Do you remember? Exam #1 – Ch. 1-4
advertisement

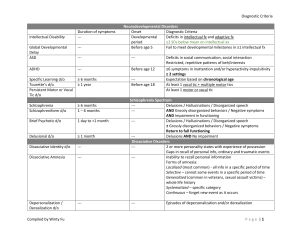
Do you remember? Exam #1 – Ch. 1-4 These questions come from the “Do You Remember” slides in the Power Points and lecture videos. They are designed to help you with the exams. I suggest printing them out, having them in front of you when listening to the videos. Finally, listen for the answers and write them in the form to study from. Ch. 1 Thinking critically What is a theory? What is a hypothesis? What types of variables are there? What types of correlation are there? If they are correlated, did one thing cause the other? What is a population? What is the difference between random sample and random assignment? What is the difference between a simple random sample and a systematic random sample? What research methods do psychologists use? What is the difference between a case study and naturalistic observation? What problems are there with an experiment? What is a double blind study? What problem does it attempt to solve? Why do psychologists want to replicate a study? What are some problems with thinking? After you know the results of a study, they appear obvious. What is this called? Ch. 2 Biology of the mind Can you draw and label the parts of a neuron? ◦ Dendrites, body, axons What is a synapse, and how do neurotransmitters aid neural communication? What are endorphins? What is the difference between the central and peripheral nervous systems? What is the difference between the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems? What is an example of a simple reflex pathway? If the spinal cord is broken, how does that effect the perception of sensation? What parts of your brain evolved first and last? What makes up the limbic system? ◦ What does each part focus on? What does the cerebellum do? What characteristic of the brain allows it to adjust after damage? How does information get from one side of your brain to the other? What does an EEG measure? What imaging method using radioactive glucose is used for identifying which of Lucy’s brain areas was most active when she talked? What does a fMRI do? Ch. 3 Consciousness and the two-track mind • What is the mind’s upper and lower track? • What is your circadian rhythm? • When do alpha and delta waves occur? • How do you feel when you are in an alpha wave state? • What are sleep spindles? • When do they occur? • What happens during REM sleep? • How long is the REM sleep cycle? • What is the difference between insomnia and narcolepsy? • You are 56 years old, and weigh 224 pounds. Are you more apt to have sleep apnea or night terrors? Why? • Do you have more or less REM sleep than your baby brother? • Can you be hypnotized against your will? • How does a posthypnotic suggestion work for Bill who smokes? • What is the social influence theory of hypnosis? • Can you tell the difference between hypnotized and unhypnotized subjects? Ch. 4 Nature & Nurture What are examples of how genes and the environment interact? What is your genome? What are genetic mutations? How could we do a study to separate the effects of genetics from nurturing? How do nature and nature interact to create a confident personality or grow more synapses in the brain? Can you give an example of the evolutionary theory of sexual behavior? How do social norms affect your behavior? How do people’s personality change throughout adulthood? How are individualism and romance related? How do gender roles affect your behavior? How do the sexes differ in “tend & befriend” behavior? What is the concept of personal space?
















![Biological Approach [Autosaved]](http://s2.studylib.net/store/data/027241410_1-b3a5a5743ebea4e096c12a11dadcd34d-300x300.png)