Adhering to Medical Advice
advertisement

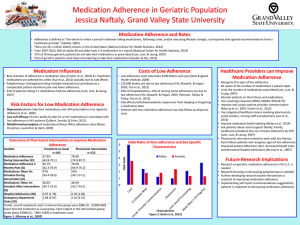
Adhering to Medical Advice Basic ideas • Do not take left over medications • Do not stop taking medicine whenever you begin to feel better • Do not quit your medication even if you feel worse after taking it • Even if it makes you feel bad, take the medicine anyway Theories for adherence • • • • Behavioral theory Self-efficacy theory Reasoned action & planned behavior Transtheoretical model Behavioral theory • Operant conditioning – Reinforcement • Positive • Negative – Punishment – Rewards • Extrinsic • Intrinsic Self-efficacy theory • Bandura’s Reciprocal determinism – Person (thinking) + Behavior + Environment • Self-efficacy (Person) – Perceived control over yourself and your environment – Situation specific Self-efficacy • • • • Beliefs predict accomplishment Acquired, increased, or decreased by: 1. Performance 2. Vicarious experience – Seeing others of similar skills perform • 3. Encouragement • 4. Physiological arousal – Anxiety, or high expectation The Transtheoretical Model • Stages of change model • 1. Precontemplation stage – Has not thought about changing • 2. Contemplation stage – Only thought about changing • 3. Preparation – Thoughts & preparation for change • 4. Action stage – Actually making the change • 5. Maintenance stage – Resists temptation to go back How do you measure adherence? • • • • • • 1. Ask Practitioner 2. Ask patient 3. Ask others 4. Monitor medication 5. Biochemical evidence 6. Combination of these Accuracy of measurement • 1. Practitioner – Slightly better than chance • 2. Patient – Inaccurate because: • Do not know • Lie to exaggerate success • 3. Others • Constant observation is impossible • Artificial - Unrealistically high reports • 4. Medicine usage • Patient may not have taken the medication • 5. Biochemical evidence (blood, urine) • People vary in response to drugs What factors predict adherence? • • • • 1. Severity of disease 2. Treatment characteristics 3. Personal characteristics 4. Environmental factors – Cultural norms – Social support Severity of disease • Pain is most likely to produce compliance with medical advice Personal characteristics • Compliance – Depends on the situation – Is not a global personality trait • Belief that treatment of ineffective or harmful – Decreases compliance Environmental factors • Social support - increases compliance – Living with a family – Being married Improving adherence • • • • Clearly written instructions Verbal rewards Prompts from patient’s spouse Simple prescriptions