Projected changes to ocean food webs and oceanic fisheries Solomon Islands Government
advertisement

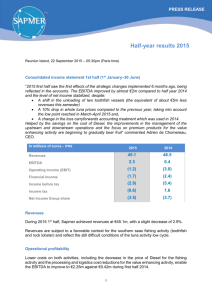
Projected changes to ocean food webs and oceanic fisheries Solomon Islands Government Based on…….. Outline • Food webs for tuna • Differences in food webs among provinces of the Pacific Ocean • Effects of CC on provinces and their food webs • Effects of climate change on tuna stocks Image: Marc Taquet, FADIO, IRD/IFREMER Tuna food web Food webs are complex Five oceanic provinces Five oceanic provinces • Warm pool Normal El Niño Five oceanic provinces • North and South Gyres (case 3) and equatorial divergence (case 4) Impact of climate change • Surface area of the provinces ↘ of rich equatorial divergence ↗ of poorer gyres and warm pool Impact of climate change present • Reduced exchange between deep, nutrient-rich water and surface waters future Impact of climate change • Effect on phytoplankton and zooplankton Present present 2035 2050 2100 Impact of climate change Image: Valerie Allain, SPC • Effect on micronekton Now, turning to tuna! Tuna habitat – temperature • Each tuna species has evolved with a preferred range in temperature • This preference affects: vertical & horizontal distribution of species where and when tuna spawn Range of sea surface temperature with substantial catches Species Temperature (°C) Skipjack 20-29 Yellowfin 20-30 Bigeye 13-27 Source: Sund et al. (1981) Tuna habitat – oxygen Estimated lower lethal oxygen concentration Species Length (cm) Lower lethal O2 levels (ml l-1) Skipjack 50 1.87 Yellowfin 50 1.14 Bigeye 50 0.40 Less tolerant to low O2 levels Skipjack Yellowfin Bigeye Most tolerant to low O2 levels Tuna habitat – oxygen + 0 0m 100 m Well oxygenated Skipjack Yellowfin 500 m Low oxygen Bigeye Typical vertical O2 profile Skipjack tuna Solomon Is = -4 Solomon Is = -3 Unexploited Fishing effort x 1.5 Bigeye projection 2050 2000 Adult biomass Larval density 2000 2050 Good fishing grounds could be displaced further eastward Conclusions • There is still uncertainty about impacts of climate change on tuna • Fishing has a strong impact and will continue to be a major driver of stocks Conclusions • Improved resolutions of SEAPODYM model are needed to update these preliminary results Resolution 2° Resolution 1° • Better projections can be achieved using an ensemble of models Resolution 0.25 °