Chap Important Not So Important … - Population vs sample (parameter vs statistic)
advertisement

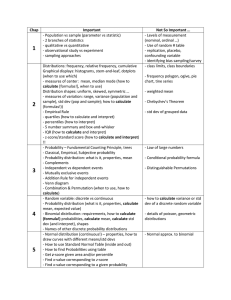
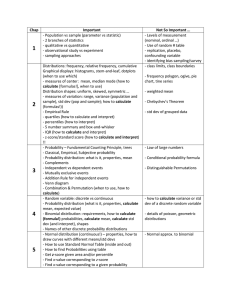
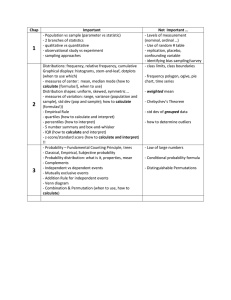
Chap 1 2 3 4 5 Important - Population vs sample (parameter vs statistic) - 2 branches of statistics - qualitative vs quantitative - observational study vs experiment - sampling approaches Distributions: frequency, relative frequency, cumulative Graphical displays: histograms, stem-and-leaf, dotplots (when to use which) - measures of center: mean, median mode (how to calculate [formulas!], when to use) Distribution shapes: uniform, skewed, symmetric … - measures of variation: range, variance (population and sample), std dev (pop and sample); how to calculate (formulas!)) - Empirical Rule - quartiles (how to calculate and interpret) - percentiles (how to interpret) - 5 number summary and box-and-whisker - IQR (how to calculate and interpret) - z-score/standard score (how to calculate and interpret) !! - Probability – Fundamental Counting Principle, trees - Classical, Empirical, Subjective probability - Probability distribution: what is it, properties, mean - Complements - Independent vs dependent events - Mutually exclusive events - Addition Rule for independent events - Venn diagram - Combination & Permutation (when to use, how to calculate) - Random variable: discrete vs continuous - Probability distribution (what is it, properties, calculate mean, expected value) - Shapes of distributions: uniform, skewed, bell … - Binomial distribution: requirements, how to calculate (formula!) probabilities, calculate mean, calculate std dev (and interpret), shapes - Names of other discrete probability distributions - Discrete versus continuous distribution -Normal distribution (continuous!) – properties, how to draw curves with different means/std devs - How to use Standard Normal Table (inside and out) - How to find Probabilities using table - Get z-score given area and/or percentile Not So Important … - Levels of measurement (nominal, ordinal …) - Use of random # table - replication, placebo, confounding variable - identifying bias sampling/survey - class limits, class boundaries - frequency polygon, ogive, pie chart, tine series - weighted mean - Chebychev’s Theorem - std dev of grouped data - Law of large numbers - Conditional probability formula - Distinguishable Permutations - how to calculate variance or std dev of a discrete random variable - details of poisson, geometric distributions - Normal approx. to binomial 6 7 - Find x-value corresponding to z-score - Find x-value corresponding to a given probability - sampling distribution of sample mean - Central Limit Theorem - Finding probability for x and mean of x - point estimate vs confidence interval for population mean - margin of error - use of t Table - how to calculate (formula) confidence interval (expression) using t or z; when to use which - how to interpret (inferential!) - Hypothesis test for population mean – what is it all about? - What is α? - What is P-value? - Type I error? - Steps to reach decision - P-Value approach (when to use) - test statistic (z? or t? neither?) - Rejection region (critical value) approach (when to use) - Interpretation of decision - minimum sample size needed for confidence interval - confidence interval for population proportion - confidence interval for variance - confidence interval for standard deviation - Type II error - Hypothesis test for population proportions - Hypothesis test for population variance - Hypothesis test for population std dev