Document 15961118
advertisement

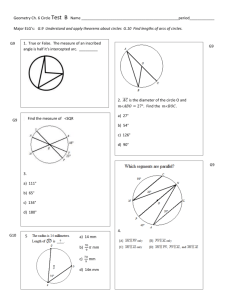
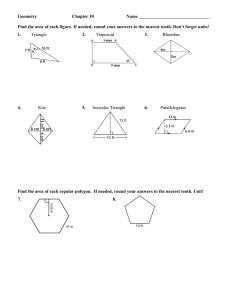
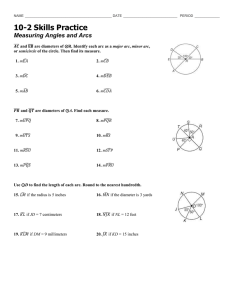
Circle: set of all points equidistant from a given point. A circle is 360°. Center of a Circle: the central point from which all the points are equidistant; a circle is named by its center Radius: segment that has one endpoint at the center and the other endpoint on the circle Congruent Circles: circles with congruent radii Diameter: a segment that contains the center of the circle and has both endpoints on the circle Central Angle: an angle whose vertex is the center of the circle Semicircle: a type of arc that is half a circle Minor Arc: smaller than a semicircle Major Arc: bigger than a semicircle Adjacent Arcs: arcs of the same circle that have exactly one point in common. Circumference: the distance around the circle Concentric Circles: circles that lie in the same plane and have the same center Arc Length: a fraction of a circles circumference Congruent Arcs: arcs that have the same measure and are in the same circle or in congruent circles. Name each of the following: 1. Circle C 2. Center 3. Radius F 4. Diameter 5. Central angle 6. Semicircle E 7. Minor arc A 8. Major arc 9. Adjacent arcs Concentric Circles D B Arc Addition Postulate (Post. 7-1): The measure of the arc formed by two adjacent arcs is the sum of the measures of the two arcs. The measure of an arc is the degree of its central angle! Circumference of a Circle (Thm. 7-13): The circumference of a circle is pi times the diameter. Arc Length (Thm. 7-14): The length of an arc of a circle is the product of the ratio, measure of the arc : 360, and the circumference of the circle.