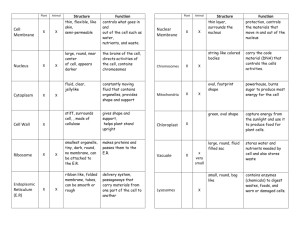
Comprehensive Final Focus 1. Negative feedback vs. positive feedback mechanisms
advertisement

Comprehensive Final Focus 1. Negative feedback vs. positive feedback mechanisms 2. Forms of stored energy used by cells 3. Enzymes: what types of molecules they are, what they do 4. pH, acids, bases, buffers 5. The structure of the cell membrane; the roles of membrane proteins 6. Movement of particles/water: diffusion, osmosis & hydrostatic pressure 7. How stuff gets in and out of cells: what types of materials can pass across the membrane without help, what materials need proteins or vesicles to pass, leak channels, facilitated diffusion, active transport, vesicular transport 8. The Na+-K+ exchange pump 9. Serous membranes 10. Osteoblasts, osteoclasts, osteocytes & osteoprogenitor cells (roles) 11. Hormones affecting bone growth and maintenance 12. Skeletal muscle cell contraction events 13. Muscle energetics 14. Nervous system organization (systems & divisions) 15. Membrane potentials: resting, depolarized, hyperpolarized. The movement of which ions leads to depolarization? The movement of which ions leads to hyperpolarization? Don’t worry about the details of the events in the action potential of a neuron. 16. Events at a synaptic terminal when an action potential reaches it 17. Absolute refractory period; what it is and its significance in cardiac muscle 18. All roles of Ca2+ discussed thus far 19. Relative concentrations between the extracellular fluid and intracellular fluid of: Na+, K+, Cl-, Ca2+, proteins20. Effects of sympathetic activity on body functions (ie, increased heart rate, nutrient mobilization, etc) and Nt used on effectors 21. Effects of parasympathetic activity on body functions and Nt used on effectors 22. Know the relationship between the hypothalamus and pituitary gland 23. Related to the above, understand the GnRH/FSH, LH system. Know the target cells of GnRH and its effect on them and the target cells of FSH and LH and their effects. 24. Know which hormone classes enter cells and activate genes, and which use second messengers to activate proteins. Know the best understood 2nd messenger by name (cAMP). Know 2nd messenger systems rely on a cascade of activations that end in the activation (or inactivation) of the target protein, but don't focus on the actual events. 25. Know the renin-Angiotensin activation system 26. Know what the receptor cells are called in the senses of hearing, equilibrium, sight, taste and smell; understand what stimulates them (ex, fluid movement, light, chemical binding); ex, in hearing, the receptor cells are mechanoreceptors called hair cells, and they are stimulated indirectly by fluid movement. 27. Know where RBC and WBC are made, know the significance of erythropoietin (what effect it has on RBC production) 28. Know the significance of fibrin. 29. Know that pacemaker cells set the basic rhythm of the heart, and that contraction is caused by ions travelling through gap junctions of adjacent cells. Know that the atria are mostly electrically isolated from the ventricles, so that they contract before the ventricles. Don't worry about the specific ions, gates, etc. 30. Know the effect that the sympathetic and parasympathetic divisions, and thyroid hormone and E/NE have on heart rate and contractility. 31. Understand complete tetanus vs. twitch, know which is most common in skeletal muscle and cardiac muscle 32. Know the significance of P, QRS and T waves on an ECG 33. Understand how all of the following are related (and, when appropriate, where structures are located) in terms of coordinating heart rate, blood pressure and respiration: chemoreceptors in the aortic and carotid bodies and at the medulla; cardiovascular centers; respiratory centers; sympathetic division, parasympathetic division, JG cells, NE, Ach, renin, ANP, CO2. 34. Mechanisms of venous return 35. Capillary dynamics (BCOP, CHP, etc) 36. Understand why air enters the lungs from the atmosphere; understand why CO2 and O2 move in the directions they do (comparing alveoli with blood with tissues) 37. Know the 3 ways CO2 is transported through the blood, understand the bicarbonate system 38. Know that the proteases all have to be activated; know ONLY pepsin in terms of the inactive form and how it's activated 39. How do parietal cells make HCl 40. List the digestive enzymes we covered and state what they hydrolyze and what is produced. (ex, amylase hydrolyzes starch into maltase). Know where each enzyme is released, and where in the GI tract certain types of nutrients are being chemically digested. 41. List several functions of hepatocytes. 42. What's the function of bile in digestion? Where is it stored? Where is it made? 43. What endocrine products does the pancreas make? Exocrine? Where does it send the exocrine products? 44. What do the terms filtration, reabsorption and secretion mean? Where does filtration occur in the kidneys? 45. What effect do PTH, ADH, ANP and Angiotensin II have on the kidneys? What other effects do these hormones have (ie, in other parts of the body)? 46. How is blood pH regulated?