How we use FAOSTAT in Nutrition BA Burlingame
How we use FAOSTAT in
Nutrition
BA Burlingame
Nutrition in FAO
• Food Consumption Surveys
• Nutrient Requirements (incl energy)
• Nutrition Country Profiles
• Total Diet Studies
• Food Systems Analysis
• Dietary Pattern Analysis
• Nutrients in agricultural production (vit A, lysine per hectare; DHA availability)
• Nutritional Epidemiology
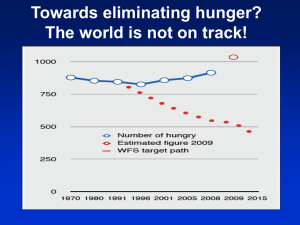
• FIVIMS, number of hungry people
Strength in time series
Food Balance Sheet Database
Food Supply Database
6
5
4
3
1
0
2
1961 1967 1977 1987 1997
Milk - Excluding Butter
Poultry Meat
35
30
25
20
15
10
5
0
Animal products
50
45
1962 1967 1972 1977 40 1987 1992 1997
35
30
25
20
15
10
5
0
1962 1967 1972 1977 1982 1987 1992 1997
China
India
30
China
25
India
40
35
50
45
15
10
5
0
Vegetal products
1962 1967 1972 1977 1982 1987 1992 1997
China
India
120
100
80
60
40
20
0
New
Zealand
Australia United
States of
America
Italy
Product Beer
Product Wine
1998
160
140
120
100
80
60
40
20
0
1961 1965 1970 1975 1980 1985 1990 1995 1997
Australia
Beer
Wine
4000
3500
3000
2500
2000
1500
1000
500
0
So m al ia
Bu ru nd i
F iji
T u rk ey
U
SA
Carb
Fat
Protein
Extent of food deprivation
Prevalence Depth of hunger (kJ)
<850
(200kcal)
< 5%
(low) 52
850-1300
(200-300kcal)
0
>1300
(300 kcal)
0
5-19% 17
(moderate)
20%
(high)
0
Total 69
29
31
60
0
23
23
Total
52
46
54
152
Average food deficit of the undernourished
< 850 kJ/person/day
850-1300 kJ/person/day
> 1300 kJ/person/day
Depth of hunger and infant mortality in developing countries
120
100
80
60
40
20
0
Low Moderate
Depth of hunger
1996-98
High
Depth of hunger and life expectancy in developing countries
80
70
60
50
40
Low Moderate High
Depth of hunger 1996-98
Depth of hunger and GDP growth in developing countries
4
3
2
6
5
1
0
Low Moderate
Depth of hunger 1996-98
High
Food deprivation and GDP per capita in developing countries
1400
0
1200
0
1000
0
8000
6000
4000
2000
0
1 2 3
Food deprivation group
4 5
Improving the quantity and quality of diets
• 6.2 MJ/day (1480 kcal)
4.7 MJ from starchy staples
1.5 MJ from other foods
• 10.5 MJ/day (2 500 kcal)
5.7 MJ from starchy staples
4.7 MJ from other foods
National
• Poland
– food consumption & eating habits
– changes in dietary pattern and diet-related disease
• Argentina
– Estimated vitamin A losses
• Finland
– lead content of foods
• Norway
– trans fatty acids
Regional
• Europe
– “Tale of two commodities”
• Mediterranean Diet
– fruits, veg, olive oil, wine
• Africa
– Famine warning
• Nordic Countries
– low-fat dairy,
edible fats
• Total Diet Studies – Regional Diets
Suggestions
• Selected ESS staff should get training on food composition because
– they are in contact with countries on these issues
– they compile compositional data for SUAs
– this would enhance communication between ESS and AGN
• Training module should be developed for food composition
• To enhance data quality, to enhance collaboration on issues mentioned earlier and work to be carried out by consultants under AGN responsibility but supported by SO H
• Systematic error reporting mechanisms (e.g., different results for undernourishment between AGN and ESS using the same data,
Cape Verde)
Future...
•
INFOODS link
• Data suppliers and data users
• International standards for compositional data (units, nutrient expressions)
• All energy-yielding components
• Some micronutrients
• Waste – household vs edible portion
• Other terminology (DEC, DES)
• Compositional databases = module in FAOSTAT
• Commodity tree updates (generic and country-specific)
• International standards for food classification/naming
(Codex, Food Comp...)
• Collaboration in related activities, e.g., ICDAM, IFDC
Final
FAOSTAT is/should be the most important output of FAO
Nutrition community uses (used) FAOSTAT data extensively
With a common platform for database development, several nutrition-related databases could be usefully linked
Time series is crucial