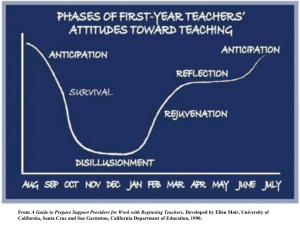
by John Mulder & Edwin Brobbel
advertisement

by John Mulder & Edwin Brobbel What it is The Benefits The Adverse Effects What is Fasting? fast·ing: [ fásting ] going without food abstention from all or certain types of food, especially as an act of religious observance The Benefits of Fasting - Detoxification - Rejuvenation - Awareness Detoxification During a fast: The natural process of toxin excretion continues, while the influx of new toxins is reduced. This results in a reduction of total body toxicity. The energy usually used for digestion is redirected to immune function, cell growth, and eliminatory processes. The immune system’s workload is greatly reduced, and the digestive tract is spared any inflammation due to allergic reactions to food. Detoxification cont’d Fat-stored chemicals, such as pesticides and drugs, are released. you heal with greater speed, cleanse your liver, kidneys, and colon, purify your blood, " fasting has been shown to be effective in treating high blood pressure." T Colin Campbell, Ph.D., professor of nutritional biochemistry at Cornell University. help you lose excess weight and water, flush out toxins, clear the eyes and tongue, and cleanse the breath Detoxification cont’d Detoxification relieves many common ills, such as headaches, joint pain, indigestion, constipation, fatigue, allergies, and anxiety. can have a favourable effect on bacteria in the gut Fasting is an effective treatment for many autoimmune diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis and lupus. It allows the immune system to normalize itself. Those who have been suffering from allergies, sinusitis and other immune sensitivities can rapidly reverse symptoms of angina (chest pain) and normalize high blood pressure, allowing them to discontinue their medication. Rejuvenation Hygienist use the term, "rejuvenation" to describe the partial restoration of youthfulness to the tissues and organs of the body This may be achieved through hygienic care including fasting. Cells may be drastically changed, but not structurally damaged. After growth, the cell will have a portion made of new protoplasm Rejuvenation cont’d Fasting rejuvenates--the feeling, the look, the utility of function; an increased energy and capacity which is visible through the disappearance of many lines, wrinkles, blotches, pimples and pathological pigmentations; The skin becomes much more youthful and acquires a better color and texture The eyes are clearer and brighter One looks younger and more vigorous. The visible regeneration and rejuvenation of the eyes, skin and superficial tissues is allied to the evidence of similar but invisible rejuvenation throughout the body. Awareness Diet- what you eat, how much, when - may trigger a change in your attitude to the food you eat and how much you eat Awareness of the plight of other who are less fortunate than you (30 hr famine) Physical awareness and sensitivity to diet and surroundings are increased. Are There Any Adverse Effects? • Physical • Digestive System • Circulatory System • Immune System • Hormones • Brain What to Watch For • • • • • • • • sudden drop in blood pressure persisting feeling of extreme cold prolonged, rapid and weak pulse extreme weakness difficulty breathing acute anxiety and emotional distress liver or kidney problems acute psychosis If you want to lose weight, Don’t fast. Your metabolism slows to such an extent that fat loss during fasting is lower than when you are on a regular diet. Who Shouldn’t Fast? • Diabetics shouldn’t fast without prior permission from their doctor. • Anyone who is severely underweight • Pregnant and Lactating females • Infants • Anyone taking prescription drugs of any kind • Anyone habitually using “social” drugs including tobacco and alcohol Conclusion Should you fast?