Types of Data
advertisement
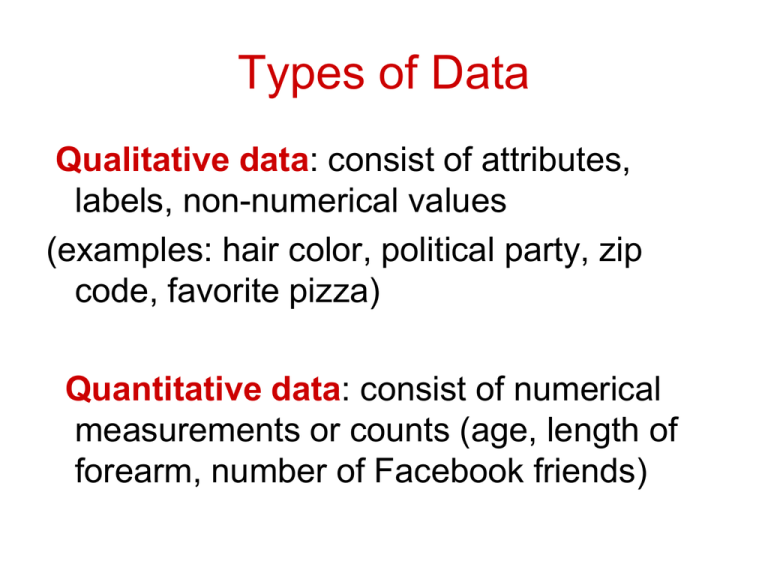
Types of Data Qualitative data: consist of attributes, labels, non-numerical values (examples: hair color, political party, zip code, favorite pizza) Quantitative data: consist of numerical measurements or counts (age, length of forearm, number of Facebook friends) Examples Qualitative? Quantitative? - salaries of teachers marital status of graduate students social security numbers number of cars in household color of family car Qualitative? Quantitative? - salaries of teachers (quantitative) - marital status of graduate students (qualitative) - social security numbers (qualitative) - number of cars in household (quantitative) - age of cars in household (quantitative) - color of family car (qualitative) Qualitative? Quantitative? City Baltimore Jacksonville Memphis Pasadena San Antonio Seattle Population 636,919 807,815 669,651 143,080 1,351,305 598,541 Levels of Measurement Nominal : qualitative only. Data are categorized using names, labels, or qualities. No mathematical computations. (names of baseball teams, social security numbers) Ordinal: qualitative or quantitative. Data are ordered or ranked, but differences between data are not meaningful (final standings of NFC West conference football teams) Levels of Measurement Interval : can be ordered; meaningful differences between data values. However a “zero” value does not imply absence of the attribute (temperature) – [no inherent zero] Ratio: like interval data, but also: - “zero” value means absence of attribute [inherent zero] (e.g. wind speed) - one data value can be expressed as a multiple of another (i.e., as a ratio) (a dog weighing 20 pounds is twice as heavy as a dog weighing 10 pounds) Example The following items appear on an employment application. Identify the level of measurement for each. - highest previous salary - gender - year of college graduation - number of years at last job Example The following items appear on an employment application. Identify the level of measurement for each. - highest previous salary (ratio; quantitative, makes sense that $45000/yr is three times $15000/yr) - gender (nominal) - year of college graduation (interval; makes sense to say that 2010 is 5 years later than 2005) - number of years at last job (ratio) A sports writer plans to list the winning times for all the swimming events in the 2012 Olympics. The writer wants to simply organize the data and compile a list (describe!) the medal winners of the Olympics descriptive study A survey conducted among 1017 men and women found that 76% of women and 60% of men had a physical examination with the previous year. Inferential? Descriptive? Both! 76% women, 60% men Descriptive (simply describes the data sample which was collected) More women than men will have physical exams during the year Inferential (use the data sample to say something about the population)


