This PowerPoint presentation of diagrams used in Bio 242 was
advertisement

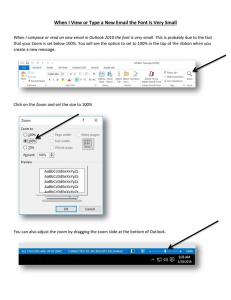
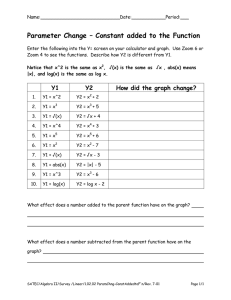
This PowerPoint presentation of diagrams used in Bio 242 was made by a student. While it looks to be complete and correct, I do not guarantee anything about the accuracy or completeness of the coverage for this class. That said, enjoy this nifty review software made by Gabriel Laigo in 2010. Note: So far I can only get this PowerPoint to run successfully on Windows using PowerPoint Player. You may need to download this player (included in this folder). Most of the buttons don’t work when using PowerPoint for Mac. Main instructions: After clicking on the diagram you want to review, write down the name of each structure in the picture according to its reference letter. Then click on the reference letter rectangle below the diagram to see to reveal the answer. Biology 242 Lab Diagram Study Guide Antibodies A.) Light chains A. B.) Antigen binding B. sites (variable) C.) Antigen binding C. sites (variable) D.) Heavy chains D. E.) Disulfide bonds E. Antibody Binding and Enzyme A.plate A.) Antigen bound to D.) Substrate D. B.antibody B.) Enzyme – labeled E.) Colored productE. C.) Enzyme attachedC.to tail of antibody AB.) ELISA test plate AB. Upper Respiratory System Click picture to ZOOM ACD. BC. A.) Sphenoid sinus A. BC.) Trachea B.) Posterior nasal aperture (internal nares) B. BD.) Frontal sinus BD. C.) Opening of pharyngotympanic (auditory) tube BE.) Nasal conchae (superior, BE. middle & inferior) C. CD.) External nares CD. (nostril) D.) Nasopharynx D. Vocal fold CE.) Hard palate CE. E. E.) Uvula DE. AB.) Oropharynx AB. DE.) Soft palate AC.) Laryngopharynx ABC.) Epiglottis ABC. AC. AD.) Laryngopharynx AD. ABD. ABD.) Vestibular fold ABE. of larynx AE.) Esophagus AE. ABE.) Thyroid cartilage Tracheal Wall Click picture to ZOOM A.) Mucosa A. D.) Submucosa D. B.) Pseudostratified ciliated B. columnar epithelium E. in submucosa E.) Seromucous gland C.) Lamina Propria (connective tissue) C. AB.) Hyaline cartilage AB. The Trachea The Lungs Click picture to ZOOM BD. BE. A.) Cardiac notch CD. A. B.) Right lower lobe B. C.) Right middle lobeC. D.) Right upper lobeD. E.) Base of lung E. AB.) Apex of lung AB. Trachea Segmental Left Lobar Inferior main (secondary) (primary) lobe (tertiary) ofAC.) left bronchus bronchus bronchus lung AC. AD.) Medial depression AD. (hilum) AE.) Pulmonary hilum AE. BC.) Superior lobeBC. of left lung CE. Alveoli and Capillaries Click picture to ZOOM A.) Macrophage A. B. secreting) cell B.) Type II (surfactantC.) Type I cell of alveolar C. wall D.) Alveolus D. E.) Alveolar pores inE.capillary Respiratory Zone Structures Click picture to ZOOM I. I.) Respiratory Bronchiole II.) Alveolar duct II. III.) Alveolus III. Spirographic Record of Healthy Adult Male Click picture to ZOOM A. volume (3100 ml) A.) Inspiratory reserve D. ml) D.) Vital capacity (4800 B.) Tidal volume (500B.ml) E.) Residual volumeE.(1200 ml) C.) Expiratory reserve C.volume (1200 ml) Digestive System Click picture to ZOOM S. T. A. J. A.) Oral cavity (mouth) J.) Anus B. B.) Tongue K. K.) Parotid salivary gland C.) Esophagus C. L. L.) Stomach M. M.) Pancreas D. D.) Liver Vermiform Sigmoid Anal Rectum canal appendix colon E. N. E.) Gallbladder N.) Spleen F.) Duodenum of the O.) Transverse colonO. F. small intestine G.) Jejunum of the small P.) Descending colonP. G. intestine H. intestine H.) Ileum of the small Q.) Ascending colonQ. R. I.) Small Intestine I. R.) Cecum U. V. The Alimentary Canal Wall Click picture to ZOOM A. A.) Gland in Submucosa E.