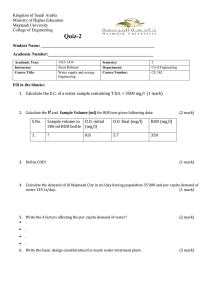
Fermentation Test (Phenol Red)
advertisement

Fermentation Test (Phenol Red) John Snow’s Cholera Spot Map Environmental Microbiology: Treatment of Waste Water and Polluted Habitats 08/09/11 Waste Water & Sewage A little history • Ancient Romans • Modern sewage system London: pipes and high pressure water New York City: 20 years later American waste amounts: (per person per day) 150 gal water 120 gallon of waste 5lbs trash http://www.kingcounty.gov/environment/wastewater/CSO/FAQ.aspx Sewage Treatment Purpose: –Eliminate potential pathogens and toxins –Decrease nutrient content (reduce microbial growth) –Reduce B.O.D. Biochemical oxygen demand (BOD): Amount of oxygen required for microbial decomposition of organic matter in sample 1. 2. 3. 4. BOD Organic Matter (waste) Determine O2 levels Incubation with microbes (5 days/20°C) Determine O2 levels Calculate difference between 1 & 3 B.O.D. Effects Raw sewage BOD: 300 to 400 mg/liter Natural water BOD: 5-10mg/L If you dump raw sewage into “receiving water”, the dissolved O2 can be quickly depleted by microbes http://www.theepochtimes.com/news/4-512/21351.html “200 million liters of sewage and industrial waste, much of it untreated, ooze into the Ganges from Varanasi” -Richard Stone, Science 2011 Large Scale Wastewater Treatment Multi-series process (US) • 1° treatment • 2° treatment (4 methods) • Advanced Treatment Effluent (treated liquid) is discharged in body of water Sludge (solid) is further treated in anaerobic digester and disposed of 1° Treatment Filter & settle steps remove ~50% of solids & 25% of BOD Anaerobic Sludge Digestion • Anaerobic organisms act on solids (sludge) • Various populations act sequentially Organic matter organic acids, CO2, H2 Organic acids acetate, CO2, H2 Acetate, CO2, H2 methane • Remaining sludge dehydrated • Disposal: incineration, landfill, fertilizer 2° Treatment • Eliminates most of remaining BOD • Microbial degradation of organic material • 4 different options Aerobic organisms degrade organic material to C02 and H2O 2° Treatment Methods 1. Activated sludge- commonly used Aerobic microbes (grown in flocs) Requires innoculation & aeration Resedimentation(save floc, treat sludge) 2. Trickling filter- smaller treatment plants Spray sewage over biofilm of aerobic microbes • • • • • Bacteria Fungi Algae Protozoa Nematodes 2° Treatment Methods continued 3. Lagoons- shallow ponds where photosynthetic organisms create aerobic environment (treatment takes months) 4. Artificial wetlands • Similar to lagoons • Aerobic & anaerobic environments • Involves bacteria, algae, plants, sedimentation • Habitat generation Advanced Treatment Physical, chemical or biological processes Increased expense over 1° and 2 ° treatment Removal of ammonia, nitrates and phosphates • Ammonia stripping: Liberates gaseous ammonia from water • Denitrification: use of bacteria (creation of N2 gas) • Chemical precipitation: phosphate removal Disinfection Performed before effluent is discharged • Chlorine • Ozone • Ultraviolet light Purpose: reduce numbers of microorganisms and viruses Septic Tanks (Rural Areas) Collection in large tank – Settling of sludge – Anaerobic degradation Outlet to drainage field – Aerobic oxidization of organic material Potential Problems: Improper aeration Presence of pathogens Improper drainage Toxic conditions Water-borne disease Giardia lamblia Entomoeba histolytica Salmonella typhimurium Vibrio cholerae Leigeonella species Clostridium botulinum Escherichia coli Rotavirus Hepatitis A Cryptosporidium parvum Polio virus Waste and Water in Underdeveloped countries Pit latrine verses Composting toilets Macha, Zambia Ground Water: a clean source of drinking water? Drinking Water Treatment Process (US) 1. Sedimentation 2. Flocculation of organic material 3. Filtration Removal of microorganisms Chemical absorption 4. Disinfection Drinking Water Testing (US) Test for indicator organisms: coliforms MPN Index: Maximum for drinking water: 0/1000ml (depends on collections per month) Example: If collect 40 samples: <5% can be positive If exceed positives/month must be reported Activity Read through “Ailing Ganges” article and identify similarities and differences (3 total) between waste-water treatment in India and in the US. The Golden Horn of Istanbul