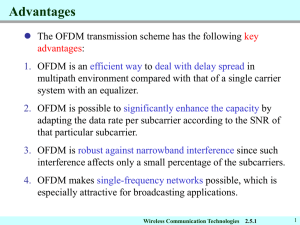
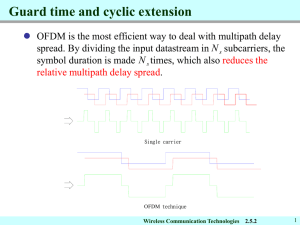
Part 2 Wireless Communication Technologies Wireless Communication Technologies Chapter 2 1
advertisement

Part 2 Wireless Communication Technologies Wireless Communication Technologies Chapter 2 1 Outline 2.5.1 Introduction 2.5.2 OFDM Basics 2.5.3 Performance Sensitivity for Imperfect Circuit 2.5.4 Timing and Frequency Synchronization 2.5.5 Example Coherent Detection and Channel Estimation 2.5.6 The Peak Power Problem 2.5.7 Summary References Problems Wireless Communication Technologies 2.5.1 2 Introduction The most suitable modulation choice for wireless broadband multimedia communication systems (WBMCS) seems to be orthgonal frequency division multiplexing (OFDM). The principle of OFDM is to split high-rate data-streams into a number of lower rate streams that are transmitted simultaneously over a number of sub-carriers. The dispersion in time from multi-path delay spread is relatively decreased per sub-carrier. Wireless Communication Technologies 2.5.1 3 Introduction The inter-symbol interference (ISI) can be eliminated by guard time and the inter-carrier interference (ICI) can be avoided by using cycle extension. Cyclic Prefix 15 10 5 0 -5 -10 -15 0 0.5 1 1.5 2 2.5 3 3.5 4 OFDM symbol time Guard Time Serial to parallel IFFT Parallel to serial Add guard time Wireless Communication Technologies 2.5.1 OFDM signal 4