Rank Ordering of Course Usefulness in 1 and Current Jobs
advertisement

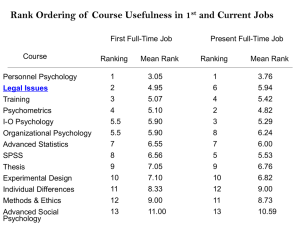
Rank Ordering of Course Usefulness in 1st and Current Jobs First Full-Time Job Course Personnel Psychology Legal Issues Training Psychometrics I-O Psychology Organizational Psychology Advanced Statistics SPSS Thesis Experimental Design Individual Differences Methods & Ethics Advanced Social Psychology Ranking Mean Rank Present Full-Time Job Ranking Mean Rank 1 2 3 4 5.5 3.05 4.95 5.07 5.10 5.90 1 6 4 2 3 3.76 5.94 5.42 4.82 5.29 5.5 7 8 9 5.90 6.55 6.56 7.05 8 7 5 9 6.24 6.00 5.53 6.76 10 11 12 13 7.10 8.33 9.00 11.00 10 12 11 13 6.82 9.00 8.73 10.59 The Amendments & EEO Law Amendment I: Congress shall make no law respecting an establishment of religion, or prohibiting the free exercise thereof; or abridging the freedom of speech, or of the press; or the right of the people peaceably to assemble, and to petition the government for a redress of grievances. >>> Used for discrimination against religion Amendment IV: The right of the people to be secure in their persons, houses, papers, and effects, against unreasonable searches and seizures, shall not be violated, and no warrants shall issue, but upon probable cause, supported by oath or affirmation, and particularly describing the place to be searched, and the persons or things to be seized. >>> Used in cases regarding drug testing The Amendments & Discrimination Law (cont.) Amendment V: No person shall be held to answer for a capital, or otherwise infamous crime, unless on a presentment or indictment of a grand jury, except in cases arising in the land or naval forces, or in the militia, when in actual service in time of war or public danger; nor shall any person be subject for the same offense to be twice put in jeopardy of life or limb; nor shall be compelled in any criminal case to be a witness against himself, nor be deprived of life, liberty, or property, without due process of law; nor shall private property be taken for public use, without just compensation. >>> Protects employees from discrmination by Federal government employers on the basis of race and other classifications Amendment XIII: Section 1. Neither slavery nor involuntary servitude, except as a punishment for crime whereof the party shall have been duly convicted, shall exist within the United States, or any place subject to their jurisdiction.Section 2. Congress shall have power to enforce this article by appropriate legislation. >>> Has been used in cases of race discrimination The Amendments & Discrimination Law (cont.) Amendment XIV: Section 1. All persons born or naturalized in the United States, and subject to the jurisdiction thereof, are citizens of the United States and of the state wherein they reside. No state shall make or enforce any law which shall abridge the privileges or immunities of citizens of the United States; nor shall any state deprive any person of life, liberty, or property, without due process of law; nor deny to any person within its jurisdiction the equal protection of the laws. >>> Permits employees to sue state and local government From Washington v. Davis (1976): “ ... the central purpose of the Equal Protection clause of the Fourteenth Amendment is the prevention of official conduct discrimination on the basis of race. It is also true that the Due Process clause of the Fifth Amendment contains an equal protection component prohibiting the United States from invidiously discriminating between individuals and groups.” Early Civil Rights Laws § 1981. Equal rights under the law (formally CRA of 1866) (a) Statement of equal rights All persons within the jurisdiction of the United States shall have the same right in every State and Territory to make and enforce contracts, to sue, be parties, give evidence, and to the full and equal benefit of all laws and proceedings for the security of persons and property as is enjoyed by white citizens, and shall be subject to like punishment, pains, penalties, taxes, licenses, and exactions of every kind, and to no other. >>> Primarily used in cases of race discrimination (although it’s been interpreted very broadly to include national origin • • • • No back pay limitations No minimum requirement of 15 employees Need to generate proof of discriminatory intent Can apply to private organizations (passed under the 13th amendment – SC, 1968) Section 1981 “ ... prohibits only race discrimination, but the definition of “race” is broad and the statute reaches both public and private employers.” (see Jones v. Alfred. H. Mayer Co., 1968; Johnson