– Planning Template Understanding by Design Desired Outcomes UbD Template
advertisement

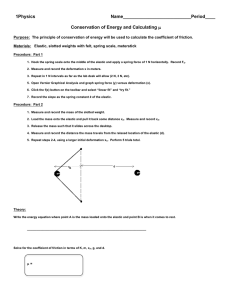
UbD Template Understanding by Design – Planning Template Desired Outcomes Established Goals: Science 7 Unit D: Structures and Forces STS 1 – identify points and modes of failure STS 2 – recognize and use units of force/mass, and identify and measure forces and loads STS 2 – identify tension … within a structure and describe how forces cause a structure to fail STS 3 - devise and use methods of testing strength and flexibility Skills – relationships between and among observable variables Skills – gather and record qualitative and quantitative data Skills – organize data using an appropriate format Skills – analyze data and develop explanations Skills – work collaboratively Established Goals: ICT Outcomes – Div 3 C1 - Students will access, use and communicate information from a variety of technologies 3.5 - analyze and synthesize information to create a product C5 - Students will use technology to aid collaboration during inquiry C6 - Students will use technology to investigate and/or solve problems Enduring Understandings: Essential Questions: “Students will understand that ….” Deformation of a structure depends on the nature and size of the forces applied. Modes of failure of structures are not necessarily dependent on the nature or extent of the deformation. Why do structures fail? Does deformation of a structure necessarily cause the structure to fail? Why does an elastic stretch? Why does it break? Knowledge: “Students will know …” Skills: - mass load on a structure (elastic) creates an applied, deforming, force - “deformation” (def) - “tension” (def) - “modes of failure” (def) - “elastic” (def” - “static” (def) - “independent/manipulated variable” (def) - “dependent/responding variable” (def) - “controlled variable(s)” (def) - work collaboratively to carry out an experimental procedure to investigate the relationship between applied force (mass) and resulting length of an elastic band - record qualitative and qualitative observations and data - use Excel (or other appropriate means) to create a data table of experimental results - use Excel (or other appropriate means) to create a linear graph from the data table - analyze tabular and graphic data to develop possible explanations for observed phenomena “Students will be able to …” Page 1 of 3 UbD Template Assessment Performance Task: Other Evidence: As a team of materials-testing engineers, you will test an elastic structure to determine (1) how the length of the elastic depends on the load applied to stretch the elastic, and (2) the maximum load which can be applied to stretch the elastic before it fails. The results of this test will be presented in a written report including tabular and graphic data. - observation of collaborative team work to design and carry out a procedure - recording of results in an appropriate tabular format - representation of results in a appropriate graphic format - anecdotal record of observations Learning Plan Teaching/Learning Activities: W: You will determine how the length (deformation) of an elastic band depends on the load applied to stretch it, and what load it can support before it breaks (fails). This is important in order to understand the difference between the deformation and failure of an elastic material. H: Can you predict how much mass an elastic an support before it breaks. How is an elastic band like your blood vessels? E: Your team will construct a testing structure as discussed. Make any modifications you decide are necessary to carry out the testing procedure. Use the Excel worksheets on the whiteboard (or another suitable method) to record your experimental results. R: As the testing proceeds, make predictions about the relation of the deformation of the elastic to the applied load and what load you think will cause the elastic to fail (break). Discuss these with your team. Revise and refine these predictions as you gather more information. Discuss your ideas with your team. E: From the data you have collected, use the Excel worksheets on the whiteboard (or another suitable method) to construct an appropriate graph of the testing results. Use this graph and your observations to determine (1) how the length of the elastic depends on the load applied to stretch the elastic, and (2) the maximum load which can be applied to stretch the elastic before it fails. Reflection: Why do you think your blood vessels (especially arteries) need to be able to deform under pressure like an elastic? Page 2 of 3 UbD Template Time 5 Min 5 Min 10 Min 5 Min 15 Min 10 Min 5 Min 5 Min Activity Class Routines and Organization Introductions & VC Etiquette Lesson Introduction, Performance Task Overview, Knowledge and Skills Review Procedure Set-up and Directions Experimental Procedure and Data Collection Sharing and Discussion of Results Wrap-Up Discussion Class Wrap-Up Routines Equipment Required for Each Group: Elastic Band Retort Stand Ring clamp (or suitable alternative) Set of Masses Metre Stick Paper & Pencils Data Management Software: Microsoft Excel spreadsheet and graphing productivity software Web Resources: www.newbaybridge.org/classroom/ www.pbs.org/wgbh/buildingbig/bridge/ www.pbs.org/wgbh/nova/bridge/ Page 3 of 3