Johannes Kepler T J Osler

Johannes Kepler
T J Osler
Johannes Kepler (pronounced /ˈkɛplɚ/ ) (December 27,
1571 – November 15, 1630) was a German mathematician , astronomer and astrologer , and key figure in the 17th century scientific revolution
The Great Comet of 1577 , which Kepler witnessed as a child, attracted the attention of astronomers across Europe
• In astronomy , Kepler's three laws of planetary motion are:
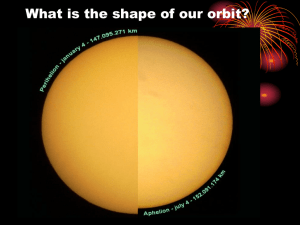
• "The orbit of every planet is an ellipse with the sun at a focus ."
• "A line joining a planet and the sun sweeps out equal areas during equal intervals of time." [1]
• "The square of the orbital period of a planet is directly proportional to the cube of the semi-major axis of its orbit."
Five Platonic Solids
Kepler's Platonic solid model of the Solar system from Mysterium Cosmographicum (1600)
Closeup of inner section of the model
A plate from Astronomiae Pars Optica , illustrating the structure of eyes
Diagram of the geocentric trajectory of Mars through several periods of retrograde motion .
Astronomia nova, Chapter 1, (1609).
Karlova street in Old Town, Prague – house where
Johannes Kepler lived
Geometrical harmonies in the perfect solids from Harmonices Mundi (1619)
The iconic frontispiece to the Rudolphine Tables celebrates the great astronomers of the past: Hipparchus , Ptolemy , Copernicus , and most prominently, Tycho Brahe
See http://www.hps.cam.ac.uk/starry/ for details of above.
Kepler's horoscope for General Wallenstein
The GDR stamp featuring Johannes Kepler.
10 euro Johannes Kepler silver coin