& Connective tissue) E.) Serosa (Epithelium B.) Mucosa (Epithelium, Lamina B. propria & Muscularis mucosae) AB.) Mucosa-associated AB. lymphoid tissue C.) Submucosa (connective tissue) C. D.) Muscularis externa D. (longitudinal & circular muscle) AC.) Lumen AC. The Stomach Click picture to ZOOM A.) Esophagus A. B.) Cardiac region B. C.) Fundus C. D.) Body D. E. E.) Greater curvature AB.) Pyloric sphincter AB.(valve) AC.) Duodenum AC. AD.) Lesser Curvature AD. The Duodenum & Related Organs Click picture to ZOOM A.) Cystic duct A. AB.) Common hepatic AB. duct B.) Gallbladder B. AC.) Bile duct and sphincter AC. C.) Major duodenal papilla C. D.) HepatopancreaticD.ampulla & sphincter E. E.) Falciform ligament AD.) Pancreas AE.) Jejunum AD. AE. BC.) Main pancreatic BC.duct and sphincter The Duodenum Kidney Click picture to ZOOM BD. A.) Renal cortex A. B.) Renal medulla B. C.) Major calyx C. AB.) Minor calyx AB. AC.) Ureter AC. Renal artery & vein AD.) Renal pyramidAD. in renal medulla D. D.) Papilla of pyramid AE.) Renal column AE. E. BC.) Fibrous capsule BC. E.) Renal pelvis Nephron Click picture to ZOOM A. A.) Glomerular capsule B.) Glomeruls B. AB.) Descending limb AB.of Loop of Henle AC.) Ascending limbAC. of Loop of Henle C.) Afferent arterioleC. AD.) Distal convoluted AD. tubule D.) Arcuate artery D. AE.) Proximal convoluted AE. tubule E.) Arcuate vein E. BC.) Collecting ductBC. External Female Genitalia Click picture to ZOOM BD. A. AB.) Labia majora AB. B. B.) Prepuce of clitoris AC.) Labia minora AC. the duct of the greater A.) Mons pubis C. Opening of AD.) Urethral orifice vestibular gland AD. D.) Vestibule D. AE.) Hymen (ruptured) AE. E.) Anus E. BC.) Vaginal orificeBC. C.) Clitoris (glans) Male Reproductive System Click picture to ZOOM A.) Ejaculatory duct A. B.) Prostatic urethraB. C.) Urinary bladder C. D. D.) Pubis E. E.) Ductus (vas) deferens AB.) Erectile tissueAB. of penis AC.) Shaft of the penis AC. AD.) Spongy urethraAD. AE.) Glans penis AE. BC. BC.) Prepuce BD.) Seminal vesicleBD. BE. BE.) Prostate CD.) Membranous CD. urethra CE. CE.) Rectum DE.) BulbourethralDE. gland ABC.) Epididymis ABC. ABD. ABD.) Testis ABE.) Scrotum ABE. Cross Section of Seminiferous Tubule Click picture to ZOOM AE. A.) Fibroblast A. E.) Early spermatidsE. B.) Meiosis B. AB.) Secondary spermatocytes AB. C.) Initial spermiogenesis C. D. D.) Late spermiogenesis Interstitial Cells AC.) Primary spermatocyte AC. AD.) Spermatogonium AD. Histologic Architecture of Graafian Follicle Click picture to ZOOM A.) Primary follicle A. D. luteum D.) Degenerating corpus B.) Growing follicles B. E.) Ruptured follicleE. C.) Mature vesicularC. (graafian) follicle Sperm A.) Midpiece A. C.) Nucleus C. B.) Head B. D.) Tail D. Spermatogenic Cells in Seminiferous Tubule Click picture to ZOOM A.) SpermatogoniumA. D. D.) Secondary spermatocytes B.) Type B daughter B. cell E.) Early spermatidsE. C.) Primary spermatocyte C. The Testis Click picture to ZOOM A.) Spermatic cord A. B. nerves B.) Blood vessels and C.) Testis C. D. D.) Seminiferous tubule E. E.) Lobule AB.) Septum AB. AC.) Tunica albuginea AC. AD.) Tunica vaginalis AD. AE. AE.) Cavity of tunica vaginalis BC. BC.) Ductus (vas) deferens BD. BD.) Head of epididymis BE. BE.) Efferent ductule CD.) Rete testis CD. CE.) Straight tubuleCE. DE. DE.) Body of epididymis ABC. ABC.) Duct of epididymis ABD. ABD.) Tail of epididymis Ovarian Tissue