Monday www.ucalgary.ca/~elsegal/TalmudMap/Mishnah. html
advertisement

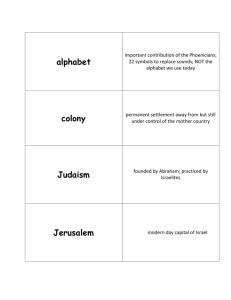
Monday www.ucalgary.ca/~elsegal/TalmudMap/Mishnah. html Overview • 70-700 CE Oral Torah Rabbinic Judaism In wake of rebellions to Rise of Islam 70 ce to 700 ce. Centre moves • Jerusalem destroyed… • Yavneh then Babylon. • Jews live all over Mediterranean world and Middle East Christianity • Begins as a Jewish sect around Jesus of Nazareth as “Messiah” or “Christ” • by 2nd century bce, “Nazarenes” take Gospel to non-Jews • Christianity becomes independent – Lingering associations with Judaism. Political changes • 0- 4th Palestine / Mediterranean century Rome Pagan • 4th century Rome • 7-8th century South / East: Islam Christian Political Changes Mesopotamia / Babylonia • to 3rd century: Parthians • 3rd to 7th centuries Sassanian (Persian) Zoroastrians Islam • 7-8th century Islam • Prophet Muhammad • 570 to 632 • Saw himself as the final prophet of the same God worshipped by Jews and Christians. Rapid Arab expansion • 7th century: Arab Muslims capture considerable territory • Many Jews now live under Islamic rule. Rabbinic Judaism • Developed 150 bce to 700 ce • TALMUD completed about the time of Muhammad. 70 to 700 • Massive Political Change • Massive Religious Change 3 religions • Islam 620-30’s • Christianity 1st century • Rabbinic Judaism 1st century b Early development of R. Judaism TWO TORAHS Torah that is in Tanakh Oral Torah: Rabbinic teachings. “TANNAIM” Early Oral Torah teachers • Tanna – Singular • Ca. 150 bce. to second century ce. • Influenced by Pharisaic ideas. • Bible and Mishnah After 70 c.e. New form of Judaism Without temple On Pharisee / Tannaim model “Oral Torah” collected to preserve teachings offer alternative to temple. Yohanan ben Zakkai • Pharisaic teacher • Made peace with Rome • Gathered surviving Jewish scholars after 70 ce. Yavneh / Jamnia New Centre of Jewish learning. Tannaim • “Repeaters” of Torah tradition. New Scholars “Rabbis” • Preserve – Old traditions – Memories of temple – Teachings of great scholars Ben Zakkai: • Yavneh is equal to Jerusalem. • Temple rites now symbolized in new rites in Yavnah Scripture • Increased accent on Scripture / Study • Temple holiness transferred to individual. Synagogues • Assume new role • Surrogate Temple – Shofar Yavneh Sanhedrin • New Leadership • Innovation and Tradition No alternative • “Old” form of Judaism beyond recovery. • No temple Diaspora life for almost all Jews. 132-135 bce Second rebellion • Attempt to rebuild temple results in disastrous war. • Simon Bar Kokhba Claims priesthood • “Messiah” Oral Torah • Basis of new Judaism alongside Tanakh • Oral Torah is Written down TANNAIM Rabbi Akiba Judah HaNasi • Judah compiled the writings & teachings of Akiba and others. MISHNAH • First major text of the Oral Torah. • 170-220 bce • Judah HaNasi. Love / justice, not offerings • Hosea 6:6 • Micah 6:6-8 • Psalm 51:16-17 Teachers, not priests • Rabbi, – by education and ordination, not birth – Remembered as “sages” Diaspora • Alexandria • Babylon • Contact with Sanhedrin. Midrash = traditions attached to Bible Mishnah = independent Mishnah: “Repetition” “Memorized” Major part of ORAL TORAH Written in land of Israel Mishnah Late 2nd Cent. early 3rd. –6 “ORDERS” – 63 “TRACTATES” • Chapters • Sections “Mishnah” Mishnah • REMEMBERS TEMPLE • TORAH INTERPRETATION • TEACHINGS OF SAGES Legitimization God Moses … Sages Hillel + Shammai J. b. Zakkai