MATH 0406 INTRODUCTORY ALGEBRA COURSE OBJECTIVES FALL 2015 Textbook
advertisement
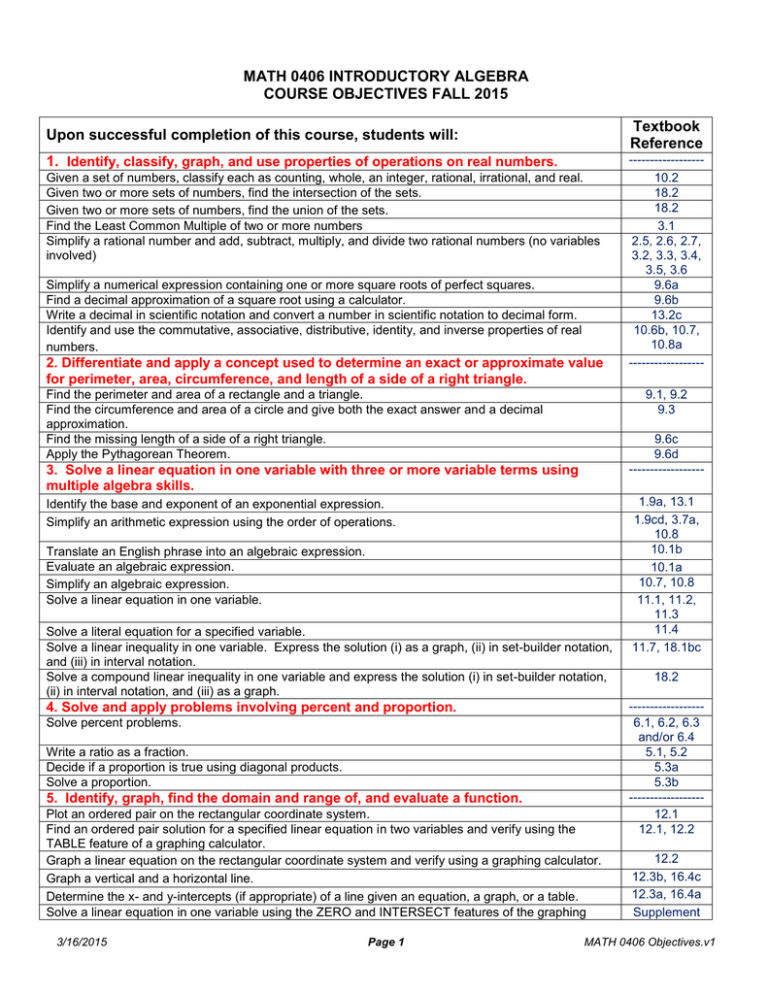
MATH 0406 INTRODUCTORY ALGEBRA COURSE OBJECTIVES FALL 2015 Textbook Reference Upon successful completion of this course, students will: 1. Identify, classify, graph, and use properties of operations on real numbers. Given a set of numbers, classify each as counting, whole, an integer, rational, irrational, and real. Given two or more sets of numbers, find the intersection of the sets. Given two or more sets of numbers, find the union of the sets. Find the Least Common Multiple of two or more numbers Simplify a rational number and add, subtract, multiply, and divide two rational numbers (no variables involved) Simplify a numerical expression containing one or more square roots of perfect squares. Find a decimal approximation of a square root using a calculator. Write a decimal in scientific notation and convert a number in scientific notation to decimal form. Identify and use the commutative, associative, distributive, identity, and inverse properties of real numbers. 2. Differentiate and apply a concept used to determine an exact or approximate value for perimeter, area, circumference, and length of a side of a right triangle. Find the perimeter and area of a rectangle and a triangle. Find the circumference and area of a circle and give both the exact answer and a decimal approximation. Find the missing length of a side of a right triangle. Apply the Pythagorean Theorem. 9.1, 9.2 9.3 9.6c 9.6d ------------------ 3. Solve a linear equation in one variable with three or more variable terms using multiple algebra skills. Identify the base and exponent of an exponential expression. Simplify an arithmetic expression using the order of operations. Translate an English phrase into an algebraic expression. Evaluate an algebraic expression. Simplify an algebraic expression. Solve a linear equation in one variable. Solve a literal equation for a specified variable. Solve a linear inequality in one variable. Express the solution (i) as a graph, (ii) in set-builder notation, and (iii) in interval notation. Solve a compound linear inequality in one variable and express the solution (i) in set-builder notation, (ii) in interval notation, and (iii) as a graph. 4. Solve and apply problems involving percent and proportion. Solve percent problems. Write a ratio as a fraction. Decide if a proportion is true using diagonal products. Solve a proportion. 5. Identify, graph, find the domain and range of, and evaluate a function. Plot an ordered pair on the rectangular coordinate system. Find an ordered pair solution for a specified linear equation in two variables and verify using the TABLE feature of a graphing calculator. Graph a linear equation on the rectangular coordinate system and verify using a graphing calculator. Graph a vertical and a horizontal line. Determine the x- and y-intercepts (if appropriate) of a line given an equation, a graph, or a table. Solve a linear equation in one variable using the ZERO and INTERSECT features of the graphing 3/16/2015 Page 1 -----------------10.2 18.2 18.2 9.1 3.1 2.5, 2.6, 2.7, 3.2, 3.3, 3.4, 