Chapter 11 - Water Section 2 Notes
advertisement

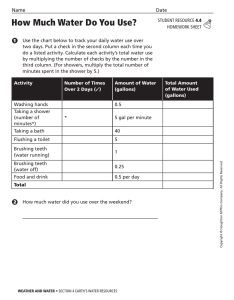
Chapter 11 - Water Section 2 Notes Did you know???? • According to the World Health Organization, more than 1 billion people lack access to a clean, reliable source of fresh water. Three Major Uses for Water • Residential • Agricultural • Industrial • See p. 277 Fig 5 • Which of the three major uses of water is used the most in almost all countries? • In how many countries does industrial use out number residential use? Which countries? Residential Water Use • The average person in 100 90 80 Water in Liters • the US uses 80 gallons of water per day. Half of this usage is for personal use the rest is for outside the home activities. Daily Water Use in the US Per Person 70 60 50 Series1 40 30 20 10 0 Law n Cooking w atering Toliet Brushing & Bathing Cleaning Flushing Teeth and Drinking pools 95 90 70 10 20 10 Series1 Uses Other 5 • Looking at this graph. Come up with 3 ways to decrease the number of liters used by each person in the US. Daily Water Use in the US Per Person 100 90 Water in Liters 80 70 60 50 Series1 40 30 20 10 0 Law n Cooking w atering Toliet Brushing & Bathing Cleaning Flushing Teeth and Drinking pools 95 90 70 10 20 10 Series1 Uses Other 5 Water Treatment • Potable – • Pathogens – • Bacteria, viruses, protozoa, and parasitic worms are common pathogens. • Water Treatment Worksheet Industrial Use • Accounts for 19% of the water used in the world. • Used to manufacture goods, dispose of waste, and generate power • Most water in industry is used to cool power plants (ie. powerton) • http://maps.google.com Agricultural Water Use • Accounts for 67 % pf the water used in the world. • It can take 300 L of water to produce one ear of corn. • 80% of the water used in agriculture evaporates and never reaches the plant roots. • Irrigations – Waste Management Projects • Nearly 2000 years ago, Romans built aqueducts to dry areas. • Examples are dams, and water diversion canals. • Goals: bringing water to a dry area, creating a reservoir for recreation or drinking water, generating electric power. Dams & Reservoirs • Dam – • Reservoir – • Advantages & Disadvantages to Dams - Water Conservation • In Agriculture – most comes from evaporation, seepage, and runoff – Drip irrigations • In Industry – recycling of cool water and wastewater – Pay business to conserve water Water Conservation • In Home – although it is a same % of use, any conservation of water will help – Take shorter showers – Low-flow toilet – Do not let water run when brushing teeth – Wash only full loads in dishwasher and washing machine – Don’t water lawn or at least sparingly or in the evening Solutions for the Future • Transporting Water – – Advantages: – Disadvantages: • Desalination – – Advantages: – Disadvantages: