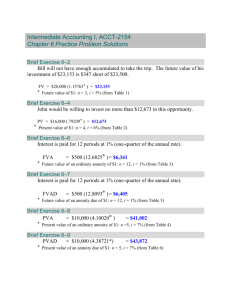
- Sample Questions for Midterm
advertisement

Sample Questions for Midterm 1- The mixture of debt and equity used by the firm to finance its operations is called: a. working capital management. b. financial depreciation. c. agency cost analysis. d. capital budgeting. e. capital structure. 2- The original sale of securities by governments and corporations occurs in the: a. b. c. d. e. Primary market. Secondary market. Dealer market. Auction market. Liquidation market. 3- The fundamental goal of financial management should be to: a. b. c. d. e. Maximize sales. Maximize the current value per share of the existing stock. Avoid financial distress. Maintain steady earnings growth. Maximize profits. 4- A(n) _________________ asset is one which can be quickly converted into cash without significant loss in value. a. b. c. d. e. current fixed intangible liquid long-term 5- Your ________________ tax rate is the amount of tax payable on the next dollar you earn. a. b. c. d. e. deductable residual total average marginal 6- Which of the following is a source of cash? a. b. c. d. e. The purchase of new fixed assets. Dividends paid. The repurchase of outstanding common stock. A decrease in long-term debt. A decrease in inventory. 7- Ratios that measure how efficiently a firm uses its assets to generate sales are known as: a. b. c. d. e. Asset management ratios. Long-term solvency ratios. Short-term solvency ratios. Profitability ratios. Market value ratios. 8- The ______________ breaks down return on equity into three component parts: operating efficiency of the firm, its asset use efficiency, and financial leverage. a. b. c. d. e. asset turnover ratio return on assets statement of cash flows Du Pont identity equity multiplier 9- In words, what does a profit margin of 0.10 mean? a. For each $1 of sales generated by the firm it incurs 10 cents in operating expenses. b. For each $1 of sales generated by the firm it earns 10 cents in net income. c. For each $1 of profits generated by the firm pretax, it keeps 10 cents aftertax. d. For each $1 of net income generated, 10 cents in sales are required. e. The firm completely sells off its production level 10 times on average during the year. 10- Interest earned on both the initial principal and the interest reinvested from prior periods is called ____________________. a. b. c. d. e. free interest annual interest simple interest interest on principal compound interest 11- The management of the firm’s short-term assets and liabilities is called: a. b. c. d. e. Capital budgeting. Capital structure. Agency cost analysis. Financial depreciation. Working capital management. 12- Which of the following is an advantage of ownership of a corporation compared to that of a sole proprietorship? a. b. c. d. e. The owners of the corporation have unlimited liability for the firm’s debts. It is the simplest to start. The corporation has an unlimited life. Dividends received by the corporation’s shareholders are tax-exempt. It is more difficult to transfer ownership in a corporation. 13- The purchase and sale of securities after the original issuance occurs in the: a. b. c. d. e. Dealer market. Auction market. Primary market. Secondary market. Liquidation market. 14- Balance sheet assets ___________________________. I. are always equal to total liabilities minus shareholders’ equity II. represent items acquired with the use of the firm’s assumed liabilities and equity III. are listed in order of increasing liquidity a. b. c. d. e. I only II only III only I and III only II and III only 15- Which of the following financial statement items is generally considered the most liquid? a. b. c. d. e. Inventory Net fixed assets Long-term debt Patents and trademarks Accounts receivable 16- Ratios that measure the firm’s financial leverage are known as: a. b. c. d. e. Asset management ratios. Short-term solvency ratios. Debt management ratios. Profitability ratios. Market value ratios. 17- The amount an investment is worth after one or more periods of time is the ____________. a. b. c. d. e. principal value present value future value compound interest rate simple interest rate 18- Which of the following fit the definition of an annuity? I. $100 a quarter for 10 years II. $200 a year forever III. $10 a week for 1,000 weeks IV $150 a month for 72 months A) I and IV only B) II only C) III and IV only D) I, III, and IV only E) I, II, III, and IV 19- Suppose you are evaluating two annuities. They are identical in every way, except that one is an ordinary annuity and one is an annuity due. Assuming an interest rate of 10%, which of the following is true? A) The ordinary annuity must have a higher present value than the annuity due. B) The annuity due must have the same present value as the ordinary annuity. C) The regular annuity must have a lower future value than the annuity due. D) The two annuities will differ in present value by the amount of exactly one of the annuity payments. E) The annuity due will be larger than the regular annuity by an amount equal to the present value of the last annuity payment. 20- Which of the following cannot be calculated? A) The present value of a perpetuity. B) The interest rate on a perpetuity given the present value and payment amount. C) The present value of an annuity due. D) The future value of an annuity due. E) The future value of a perpetuity. 21- In order to compare different investment opportunities (each with the same risk) with interest rates reported in different manners you should: A) Convert each interest rate to an annual nominal rate. B) Convert each interest rate to a monthly nominal rate. C) Convert each interest rate to an effective annual rate. D) Compare them by using the published annual rates. E) Convert each interest rate to an APR. 22- Which one of the following will increase the future value of a stream of unequal payments for a ten year project? The rate of return is positive. A) Delaying some cash inflows from years 1 and 2 until year 9 B) Lowering the discount rate applicable to all ten years C) Increasing the initial cash outflow to start the project D) Moving more of the cash inflows to the earlier years of the project E) Lowering the effective annual rate applicable to the project 23- As long as the interest rate is greater than zero, the present value of a single sum will always: A) Increase as the interest rate increases. B) Be less than the future value. C) Decrease as the period of time decreases. D) Equal the future value if the time period is one year. E) Increase as the number of periods increases. 