Crater Lake, Oregon -589 m deep and possibly the... Transparency up to 90 m.
advertisement

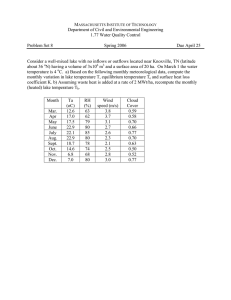
Crater Lake, Oregon -589 m deep and possibly the clearest lake in the world, Transparency up to 90 m. Thermocline very deep for its size No rooted plants. Mud doesn’t accumulate on the bottom till > 90 m depth Why is this lake so different from most lakes? Some of the most spectacular tectonic lakes are formed in volcanic craters. Physical features of lakes that determine habitat characteristics •inflow from the watershed/Catchment •Water residence time •Morphometry, Mean depth and volume •Thermal stratification and physical mixing •wind./currents/wave action •Sediment deposition •Light extinction How much water flows into lake Beauvais lake in a year from its watershed? Assume runoff coefficient of 0.15 m Drainage area =7.9 km2 Lake area =0.9 km2 How much water would you expect flows into this lake /yr? Evaporation from lake surface exceeds precipitation by 0.085 mm/yr How much water flows out of the lake? Assume runoff Drainage area =7.9 km2 coefficient of Lakearea 0.15 m =0.9 km2 P─ E on lake surface = ─ 0.085 m/yr How much water would you expect flows into this lake /yr? Qi = r * DA = 0.15 m/yr * 7 x 106 m2 = 1.05 x 106m3/yr What is the net evaporation in a year? (P-E)*A = ─ 0.085 m * lake area = ─ 0.085m/yr * 9 x 105 m2 = -7.65 x 104 m3/yr How much water flows out of the lake in a year? Qo = Qi + (P-E)*A = 1.05 x 106m3/yr + (─ 7.65 x 104 m3/yr) = 9.75 x 105 m3/yr Definition of water residence time and flushing rate Chapter 4 Water residence time w (time units) How long would it take for the entire volume to drain out of the lake if no new water wer e entering it. V L3 V w , units 3 t , renewal time Qo L /t Qi Qo mean discharge out of the lake Qi mean discharge from watershed into the lake Qo Qi P E A The approximat e inverse is flushing or renewal rate, How many times a year can the inflow fill the lake Qi L3 / t 1 h , units 3 V L t Lake Area = 0.9 km2 Mean depth= 4.3 m Lake Volume = 3.8 x 106 m3 Water residence time= Mean renewal rate= Lake Area = 0.9 km2 Mean depth= 4.3 m Lake Volume = 3.8 x 106 m3 Water residence time= Mean renewal rate= Water residence time Mean flushing rate V 3.8 106 m3 w 3.9 yr 5 3 1 Qo 9.7 10 m yr Qi 1.05 106 m3 yr 1 1 h 0 . 28 yr V 3.8 106 m3 How much of the water flowing into this lake from its watershed could you allocate for irrigation before the lake would gradually begin to disappear? Answer Over 92% Lake management—the water inflow budget or what happens when you over allocate? The Aral Sea in the former Soviet Union—mismanaging the river water inflow Allocation to desert irrigation > inflow minus evaporation Fig. 5.19 . Effects Ecosystem collapse, loss of biodiversity, worsening of water-salt balance in the agricultural areas, pollution of rivers and drinking water, changing of the regional climate – all these are new environmental developments in Central Asia. Calculating volume and mean depth Mean depth = Volume/surface area The hypsographic curve Area under the curve = volume Fig. 7.1 in text Lakes partition themselves into temperature zones Thermal stratification in lakes •In deep lakes only the surface layers are well mixed and quite warm, whereas the deeper parts remain cold. •The thermocline occurs deeper in large lakes because wind energy is transmitted to greater depths •Wind energy increases with fetch •In small lakes convection also plays a role in determining thermocline depth Fig. 11.8 in text