Unit 3: Adulthood
advertisement

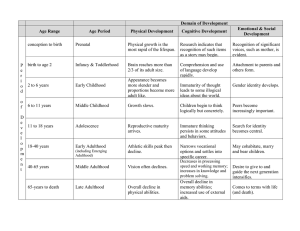
Unit 3: Adulthood Chs. 13-14: Early (18-40), Chs. 15-16: Middle (40-65) , Chs. 17-18: Late (65-death), and Ch. 19: The End of Life Periods of Development Prenatal Conception to birth Infancy and toddlerhood Birth–2 years Early childhood 2–6 years Middle childhood 6–11 years Adolescence 11–18 years Early adulthood 18–40 years Middle adulthood 40–65 years Late adulthood 65 years–death Overview of Early Adulthood Physical Development • Overall athletic skills peak, then slowly begin to decline • Cardiovascular and respiratory capacity and immune system functioning slowly begin to decline • Sexual activity and reproduction peak Cognitive Development • Post-formal cognition • Expertise and creativity improve • Narrowing of vocational options and settling into career Emotional and Social Development • Erikson identifies intimacy as the key task • Moving out of parental home and establishing independence • Most cohabitate, marry and have children • Sibling relationships become more companionate Quiz 13 1. True/False Early adult is a period of senescence, or biological aging. 2. True/False: Age-related declines in athletic skill are almost entirely attributable to biological aging. 3. Men who choose traditionally female occupations, such as nursing or teaching, often a. express regret about their choice. b. have more conservative social views. c. feel stigmatized and questioned about their career. d. report few opportunities for advancement. 4. According to some theorists, cognitive development continues past the periods identified by Piaget, leading to a stage called ________________________________________.