What is Culture?
advertisement

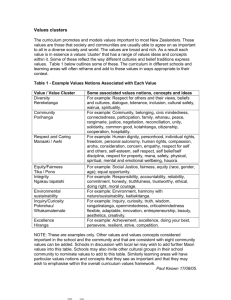
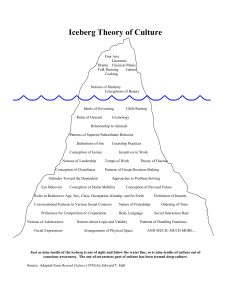
What is Culture? Some definitions Culture as Knowledge • “Culture is the acquired knowledge people use to interpret experience and generate behavior.” -- James Spradley, anthropologist A word that means several different things • National / ethnic culture (meanings and behaviors groups of people develop and share over time) • A subgroup – organizational or educational culture Characteristics of Culture • CULTURE IS LEARNED and passed generation to generation • CULTURE IS SHARED by a group of people • CULTURE IS BASED ON SYMBOLS that have meaning only understood by those within the culture • CULTURE IS DYNAMIC – always moving (but slowly) • CULTURE IS AN INTEGRATED WHOLISTIC SYSTEM Culture is like an Iceberg Surface Culture Food, dress, music visual arts, drama, crafts, dance, literature, language, celebrations games Surface level (Concrete) Deep Structure Unspoken Rules (Behavioral Unconscious Rules - Symbolic Concept of time, personal space, rules of conduct, facial expressions, nonverbal communication, body language, touching, eye contact, patterns of handling emotions, notions of modesty, concept of beauty, courtship practices, relationships to animals, notions of leadership, tempo of work, ideals of childrearing, theory of disease, social interaction rate, nature of friendships, tone of voice, attitudes toward elders, concept of cleanliness, notions of adolescence, patterns of group decision-making, definition of insanity, preference for competition or cooperation, tolerance of physical pain, concept of “self,” concept of past and future, definition of obscenity, attitudes toward dependents, problem-solving, roles in relation to age, sex, class, occupation, kinship, and so forth Deep Structures of Culture Roots of Reality – the “how” and “why” The Deep Structures of a Culture: • carry a culture’s most important beliefs (family, state, religion) • have messages that endure, are deeply felt and supply much of a person’s identity (one of its most important roles for a culture is to assist a person in their sense of identity) Deep Structures of Culture Family Provide definition and form (nuclear, extended) The functions of family are to: •teach socialization; •pass on core values; •share a worldview; •foster identity development; •provide communication training and social skills; •establish gender roles; •determine individualism vs. collectivism; •define aging; •teach social skills What sunk the Titanic?