AMA 171 - Anatomy & Physiology/Medical Terminology/Pathology 2 Skin and Senses
advertisement

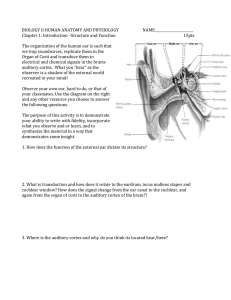
AMA 171 - Anatomy & Physiology/Medical Terminology/Pathology 2 Skin and Senses Skin: (Integumentary System) Interesting fact: weighs 8-10lbs and covers an area of 22 square feet (in an average adult) Functions: Covers and protects the internal organs and tissues Produces important secretions: oil and sweat to lubricate and cool the body Contains nerves that are receptors for sensations such as pain, temperature, pressure and touch Thermoregulation of the body Structure (layers of the skin): Epidermis: outermost layer made of squamous epithelial cells; the basal layer of the epidermis is always growing and multiplying Dermis: middle layer composed of blood and lymph vessels, nerve fibers and accessory organs, such as hair follicles, sweat and sebaceous glands Subcutaneous: deepest layer specializing in the formation of fat; important in the protection of the deeper tissues of the body, as a heat insulator and for energy storage Accessory organs: hair, nails & glands Hair: fibers composed of keratin, a hard protein Nails: hard keratin plates covering the last bones of each toe and finger Glands: Sebaceous (oil): found almost everywhere, except hands and feet. Lubricate the skin through the hair follicle and minimize water loss from the body; influenced by sex hormones Sweat: most numerous on hands and feet but found on almost all body surfaces. Almost pure water with dissolved materials such as salt; odor comes from bacteria, not sweat. Sweat (perspiration) cools the body as it evaporates into the air. Sense Organs: Receptors that are activated by stimuli from the external or internal environment. Eye: light rays enter the eye and are sent to the cerebral cortex of the brain, fusing to form a visual sensation with three-dimensional effect Ear: sound waves are received by the ear and sent to the auditory region of the brain in the cerebral cortex Structure of the eye Cornea: fibrous tissue covering pupil and iris, light enters here first, is bent or refracted Anterior chamber: contains aqueous humor a fluid produced by the ciliary body to nourish the eye and help maintain its shape Pupil: dark center of the eye, light rays enter here after passing through the cornea Iris: colored portion of the eye, contains muscles that constrict pupil to regulate light Conjuctiva: membrane that lines the eye and eyelids; clear and colorless unless irritated Sclera: white of the eye, provides nourishment via blood vessels Choroid: dark brown membrane inside of sclera, contains blood vessels Lens: changes shape to refract light and to flatten or round the lens for distance or close vision (accommodation) Structure of the eye cont… Ciliary body: muscles that control the lens Vitreous humor: jelly-like fluid that helps maintain eye’s shape Retina: sensitive nerve layer of the eye, contains rods and cones that are receptor cells responsible for color and central vision Optic nerve: chemical change from rods and cones cause nerve impulses to send visual signal to brain through this nerve Optic disc: region where optic nerve meets the retina Macula: area that contains the fovea centralis Fovea centralis: depression in macula that is the location of the sharpest vision in the eye Structure of the ear: three regions of the ear Outer ear: conducts sound waves Pinna (auricle): flap of the ear External auditory meatus (auditory canal): ear canal that secretes ceruman (ear wax) Middle ear: conducts sound waves Tympanic membrane (eardrum): sounds waves make this vibrate Ossicles: three small bones that are vibrated by the sound on the tympanic membrane: Maleus, Incus & Stapes Oval window: vibration from stapes touches this membrane that separates the middle and inner ear Inner ear (labyrinth): receives auditory waves and relays them to the brain Cochlea: looks like a shell; contains liquids that transmit the sound waves/vibrations Auditory nerve fibers: connect the cochlea to the brain so the brain “hears” sounds