • Why not pulmonary perfusion too? – Possible but hard! – Low signal to noise ratio (SNR) (with blood pulsatile signal) • Borges et al. 2012 and Frerichs et al. 2002: – – – – Contrast impedance bolus based on hypertonic NaCl to improve SNR 10 ml of 20% NaCl and 5.6% NaCl, respectively Medium animal study (23 kg piglets) 2 minutes of apnea Pulmonary Embolism • 1.08 in 1000 people affected • Pregnant, hospitalized patients are at 100 times higher risk • Non-specific symptoms: chest pain, shortness of breath • No positive predictive molecular marker: D-dimer test • Imaging diagnosis: CTPA and V/Q R A Douma et al. (2010) CTPA scan (W S Choe et al. (2011)) V/Q Scan (Wikipedia) Overview of this study • Use of contrast enhanced EIT for V/Q scan • Low concentration saline as contrast – 60 ml of 3% saline solution • No apnea • Artificially induced PE in large ovine model (N=3, 83.7 ± 7.7 kg ) Materials and Methods • Animal: – Ovine model: 3 males, Merino cross, 83.7 ± 7.7 kg, healthy – Mechanically ventilated (inspiration to expiration ratio of 1:1.5) – Under general anesthesia Materials and Methods (cont.) • Agilis catheter (St Jude Medicals): – From right femoral vein to IVC for contrast injections • Electrode rings: – 32 electrodes for EIT – Novel multi-point, bronze coated electrodes Materials and Methods (cont.) • Pulmonary embolism induction: – Artificially induced – Balloon catheter blocking blood supply in one the of pulmonary arteries • 3 Injection repetitions with PE and 3 without Before Balloon inflation Balloon inflated Balloon deflated Methods • EIT: – Swisstom Pioneer, 32 electrodes – 5 mA, 100 kHz – 10 frames per second • GREIT reconstruction (EIDORS 3.7, Matlab 2014a) a 64 x 64 rasterized image/frame • Time difference: v = v(t)- v0 • 2.5 D model 2 1.5 L R 1 0.5 0 4 3 2 1 2 0 1 0 -1 -1 -2 -2 -3 -3 Posterior EIT image analysis Raw EIT Image series • 64 x 64 • Ventilation + Contrast dilution • Daubechies level 4 Filtered • 8 level decompositions EIT image • Only keep levels 7 and 8 series • Using ventilation signal • Thresholding of FFT within ROIs definition respiration range • For each ROI (left or right lung) • Ventilation: sum of all frequencies within respiration Ventilation range (of raw series) and Perfusion • Perfusion: from filtered series estimation • Averaged V and Q for each ROI R L Results – Perfusion at baseline R Dorsal Results – Perfusion with defect (right lung PE) R Dorsal Results - Ventilation Baseline R Dorsal Right Lung PE Results – Change in Perfusion due to PE R Dorsal R Dorsal Quantitatively • Compute and compare right lung to left lung (R2L) V and Q in each state (PE and baseline) of all subjects. • Significant change in perfusion • Reduction in R2L because of right lung PEs • Insignificant change in ventilation • S3: imbalance in ventilation but normal perfusion Discussion • Contrast dilutions at each pixel after filtering is similar to literature • Dilution curve can be extracted with filtering • In three subjects with induced PE, we showed that contrast enhanced EIT can detect the change in perfusion Future works • This is a pilot study for proof of concept • Lots more to be done: – Localization of the defects – Superimpose perfusion and ventilation images – More data required for optimization of the algorithm sensitivity and specificity – Gold standard comparison • But it’s worth it: – Diagnosis of PE in “difficult patients” (renal problems, pregnant, highly instrumented, etc.) – Monitoring during treatment – Radiation free routine check for at risk patients Thanks • To my co-authors • Westmead Vivarium and research holding staffs • And past colleagues: – Dr William Chik – Dr Roman Kosobrodov • Supporting organizations: – University of Sydney, Westmead and ARC grant Thank you for listening !!!