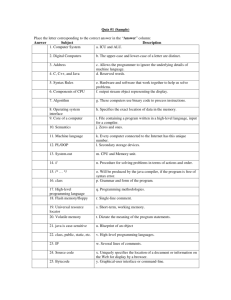
Java Syntax Part I •Comments •Identifiers •Primitive Data Types

Java Syntax Part I
•Comments
•Identifiers
•Primitive Data Types
•Assignment
Java Syntax - Comments
• Type 1:
– begins with /*
– continues till the next */
• Type 2:
– begins with //
– continues till the end of the line
• Type 3:
– begins with /**, and continues till the next */
Java Syntax -- comments (style)
• Good programming practice
– Put helpful comments
• at the beginning of a big block
• on the same line of certain statements
– Good internal documentation is very important
Java Syntax -- comments (example)
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------
// withdraw: withdraw money from banking_account
// Input : amount = the amount of money to withdraw
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------void withdraw(float amount)
{
//----------- if not enough money in the account ----
…
//----------- else, we have enough money in the account ----
...
}
Java Syntax -- Identifiers
• Names of declared entities
– variables, constans, labels…
• Must start with a letter: [A..Z][a..z]
– including _ (underscore) or $ (dollar sign)
• Followed by letters or digits
• Java language keywords can not be used as identifiers.
Java Syntax -- Identifiers (example)
accountNumber length1 length_2
Java Syntax -- Primitive Data Types
• boolean: takes only 2 values true or false
• Example: boolean done = false;
• char : contains a character
• Example: char ch;
• byte, short, int and long : Integral Types
• Example: int num = 3;
• float, double : Floating-Point Types
• Example: float temperature = 37.6;
Java Syntax -- Assignment
• Example using integers: int i = 2; // create an integer variable i = 5; // change i to 5 int j = 6; // create an integer variable j i = j*3 // multifply the value of j by 3
// now i = 18 i = i + 4; // NOT AN EQUATION!
// i was 18, i+4=22; new i=22.
• Calculate the value on the RIGHT HAND SIDE
• Assign the result to the variable on the
LEFT HAND SIDE
Java Syntax -- Assignment (Abbreviations)
• Examples: j = j + 1; // as before j += 1; // same as j = j + 1; j += 5; // same as j = j + 5; j++; // same as j = j + 1;