An Analysis of the Skype Peer-to-Peer Internet Telephony Protocol
advertisement
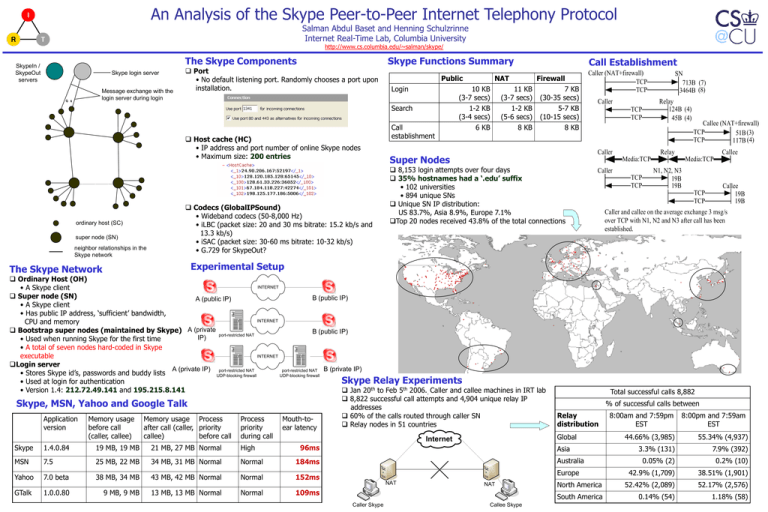
An Analysis of the Skype Peer-to-Peer Internet Telephony Protocol Salman Abdul Baset and Henning Schulzrinne Internet Real-Time Lab, Columbia University http://www.cs.columbia.edu/~salman/skype/ The Skype Components SkypeIn / SkypeOut servers Skype login server Message exchange with the login server during login Port • No default listening port. Randomly chooses a port upon installation. Skype Functions Summary Public Login Search Host cache (HC) • IP address and port number of online Skype nodes • Maximum size: 200 entries Codecs (GlobalIPSound) • Wideband codecs (50-8,000 Hz) • iLBC (packet size: 20 and 30 ms bitrate: 15.2 kb/s and 13.3 kb/s) • iSAC (packet size: 30-60 ms bitrate: 10-32 kb/s) • G.729 for SkypeOut? ordinary host (SC) super node (SN) neighbor relationships in the Skype network Call establishment NAT 10 KB (3-7 secs) 1-2 KB (3-4 secs) 6 KB 11 KB (3-7 secs) 1-2 KB (5-6 secs) 8 KB Call Establishment Firewall 7 KB (30-35 secs) 5-7 KB (10-15 secs) 8 KB Relay 124B (4) 45B (4) TCP TCP Caller Super Nodes 8,153 login attempts over four days 35% hostnames had a ‘.edu’ suffix • 102 universities • 894 unique SNs Unique SN IP distribution: US 83.7%, Asia 8.9%, Europe 7.1% Top 20 nodes received 43.8% of the total connections Callee (NAT+firewall) TCP 51B (3) TCP 117B (4) Relay Callee Media:TCP Ordinary Host (OH) INTERNET • A Skype client Super node (SN) B (public IP) A (public IP) • A Skype client • Has public IP address, ‘sufficient’ bandwidth, INTERNET CPU and memory Bootstrap super nodes (maintained by Skype) A (private B (public IP) port-restricted NAT IP) • Used when running Skype for the first time • A total of seven nodes hard-coded in Skype INTERNET executable Login server A (private IP) port-restricted NAT port-restricted NAT B (private IP) • Stores Skype id’s, passwords and buddy lists UDP-blocking firewall UDP-blocking firewall Skype Relay Experiments • Used at login for authentication • Version 1.4: 212.72.49.141 and 195.215.8.141 Jan 20th to Feb 5th 2006.. Caller and callee machines in IRT lab 8,822 successful call attempts and 4,904 unique relay IP Skype, MSN, Yahoo and Google Talk addresses 60% of the calls routed through caller SN Application Memory usage Memory usage Process Process Mouth-to Relay nodes in 51 countries version before call after call (caller, priority priority ear latency (caller, callee) callee) before call during call Caller TCP TCP Media:TCP N1, N2, N3 19B 19B TCP TCP Callee 19B 19B Caller and callee on the average exchange 3 msg/s over TCP with N1, N2 and N3 after call has been established. 1.4.0.84 19 MB, 19 MB 21 MB, 27 MB Normal High MSN 7.5 25 MB, 22 MB 34 MB, 31 MB Normal Normal 184ms Yahoo 7.0 beta 38 MB, 34 MB 43 MB, 42 MB Normal Normal 152ms 9 MB, 9 MB 13 MB, 13 MB Normal Normal Total successful calls 8,882 % of successful calls between Relay distribution Global Internet Skype 1.0.0.80 Caller SN 713B (7) 3464B (8) Experimental Setup The Skype Network GTalk Caller (NAT+firewall) TCP TCP 96ms 55.34% (4,937) 3.3% (131) 7.9% (392) 0.05% (2) 0.2% (10) 42.9% (1,709) 38.51% (1,901) North America 52.42% (2,089) 52.17% (2,576) South America 0.14% (54) 1.18% (58) Australia Europe NAT 109ms Caller Skype Callee Skype 8:00pm and 7:59am EST 44.66% (3,985) Asia NAT 8:00am and 7:59pm EST