THOSE PESKY VERBS!
advertisement

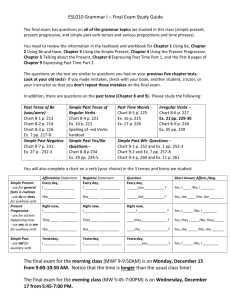
THOSE PESKY VERBS! Knowing which tense you want, how to make it, and why you want to use it SIMPLE PRESENT TENSE Looks like: • I/you/we/they talk • She/he/it talks Tricky things: • A few irregular verbs (is, does, has, goes) • That “s” ending!!! [Error correction symbol: AGR] WHEN DO WE USE IT? Habits & Facts • I usually come to class on time. • She has a dog. Summaries of texts! • In his essay, Lederer claims that short words are powerful. P R E S E N T P RO G R E S S I V E T E N S E Looks like: • • • • “be” and “verb+-ing” ending I am talking She is talking They are not talking Tricky things: • You must have both parts! • Some verbs can’t be progressive (feeling, thinking, etc verbs) WHEN DO WE USE IT? To describe something happening at the moment • Right now, you are reading a PowerPoint slide. • The world is rotating on its axis. • We are not playing soccer at the moment. FYI, You won’t often use this tense in academic essays for this class. PA S T P RO G R E S S I V E T E N S E Looks like: • • • • Past tense of “be” and “verb+-ing” ending I was talking She was talking They were not talking Tricky things: • You must have both parts! • You must have the –ing ending on the main verb! • Some verbs can’t be progressive (feeling, thinking, etc verbs) WHEN DO WE USE IT? Situation 1: To emphasize that two events were in progress at the same time time in the past. • Last week, you were practicing writing paragraphs while you were learning about appositives and adjective clauses. It was a lot of work to juggle at one time! We choose past progressive here because they were two long, difficult processes happening at the same time in the past(not one after the other). WHEN DO WE USE IT? Situation 2: Past progressive is often juxtaposed with simple past tense to emphasize that something was in progress at some time in the past when the other thing interrupted it. • • They were driving downtown when they ran out of gas. Marcie was still talking when the teacher for the next class came into the room. Tricky! Students often use past progressive when simple past would be better. Ask me (or a tutor) if you’re not sure! S I M P L E PA S T T E N S E Looks like: • • • • verb + -ed ending He talked They cooked I didn’t walk Tricky things: • Irregular past tense verbs are numerous!!! * link to a list * link to Quizlet flashcards WHEN DO WE USE IT? To describe something finished in the past. • She got her bachelor’s degree in 2002. • Last week, we listened to a presentation about academic success. • She went home, played with the dog, and did her homework. You will probably use this verb a lot when you write narratives (stories) about the past. You will also use it when you summarize something you experienced (an event, not a text). PRESENT PERFECT TENSE Looks like: • “have” + past participle of the main verb • Past participle looks like a past tense verb or it’s irregular • I have read • She has talked • They have written Tricky things: • You must have both parts! • Don’t use “be” with this! • Don’t interchange with simple past tense. WHEN DO WE USE IT? Situation One: To describe something that happened in the past, but we don’t know when (and when it happened is not important). We just know it happened before now. • I have graded your homework. It doesn’t matter when I did it – it just matters that I did it so you can get it back and learn from your mistakes and my comments. WHEN DO WE USE IT? Situation Two: To describe something that started in the past, but we don’t know when, and it is continuing. This happens with some special verbs. • I have lived in Seattle since 2007. • I have lived in Seattle for 7 years. • She has worked for the company since 2010. P R E S E N T P E R F E C T P RO G R E S S I V E TENSE Looks like: • • • • “have” + “been” + “verb + -ing” ending I have been reading She has been talking They have been writing Tricky things: • You must have all parts! • Don’t interchange with simple past tense or present perfect* • *Special verbs only WHEN DO WE USE IT? Again, the progressive form is used to emphasize duration: • They have been writing for two hours! • She has been sleeping for nineteen hours. She must be really, really tired. • If you’re not wanting to emphasize how much time something is taking, don’t use it. PAST PERFECT TENSE Looks like: • I/you/we/they/she/he had talked Tricky things: • Isn’t the same as simple past • Isn’t the same as present perfect WHEN DO WE USE IT? The past perfect tense is used to describe the first of two actions that were completed in the past. Note that the second action has a simple past tense verb. The tenses tell us which action happened first in time and which happened second. • I had come to class when I realized my backpack was on the bus. • You had written a journal entry before I asked you to write your paragraph. • Past perfect tense verb clauses often come with simple past tense verb clauses in complex sentences. RESOURCES Simple vs. Progressive verb chart Perfect Tenses verb chart Present Perfect and Present Perfect Progressive PPT