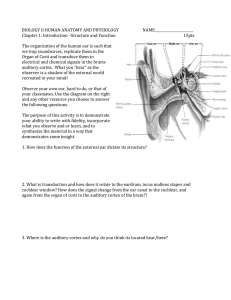
Ear Anatomy of the Ear
advertisement

Ear Anatomy of the Ear Divided into 3 major areas: outer, middle, inner Outer and middle deal with hearing only Inner deals with hearing and equilibrium Outer or External Ear Auricle (pinna): skin covered cartilage Encircles the auditory canal opening Lobule: inferior portion of the pinna External Acoustic Meatus (external auditory canal): short, narrow chamber Opening in the temporal bone Skin lines Ceruminous Glands: wax secreting glands found in the walls of the external acoustic meatus Tympanic Membrane (eardrum): membrane that separates outer from middle ear Vibrates at the exact frequency as sound wave on it Middle Ear: small chamber Tympanic Cavity: another name for middle ear Ossicles: 1. Malleus 2. Incus 3. Stapes Form a lever system that amplifies and transmits vibrations of the eardrum to the fluids of the inner ear Pharyngotympanic Tube (auditory tube): connects the middle ear with the nasopharynx Is normally flattened and closed Swallowing or yawning causes it to open temporarily to equalize pressure of the middle ear Otitis Media: inflammation of the middle ear Fairly common condition in children and adults prone to sore throats If large amounts of fluid or pus accumulate, the eardrum may need to be lanced to relieve pressure Inner Ear (internal ear) Osseous Labyrinth (bony labyrinth): bone chambers 3 subdivisions: cochlea, vestibule, semicircular canals Perilymph: aqueous fluid that fills the osseous labyrinth Membranous Labyrinth: suspended in the perilymph Follows the contours of the osseous labyrinth Endolymph: more viscous fluid that fills the membranous labyrinth Vestibule and Semicircular Canals: involved with equilibrium Cochlea: contains the sensory receptors for hearing Cochlear Duct: winds through the cochlea Separates the cochlear cavity into upper and lower chambers Scala Vestibuli Scala Tympani Spiral Organ of Corti: contains the receptors for hearing called the sensory hair cells Cochlear Nerve: division of nerve VIII Microscopic Anatomy of the Organ of Corti and the Mechanism of Hearing Basilar Membrane: holds the hair cells Tectorial Membrane: gelatinous membrane that lies over the hair cells Vestibular Membrane: the roof of the cochlear duct Scala Media: endolymph filled chamber of the cochlear duct Presbycusis: a type of sensorineural deafness Specifically, the inability to hear high tones or speech sounds Caused by deterioration of the organ of Corti Caused by aging or loud sounds