Review for Exam #3 Chapter 9
advertisement

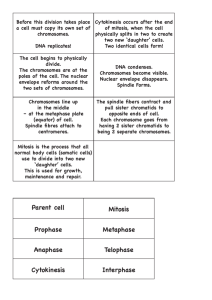
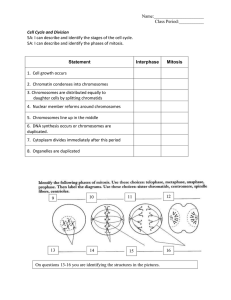
Review for Exam #3 Dr. Orr Chapter 9 Cell Respiration What is the reaction? Why does the cell do this? What kind of cells do this? What does it mean to be oxidized? Reduced? What is oxidized in the process? Reduced? What carries energized electrons? Where do the electrons go? How much ATP results from the complete metabolism of a molecule of glucose? Can you follow the energy, starting at glucose? Can you follow the electrons, starting with glucose? What is the relationship between energy, electrons, and the carbon skeleton in an anabolic process? A catabolic process? How efficient is this process? % energy? Number of ATP? Glycolysis What is the substrate? What are the products (include name and number per glucose)? Where in the cell does this occur? Does this require oxygen? What is being oxidized? Reduced? Is ATP being made? How much? By what process? Is Carbon Dioxide produced? Is it required? Citric Acid Cycle What is the substrate? What are the products? Where in the cell does this occur? Does this require oxygen? What is being oxidized? Reduced? Is ATP being made? How much? By what process? Is Carbon Dioxide produced? Is it required? Oxidative Phosphorylation What is the substrate? What are the products? Where in the cell does this occur? Does this require oxygen? What is being oxidized? Reduced? Is ATP being made? How much? By what process? How many ATP result per NADH? How many ATP result per FADH2? What is the final electron acceptor for cell respiration? What is chemiosmosis? What does it generate? Produce? Fermentation What is the purpose? Under what conditions does this occur? Which of the above processes always happens first? What are the two different end products (where electrons end up)…depending on the organism? Humans? Yeast? Control? What main enzyme is targeted to control cell respiration? What process regulates this enzyme? What would happen if you did not have this enzyme? Are you sure? Cell respiration- catabolic or anabolic? Photosynthesis- catabolic or anabolic? What carries energized electrons? Where do the electrons go? If an individual goes on a low carb diet, where does the fat go? In other words, how do the atoms leave his/her body? Chapter 10 Photosynthesis Photosynthesis- catabolic or anabolic? What parts of the parts of the plant are involved in this process, and how? Stomata? Chloroplasts? Chlorophyll? Thylakoid membranes? Stroma? What is an autotroph? Photoautotroph? Heterotroph? What is the relationship between wavelength and light energy? What wavelengths do plants use? What color do we perceive these as? What wavelengths (and color) do they not use? Why don’t they utilize these? Why do leaves change color in the fall? Relate this specifically to pigments. What is the reaction? Why does the cell do this? What kind of cells do this? Can you follow the energy through this process, starting with light energy? Can you follow the electrons through this process, starting with water? Light Reactions What is the substrate? What are the products? Where does this occur? Does this require oxygen? What is being oxidized? Reduced? What does Photosystem II do? What does Photosystem I do? Which occurs first? What is the energy source? What is the source of electrons? Is ATP being made? By what process or processes? What is the purpose of these reactions? Is Carbon Dioxide produced? Is it required? Compare Chemiosmosis in the thylakoid membranes to this process in the mitochondria. Where are protons pumped in each? From where to where? In what membrane do you find ATP synthase for each? Calvin Cycle What is the substrate? What are the products? Where does this occur? Does this require oxygen? What is being oxidized? Reduced? Is ATP being made? What main enzyme regulates the activity of the Calvin Cycle? What are the three phases of this cycle? How many carbon atoms are incorporated per Calvin Cycle? How many turns of this cycle are required to produce a G-3-P? One glucose molecule? How do these reactions benefit the cell? Is Carbon Dioxide produced? Is it required? Chapter 12 What are the two broad phases of the cell cycle in which a cell can be found? What are the subphases of Interphase? What are the subphases of mitosis vs. M-phase? (hint…M phase will include cytokinesis, whereas mitosis includes only nuclear division) In which phase would you expect DNA (chromosomes) to be duplicated? What is the shortest phase of mitosis? The longest phase? For the next 9 questions, use your ability to draw mitosis in order to prove your answer! Hint: the number of chromosomes in the cell will always be the same as the number of centromeres! In which phase would you expect to see duplicated chromosomes lining up in the middle of a cell? In which phase would you expect to see chromosomes separating and migrating to opposite poles of a cell? If a cell has 5 chromosomes at the beginning of G1: a. how many chromosomes are present in the cell at metaphase? In anaphase? b. How many sister chromatids are present at the end of prophase? If a cell has 10 sister chromatids at the beginning of prophase, how many chromosomes are in the cell at the end of metaphase? If a cell has 20 centromeres in metaphase, how many centromeres will be in each of the daughter cells? If a cell has 20 centromeres in anaphase, how many chromosomes do each of the daughter cells have? If a cell that has 24 chromosomes at the end of cytokinesis commits to proceeding through another round of mitosis, how many chromosomes will it have in prometaphase? Compare the DNA content and the number of chromosomes in a cell in G2 vs. a daughter cell. Are each the same? Reduced? By how much? ½? ¼? Now compare the DNA content and the number of chromosomes in a cell in G1 vs. a daughter cell. Are each the same? Reduced? By how much? ½? ¼? What domains of biological life utilize mitotic division? Binary fission? Be able to identify cells in prophase, metaphase, anaphase and telophase if given an illustration. What is the spindle apparatus responsible for? What is the difference in cytokinesis in a plant cell vs. an animal cell? What phase is termed a “non-dividing” state? This is the phase in which cells that do not get the “go-ahead” signal enter. What properties characterize a cancer cell?