Figure 1 Economists versus accountants
advertisement

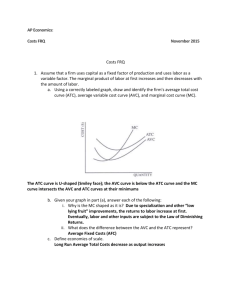
Figure 1 Economists versus accountants > Normal ROR = Normal ROR Economists include all opportunity costs when analyzing a firm, whereas accountants measure only explicit costs. Therefore, economic profit is smaller than accounting profit 1 The Various Measures of Cost • Fixed costs (short-run) – Do not vary with the quantity of output produced • Variable costs (short and long-run) – Vary with the quantity of output produced • Average fixed cost (AFC) – Fixed cost divided by the quantity of output • Average variable cost (AVC) – Variable cost divided by the quantity of output 2 EXHIBIT 5.1 Daily Costs of Manufacturing Pine Lumber 5-3 EXHIBIT 5.2 The Marginal Cost of Manufacturing Pine Lumber 5-4 EXHIBIT 5.3 The Cost Curves 5-5 The Various Measures of Cost • Cost curves and their shapes • U-shaped average total cost: ATC = AVC + AFC – AFC – always declines as output rises – AVC – typically rises as output increases • Diminishing marginal product • At the minimum of ATC or AVC – The bottom (lowest point) of the U-shaped curve – MC = min(ATC) and MC = min(AVC) 6 The Various Measures of Cost • Cost curves and their shapes • Efficient scale – Quantity of output that minimizes average total cost • Relationship between MC and ATC – When MC < ATC: average total cost is falling – When MC > ATC: average total cost is rising – The marginal-cost curve crosses the averagetotal-cost curve at its minimum 7 Figure FIGURE 9.2 Short-Run Supply Curve of a Perfectly Competitive Firm At prices below average variable cost, it pays a firm to shut down rather than continue operating. Thus, the short-run supply curve of a competitive firm is the part of its marginal cost curve that lies above its average variable cost curve. Costs in Short Run and in Long Run • Many decisions – Some inputs are fixed (unalterable)in the short run – All inputs are variable in the long run, • Firms – greater flexibility in the long-run – Long-run cost curves • Differ from short-run cost curves • Much flatter than short-run cost curves – Short-run cost curves • Lie on or above the long-run cost curves 9 Figure 6 Average total cost in the short and long runs Average Total Cost ATC in short run with small factory ATC in short run with medium factory ATC in short run with large factory ATC in long run $12,000 10,000 Economies of scale 0 Constant returns to scale 1,000 1,200 Diseconomies of scale Quantity of Cars per Day Because fixed costs are variable in the long run, the average-total-cost curve in the short run differs from the average-total-cost curve in the long run. 10 Costs in Short Run and in Long Run • Economies of scale – Long-run average total cost falls as the quantity of output increases – Increasing specialization • Constant returns to scale – Long-run average total cost stays the same as the quantity of output changes 11 Costs in Short Run and in Long Run • Diseconomies of scale – Long-run average total cost rises as the quantity of output increases – Increasing coordination problems 12 (Economic) Profit Maximization Calculating Profit • To find profit, we need to know revenues and costs – For a perfectly competitive firm, revenues can be found by looking at the price (determined by the market) and the quantity sold – Costs are determined by the quantity sold • For the firm, q P ATC • Intuition: Profit = (units sold) ×(average profit per unit) When to Operate or Shut Down Profit and Loss in the Short Run Condition Outcome P > ATC The firm makes a profit ATC > P > AVC The firm will operate to minimize loss AVC > P The firm will temporarily shut down Short Run Supply Curve Long Run Supply Curve Long Run Shut Down Criteria Condition Outcome P > ATC The firm makes a profit P < ATC The firm should shut down Long-run Profitability • Positive economic profit cannot be sustained – Entry of new firms causes: • Market supply curve to shift to the right • Lowering the market equilibrium price and • Lowering each firm’s demand curve (or constant price) – In the long run, the firm will make only normal profit (zero economic profit). Its horizontal demand curve will touch its average total cost curve at its lowest point 2 In the long-run, entry will dissipate short-run economic profits 2