Thévenin's Theorem (5.3, 8.8) Dr. Holbert March 8, 2006 ECE201 Lect-13
advertisement

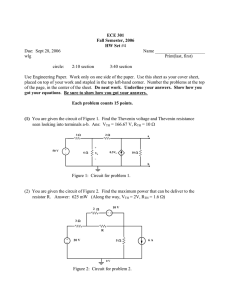
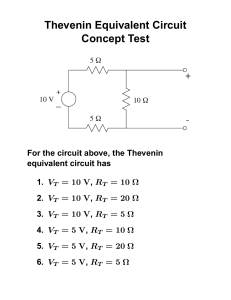
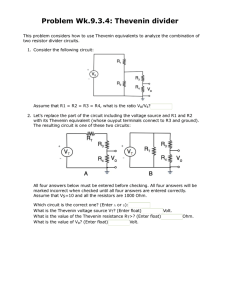
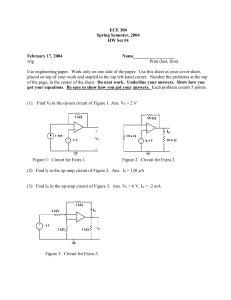
Thévenin's Theorem (5.3, 8.8) Dr. Holbert March 8, 2006 ECE201 Lect-13 1 Thevenin’s Theorem • Any circuit with sources (dependent and/or independent) and resistors can be replaced by an equivalent circuit containing a single voltage source and a single resistor. • Thevenin’s theorem implies that we can replace arbitrarily complicated networks with simple networks for purposes of analysis. ECE201 Lect-13 2 Implications • We use Thevenin’s theorem to justify the concept of input and output resistance for amplifier circuits. • We model transducers as equivalent sources and resistances. • We model stereo speakers as an equivalent resistance. ECE201 Lect-13 3 Independent Sources (Thevenin) RTh Voc Circuit with independent sources + – Thevenin equivalent circuit ECE201 Lect-13 4 No Independent Sources RTh Circuit without independent sources Thevenin equivalent circuit ECE201 Lect-13 5 Example: CE Amplifier +10V Vin + – 1kW + 2kW ECE201 Lect-13 Vo – 6 Small Signal Equivalent Ib Vin + – 1kW 50W 100Ib 2kW + Vo – ECE201 Lect-13 7 Thevenin Equivalent @ Output Ib Vin + – 1kW 2kW 50W 100Ib + Vo RTh + Voc + – Vo – ECE201 Lect-13 8 Computing Thevenin Equivalent • Basic steps to determining Thevenin equivalent are – Find voc – Find RTh (= voc / isc) ECE201 Lect-13 9 Thevenin/Norton Analysis 1. Pick a good breaking point in the circuit (cannot split a dependent source and its control variable). 2. Thevenin: Compute the open circuit voltage, VOC. Norton: Compute the short circuit current, ISC. For case 3(b) both VOC=0 and ISC=0 [so skip step 2] ECE201 Lect-13 10 Thevenin/Norton Analysis 3. Compute the Thevenin equivalent resistance, RTh (or impedance, ZTh). (a) If there are only independent sources, then short circuit all the voltage sources and open circuit the current sources (just like superposition). (b) If there are only dependent sources, then must use a test voltage or current source in order to calculate RTh (or ZTh) = VTest/Itest (c) If there are both independent and dependent sources, then compute RTh (or ZTh) from VOC/ISC. ECE201 Lect-13 11 Thevenin/Norton Analysis 4. Thevenin: Replace circuit with VOC in series with RTh, ZTh. Norton: Replace circuit with ISC in parallel with RTh, ZTh. Note: for 3(b) the equivalent network is merely RTh (or ZTh), that is, no voltage (or current) source. Only steps 2 & 4 differ from Thevenin & Norton! ECE201 Lect-13 12 Class Examples • Learning Extension E5.3 • Learning Extension E5.5 ECE201 Lect-13 13 Thevenin AC Steady State • Thevenin’s theorem also applies to AC steady state analysis. • An arbitrary linear circuit can be replaced by an equivalent source and impedance. • The determination of source and impedance values is essentially the same as for resistor circuits. ECE201 Lect-13 14 Independent Source(s) ZTh Voc Circuit with one or more independent sources + – Thevenin equivalent circuit ECE201 Lect-13 15 No Independent Sources ZTh Circuit without independent sources Thevenin equivalent circuit ECE201 Lect-13 16 Class Example • Learning Extension E8.14(b) ECE201 Lect-13 17