3.5, 3.6 9.6a 9.6b 13.2c 10.6b, 10.7, 10.8a 1.8 ------------------ 1.9a, 13.1 1.4 1.9cd, 3.7a, 1.4 10.8 10.1b 1.4,2.1.2.2 10.1a 1.4 10.7, 10.8 1.4, 2.1 2.3 11.1,2.2, 11.2, 11.3 11.4 2.5 11.7, 18.1bc 18.2 -----------------6.1, 6.2, 6.3 and/or 6.4 5.1, 5.2 5.3a 5.3b -----------------12.1 3.1 12.1, 12.2 12.2 3.2 12.3b, 16.4c 3.3 12.3a, 16.4a 3.3 Supplement MATH 0406 Objectives.v1 Textbook Reference Upon successful completion of this course, students will: calculator. Find the slope of a line given: (i) two points on the line, (ii) an equation of the line, (iii) a table of values, or (iv) a graph. Write an equation in slope-intercept form, if applicable, given a linear equation. Write an equation of the line using point-slope or slope-intercept form given the slope and a point or given two points. Determine whether a set of points, an equation, or a graph represents a function. Identify the domain and range from a graph in interval notation. Evaluate a function for a specified value. 6. Solve a system of two linear equations and interpret the solution graphically, algebraically, and in the context of the information provided, if necessary. Solve a system of linear equations in two variables by: (i) graphing manually and with a graphing calculator, (ii) substitution, and (iii) elimination. Write a system of linear equations in two variables describing an application, solve the system, and interpret the solution. Determine whether two equations represent parallel lines, perpendicular lines, or neither. 7. Factor a polynomial and solve a quadratic equation by factoring. Simplify an expression, which contains an exponent that is an integer. Identify a coefficient, term, factor, constant, and the degree of a specified polynomial. Classify a polynomial as a monomial, binomial, or trinomial as appropriate. Add, subtract, and multiply two polynomials. Simplify a polynomial in two or more variables. Divide a polynomial by a monomial or a binomial. Factor a polynomial by finding the greatest common factor. Factor a polynomial by grouping. Factor a trinomial in the form ax2 + bx + c, where a ≠ 0, a = 1 or a is a common factor. Factor a trinomial in the form ax2 + bx + c, where a ≠ 0, a ≠ 1. Factor the difference of two squares. Solve a quadratic equation by factoring. 8. Set up and solve an application with an appropriate linear, quadratic, or system of linear equations. Solve an application involving a linear equation in one variable. Solve an application involving percent. Use a proportion to model an application. Solve an application involving a quadratic equation. Solve an application requiring the Pythagorean Theorem. Solve an application requiring a system of equations. 3/16/2015 Page 2 12.4, Supplement for (iii) 12.2, 16.3 3.5 16.5 16.1, 3.6 Supplement for points and equation 16.2, 18.1b 3.6 16.1 3.6 -----------------17.1, 17.2, 17.3 17.4 16.4d 4.1 -----------------1.9c,5.1,5.5 10.8d, 13.1b,f, 13.2 13.3c 5.2 13.3b 5.2 13.4, 13.5, 5.2,5.3,5.4 13.6 13.7 5.2,5.3 13.8 5.6 14.1 6.1,6.2 14.1 6.1 14.2 6.2 14.3, 14.4 6.2 14.5 6.5 14.8 6.6 -----------------11.6 2.4 6.5, 6.6, 6.7a 5.4, 6.4 14.9 6.7 9.6d, 14.9, 6.7 19.7 17.4 4.5 MATH 0406 Objectives.v1