Choice Modeling Externalities: A Conjoint Analysis of Transportation Fuel Preferences
advertisement
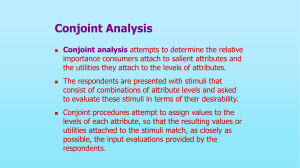
Choice Modeling Externalities: A Conjoint Analysis of Transportation Fuel Preferences Matthew Winden and T.C. Haab, Ph.D. Agricultural, Environmental, and Development Economics The Ohio State University Outline • Motivation • Methodology • Results • Conclusions Motivation • Transportation Fuel Consumption Creates Large Externalities • Market Pricing Mechanism Has Failed -Public Goods Nature of Externalities • Government Correction Has Failed -Regressive Nature of Price Correction -Lack of Political Will Power Motivation • Correct price is necessary to achieve efficiency So, • What are the optimal levels (costs) of externalities to society? • Knowing allows internalization (MSC=MPC) Motivation • Are externality types valued differently? • Impacts on: (1) Human Health Risk Vs (2) Natural Resource Depletion Vs (3) Environmental Damage Motivation Attribute Env. Damage: Examples of Attribute Components Fish and Animal Populations Levels of Air and Water Pollution Nat. Res. Use: Extraction Rates and Stocks for Ores, Minerals, Oil, Natural Gas Hum. Health Risk: Incidence Rate of Asthma & Cancers Motivation • Goals: 1.) Establish Willingness-To-Pay estimates for reductions in damages 2.) Establish Marginal Price estimates for externality classes Methodology: Conjoint Analysis • Estimates the structure of preferences • Specify attributes & bundle into alternatives • Respondent chooses preferred alternative • Resultant choices allow for statistical inference Methodology: Conjoint Analysis • Each alternative represents potential fuel profile (i.e. mix of fuel types used) • Different profiles embody different levels of externalities (attributes) imposed on society • Impacts of profile measureable and capable of aggregation into an index for each externality Methodology: Conjoint Analysis Attribute Env. Damage Levels of Attribute Components 37.5, 45, 50, 55, 62.5 Nat. Res Use 37.5, 45, 50, 55, 62.5 Hum. Health Risk 37.5, 45, 50, 55, 62.5 Price ($/gallon) -10%, -5%, 0%, 5%, 10% Methodology: Conjoint Analysis • Based in RUM Framework • Respondent chooses 1 of 3 alternatives • Attributes: Environmental Damage Natural Resource Usage Human Health Risk Price Methodology: Conjoint Analysis Current Fuel Mix $[GASPRICE] per gallon 100 90 80 70 60 50 40 30 20 10 0 50 50 50 Environmental Damage Natural Resource Use Human Health Risk Methodology: Conjoint Analysis Fuel Mix A 100 90 80 70 60 50 40 30 20 10 0 $[GASPRICE] per gallon 62.5 Environmental Damage 37.5 50 Natural Resource Use Human Health Risk Methodology: Conjoint Analysis RUM framework Vij = V(xij , β) + εij i = individual j = alternative x = vector of attributes and characteristics ε = stochastic error term Methodology: Conjoint Analysis RUM Formalized: Linear and IID Vij = β0 + xij β1 + (Mi - pij) β2 + εij M = Income p = price Methodology: Conjoint Analysis Probability of K chosen over j, for all j≠k Pr(dVij>0) = ϑ (Δ(x) β1 – Δ(p) β2) (See Kanninen 2007) Results Survey Representative Sample of 857 Ohio Adults Completed by 537 (62.5%), 532 useable; met criteria of (1) Adult Resident of Ohio (2) Estimate Vehicle MPG (3) Estimate price of fuel at last fill-up Results • Homeowner, Older, and Driver (more likely) • Price (self-reported) mean = $1.88 min = $1.00 max = $2.99 • Attribute means 49.9(ED), 50.2(NR), 50.3(HH) Results Attribute Price Env. Damage Nat. Res. Use Hum. Health Risk (Environmental Damage)2 (Nat. Res. Use)2 (Hum. Health Risk)2 EnvDam × NatRes NatRes × HumHea HumHea × EnvDam EnvDam×NatRes×HumHea Conditional Logit Parameter Estimates -1.722* -0.099 -0.427* 0.142 -0.0003 0.003* -0.002* 0.003 0.002 0.001 -0.0001 Results Alternative (Difference from Current) 10% Reduction in Each Attribute 25% Reduction in Each Attribute WTP ($/Alternative) $0.84/gal $2.98/gal Attribute Environmental Damage Reduction Natural Resource Use Reduction Human Health Risk Reduction MP ($/Alternative) $0.030/gal $0.035/gal $0.036/gal Conclusions • Demand (WTP) for reduction in externalities related to transportation fuel usage exists • Current (baseline situation) reveals one class of externality is not viewed as more important • Starting point for policy discussions Limitations • Price increase still necessary (political will) • Less impact, result in more driving? • Do respondents accurately understand and value indexes? • Accurate measurement and combination of attribute components into indexes • Uncertainty of externality impacts Future Research • Income element of utility function may be non-linear • Fatigue/Learning Effects • Exploration of demographic differences (mixed logit) • Relaxation of IIA (multinomial probit) Special Thanks • National Science Foundation • Agricultural, Environmental, and Development Economics: The Ohio State University • Wisconsin Economic Association