v. Railway Express Agency, 1975) Early Civil Rights Laws (cont.) § 1983. Civil action for deprivation of rights (formally CRA of 1871) Every person who, under color of any statute, ordinance, regulation, custom, or usage, of any State or Territory or the District of Columbia, subjects, or causes to be subjected, any citizen of the United States or other person within the jurisdiction thereof to the deprivation of any rights, privileges, or immunities secured by the Constitution and laws, shall be liable to the party injured in an action at law, suit in equity, or other proper proceeding for redress, except that in any action brought against a judicial officer for an act or omission taken in such officer’s judicial capacity, injunctive relief shall not be granted unless a declaratory decree was violated or declaratory relief was unavailable. For the purposes of this section, any Act of Congress applicable exclusively to the District of Columbia shall be considered to be a statute of the District of Columbia. >>> Covers discrimination by State and local government organizations (simialr to 14 Amendment protections) Major EEOC Responsibilities Enforcement of the following laws: • • • • • • Title VII of the Civil Rights Act Pregnancy Discrimination Act Equal Pay Act The ADEA The ADA Workplace retaliation Investigates charges of alleged discrimination (and issues findings) Settles charges through conciliation or other informal methods Files lawsuits Develops procedural regulations and issuing interpretive guidelines on various laws Conducts prevention efforts via education and technical assistance programs Total EEOC Charges By Year Claims must be filed within 180 days of the alleged discriminatory behavior in states without EEO laws (non-deferral states), or within 300 days in states with EEO laws (deferral states; a state agency exists). ~ OFCCP Relevance ~ • I-O folks work a lot for federal contractors • OFCCP has become aggressive in pursuing “class actions‟ rather than individual actions and highlighting companies that use selection procedures locally, by region, and nationwide • This enforcement has has focused on hiring practices and resulted in record financial settlements. Likely that more I-Os folks are dealing with OFCCP enforcement today than in the past • In recent years OFCCP has: – Hired statisticians to conduct adverse impact analyses – Hired psychometricians to evaluate the “adequacy‟ of selection procedures – Adopted guidelines and strategies that may be controversial with contractors and assessment professionals. Source: Eric M. Dunleavy, Ph.D. Senior Consultant DCI Consulting, SIOP Session, April, 2010 Overview of OFCCP Investigative Process OFFCP compliance review (e.g., conducts desk audits using EEO-1 and AAP data). Also performs onsite reviews OFCCP attempts to gain voluntary compliance if a contractor is found to be in violation If voluntary compliance fails (agreement not reached), OFCCP can issue sanctions and fines Contractor can appeal OFCCP ruling; case goes to an Administrative Law Judge (ALJ) from the Department of Labor (DOL) The contractor must then appeal to the Secretary of Labor (and lose) in order to gain access to federal district court In federal district court, contractor bears the burden that a violation was not committed Adapted from: Dunleavy & Gutman, On the Legal Front: OFCCP Settlement Review: What Was the Burden on Bank of America? Get article here US Courts of Appeals and US District Courts Map See details of each District Court here Listing of Federal Circuit Court of Appeals 1st - ME, MA, NH, PR, RI 2nd - NY, VT, CT 3rd - PA, NJ, DE, VI 4th - MD, NC, SC, VA, WV 5th - LA, TX, MS 6th - MI, OH, KY TN 7th - IL, IN, WI 8th - ND, SD, MN, NE, IA, MO AR 9th - CA, OR, WA, AZ, MT, ID, NV, AK, HI 10th - CO, KS, NM, OK, UT, WY 11th - AL, GA, FL DC - DC, Tax Court, fed admin agencies. Federal - Patent, Int'l Trade, Claims Court and Veterans' Appeals. From: Findlaw.com Federal Circuit Court of Appeals Map U.S. Supreme Court Background: Court established by Article III, Section 1 of the Constitution: "[t]he judicial Power of the United States, shall be vested in one Supreme Court, and in such inferior Courts as the Congress may from time to time ordain and establish.” The Act also created the federal circuit courts and the federal district courts, the Office of the Attorney General, and granted the President the right to nominate justices for appointment to the United States Supreme Court with the advice and consent of the Senate. In its 1st year, the Court consisted of 6 justices (one Chief Justice and 5 