Chapter 10
advertisement

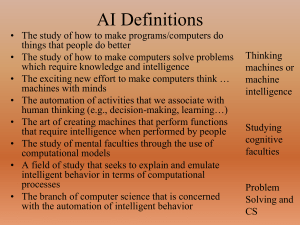
Chapter 10 Global Village “… is the shrinking of the world society because of the ability to communicate.” Positive: The best from diverse cultures will emerge and be shared by all. Negative: Even on the other side of the world, Britney Spears is playing on a radio somewhere. Telecommunication Models Tree-and-branch model: a centralized provider sends out information through many channels to consumers Radio Cable TV Switched-network model: people on the system are consumers and possibly providers Internet Artificial Intelligence (AI) AI is a group of related technologies used for developing systems (hardware or software) that behave intelligently or emulate human qualities such as learning, reasoning, language, vision, and recognition It’s also my field of research. VR VR stands for Virtual Reality VR by itself is not really an area of AI, but it is used by some AI systems Here at IU we have a VR room called the CAVE (CAVE Automated Virtual Environment) Robotics Not all robotics is properly classified as AI, but much of it is Industrial robots that build cars, robotic lawnmowers and vacuum cleaners and robots that emulate the way we move use “simple” AI programs Robotic guides or waiters use more sophisticated AI systems NLP Natural Language Processing is an extremely difficult area of AI where we try to create a system that can understand and/or produce human natural languages with some accuracy NLP is especially hard because of all the things that make human language interesting – words with double meanings, symbolism, sarcasm, puns, etc. Fuzzy Logic Fuzzy Logic systems deal with imprecise data and uncertainty, and problems that often have multiple solutions They are designed to find good solutions quickly with imperfect data, instead of perfect solutions slowly Expert Systems Expert Systems are computer programs used to solve problems in a very specific domain One expert system for diagnosing and classifying bacterial infections (MYCIN) was more accurate on the whole than the doctors that trained it Once, they were considered to be the culmination of AI research Problems: It takes a real expert to train one, and they are useless outside of their field. Unlike real humans, they have no direct way of learning new material. Neural Networks Neural Networks (NN) are computer simulations of the way neurons are connected in our brains. Neural Networks are exceedingly good at learning patterns. You present them with a set of training cases, which they use to learn general association patterns, then you test the system on a set of test cases and evaluate it. Genetic Algorithms Some problems are very hard to solve directly, or may have many “ok” solutions but only a few “good” ones. Genetic Algorithms (GAs) are commonly used to “evolve” good solutions GAs simulate organic reproduction, mutation, and natural selection (i.e. Evolution) The Turing Test How do we tell when an AI system is “truly” intelligent? The main problem is we cannot explain intelligence yet. We regard each other as intelligent because we’re human, and we tend to act reasonably rationally. We conclude that someone is intelligent if they “act” intelligent. The Turing Test Alan Turing, the founding father of much modern CS, addressed this question in 1950. His proposal, not entirely serious, is that a human judge talk with 2 “people” over some sort of remote connection. If at the end of the conversation, he could not be sure which “person” was human and which was an AI, the AI was intelligent for all practical purposes. The Turing Test The Turing Test is a nice idea, but it’s not taken very seriously by many scientists right now for several reasons: It’s extremely difficult to build a system with enough reasoning and NLP to be able to handle the TT for more than one area ELIZA, an early AI program, fooled many people into thinking it was a real human psychologist. But ELIZA was very clearly not “intelligent”.