24- The greater the number of years, the: A) Smaller the future value of a single sum. B) Larger the present value of a single sum. C) Larger the present value factor. D) Smaller the future value factor. E) Greater the compounding effect. 25- Tom and Antonio both want to open savings accounts today. Tom wants to have $1,000 in his savings account six years from now. Antonio wants to have $1,000 in his savings account three years from now. Which of the following statements is(are) correct assuming that both Antonio and Tom earn the same rate of interest? I. Tom needs to deposit more money into his account today than does Antonio. II. Tom will need to deposit twice the amount of money today as Antonio. III. Antonio needs to deposit more money into his account today than does Tom. IV. Antonio needs to deposit twice the amount of money today as Tom. A) I only B) III only C) I and II only D) III and IV only 26- Neal wants to borrow $2,500 and has received the following offers from his local banks. Which offer should Neal accept if he wants to repay the loan in one single payment two years from now? A) Bank A, which offers a simple rate of 4%. B) Bank B, which offers a simple rate of 5%. C) Bank C, which offers a rate of 4% compounded annually. D) Bank D, which offers a rate of 5% compounded annually. E) Bank E, which offers a rate of 5% compounded monthly. 27- An increase in a/an _____________ account would be considered a/an __________ of funds. I. asset; source II. liability; source III. expense; source A) I only B) II only C) I and II only D) I and III only E) II and III only 28- Which of the following statements about the current ratio is accurate? A) Use of book values in calculation of this ratio is unacceptable because the market values of these assets and liabilities tend to deviate from book values. B) This ratio is calculated by dividing current liabilities by current assets. C) It will always be greater than the quick ratio in companies that carry inventory. D) This ratio is intended to indicate the long run liquidity position of the firm. E) The higher the current ratio, the higher the level of cash in a firm. 29- The financial manager of Mystery, Inc., tells her banker that Mystery's accounts receivable declined by $275,000 that day. Based on this, the bank knows that Mystery's current ratio: A) Must have increased from the day before. B) Must have decreased from the day before. C) Did not change from the day before. D) Declined but the quick ratio was unchanged from the day before. E) Would possibly be affected, but more information is needed to know in which direction. 30- All else unchanged, which of the following is true when a firm sells a fixed asset on credit? A) The current ratio goes up but the quick ratio is unchanged B) The current ratio goes up but the quick ratio declines C) The quick ratio goes up but the current ratio is unchanged D) The quick ratio goes up but the current ratio declines E) The quick ratio and the current ratio both go up 31- In addition to days' sales in receivables and days' sales in inventory we could calculate "days' sales in payables" by computing the accounts payable turnover and dividing it into 365 days. In words, what do these ratios tell us? A) The number of days it takes before the current ratio falls to zero. B) How long it takes, on average, to entirely deplete these accounts. C) The time it takes to completely replace total current assets. D) The rate at which assets are replaced. E) The number of days of sales needed to make a profit. 32- Which of the following income statement accounts is a non-cash item? A) Wages and salaries B) Interest expense C) Cost of goods sold D) Depreciation E) Income taxes 33- The management of the firm's short-term assets and liabilities is called: A) Working capital management. B) Financial depreciation. C) Agency cost analysis. D) Capital budgeting. E) Capital structure. 34- The primary goal of financial management is to: A) Maximize current sales. B) Maximize the current value per share of the existing stock. C) Avoid financial distress. D) Minimize operational costs. E) Maintain steady earnings growth. 35- The possibility of conflict of interest between the stockholders and management of the firm is called: A) The shareholders' conundrum. B) Corporate breakdown. C) The agency problem. D) Corporate activism. E) Legal liability. 36- The original sale of securities by governments and corporations occurs in the: A) Primary market. B) Secondary market. C) Dealer market. D) Auction market. E) Liquidation market. 37- The secondary market is A) the market for the original sale of securities by governments and corporations B) the market in which dealers buy and sell for themselves, at their own risk C) the market in which purchasers are matched with those who wish to sell D) a market which has no central location E) the market in which securities are bought and sold after original sale 38- Deciding whether or not to open a new store is part of the process known as: A) Capital budgeting. B) Credit management. C) Capital structure. D) Cash management. E) Working capital management. 39- Which of the following is NOT considered one of the basic questions of corporate finance? A) What long-term investments should the firm choose. B) At what rate of interest should a firm borrow. C) Where will the firm get the long-term financing to pay for its investments. D) What mixture of debt and equity should the firm use to fund its operations. E) How should the firm manage its working capital, i.e., its everyday financial activities. 40- A financial manager is responsible for determining the firm's appropriate level of inventory. Which of the financial management areas addresses this decision? I. Capital budgeting II. Capital structure management III. Working capital management A) I only B) II only C) III only D) I and II only E) I, II, and III