associate justices). The present composition of one Chief Justice and eight Associate Justices was established under an Act passed in 1948 (28 U.S.C. 1) Relatively weak branch of government in the early years Reasons Why the Court Takes a Case 1) Conflicting opinions between the circuit courts 2) Lower court decision that conflicts with previous Supreme Court ruling 3) Issues of constitutional importance Legal Citations U.S. Supreme Court Cases Teamsters v. U.S., 431 U.S. 324 (1977) Volume # Petitioner Respondent Reporter Year of decision Beginning page # of case The U.S. Reporter is the preferred cite, but sometimes others are used instead. One is the Supreme Court Reporter. The format for this is: Teamsters v. U.S., 97 S. Ct. 1843 (1977). There is also a Lawyers Edition that is used: Teamsters v. U.S., 52, L. Ed.2nd 396. Legal Citations (cont.) Quotations Teamsters v. U.S., 431 U.S. 324, 328 (1977) A second page number can be used to indicate the page location of a quote or specific point of law Legal Citations (cont.) Federal Circuit Court of Appeals Cases Glover v. Johnson, 75 F.3d 264 (6th Cir.1996) Volume # Appellant Appellee Circuit Court Beginning page # of case Reporter Year of decision Format used in the text: Glover v. Johnson (CA 6, 1996) 75 F.3d 264 The terms Appellee v. Appellant are used in the Court of Appeals. Therefore, it is possible that the order of the parties in the original case may be reversed. For instance, in a case that started as Johnson v. Glover may be reported as Glover v. Johnson in the in the Court of Appeals reporter. Federal Circuit Court of Appeals Reporters • Federal Reporter (Cited as F.) - 1880-1924 • Federal Reporter, 2d series. (Cited as F. 2d) - 1924-1993 • Federal Reporter, 3d series. (Cited as F. 3d) – 1993 + Legal Citations (cont.) Federal District Court Cases Glover v. Johnson, 478 F. Supp. 1075 (E.D.Mich.1979) Volume # Respondent Petitioner Reporter District Court Beginning page # of case Year of decision Overall, there are 94 federal judicial districts, The number of districts vary within each State. Some states have only one district (e.g., Arizona, Colorado, Delaware), while others have multiple districts (e.g., California, Florida, Texas). Legal Citations (cont.) Statutes --- Session Law Civil Rights Act of 1964, P.L. 88-353, 78 Stat. 241 1964). Page # Title of book Popular Name Volume # Year Public Law # or Chapter # Stat. = Abbreviation for Statutes at Large. Session laws are passed during a given legislative session and are published in the order of their passing. These are the most authoritative version of a law (e.g., the actual wording in the session law is controlling). Legal Citations (cont.) Statutes --- Code Means “add the following.” Used to include numbered lists, pages or sections after the first number is stated Civil Rights Act of 1964, 42 U.S.C. §1971 et seq. (1988). Section # or Part # Title of book Popular Name Title # or Chapter # Year of compilation U.S.C. = Abbreviation for U. S. Code. The United States Code is the collection of laws of the United States arranged within 50 topic areas. The U.S. Code is published every six years, with supplements added annually. Citing Sections and Subsections 17 U.S.C. § 102(a)(1) Second sublevel of organization uses numbers Subsection uses lowercase letters A 3rd sublevel uses upper-case letters [e.g., (B)]. The fourth sublevel uses lower-case roman numerals [e.g., VI)]. Each level of organization is contained within separate parentheses. For example: 42 U. S. C. §2000e-2(k)(1)(A)(i) Legal Citations (cont.) Regulations --- As Promulgated (put into action, to set forth) 44 Fed. Reg. 29375 (May 18, 1979). Year of publication Page # Title of Book Volume # Fed. Reg. = Abbreviation for Federal Register. The Federal Register is the official daily publication for rules, proposed rules, and notices of Federal agencies and organizations, as well as executive orders and other presidential documents. It is published by the Office of the Federal Register, National Archives and Records Administration (NARA). Legal Citations (cont.) Regulations --- As Codified 42 C.F.R. §124.501 (1991). Section # Title of Book Title # Year of Compilation C. F. R. = Abbreviation for Code of Federal Regulations. The CFR is the collection of rules published in the Federal Register by the executive departments and agencies of the Federal Government. It is divided into 50 titles that represent broad areas subject to Federal regulation. Title 29 covers rules related to labor. Each CFR volume is updated once each calendar year and is issued on a quarterly basis. See link