End of year Objectives grid for
advertisement

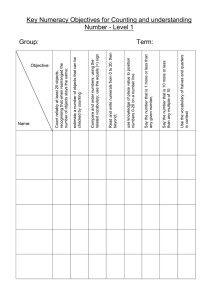
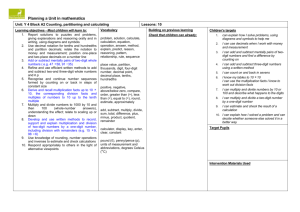
End of year Objectives grid for The Primary Framework for Mathematics (seven strands) For use as - A class record of objectives taught - An individual record of progress and attainment passed on to the next teacher at end of year. Record class number under term objective achieved. Name: Date of birth: Foundation – END of YEAR OBJECTIVES 1) Use developing mathematical ideas and methods to solve practical problems. 2) Talk about, recognise and recreate simple patterns. 3) Say and use number names in order in familiar contexts. 4) Count reliably up to 10 everyday objects. 5) Use language such as ‘more’ or ‘less’ to compare 2 nos. a) Use language: ‘more’ to compare two numbers b) Use language: ‘less’ to compare two numbers. 6) Recognise numerals 1 to 9. 7)Find one more or one less than a number from 1 to 10 a) Find one more than a number from 1 to 10 b) Find one less than a number from 1 to 10 8) Begin to relate addition to combining two groups of objects, and subtraction to ‘taking away’ a) Begin to relate addition to combining two groups of objects b) Begin to relate subtraction to ‘taking away’ 9) In practical activities and discussion, begin to use the vocabulary involved in adding and subtracting. a) In practical activities and discussion, begin to use the vocabulary involved in adding b) In practical activities and discussion, begin to use the vocabulary involved in subtracting 10) Use language such as circle or bigger to describe the shapes and size of solids and flat shapes 11) Use everyday words to describe position 12) Use language such as ‘greater’, ‘smaller’, ‘heavier’ or ‘lighter’ to compare quantities. a) Use language such as greater or heavier to compare two quantities b) Use language such as smaller or lighter to compare two quantities Autumn Spring Summer Comment Name: Date of birth: Year 1 – END of YEAR OBJECTIVES 1) Read and write numerals from 0 to 20, then beyond; use knowledge of place value to position these on a number track and number line. a) Read numerals from 0 to 20, then beyond. b) Write numerals from 0 to 20, then beyond. c) Use place value to position on a number track and number line. 2) Derive and recall all pairs of numbers with a total of 10 and addition facts for totals to at least 5; work out the corresponding subtraction facts. a) Derive all pairs of numbers with a total of 10. b) Recall all pairs of numbers with a total of 10. c) Work out the corresponding subtraction facts. d) Derive all pairs of numbers for totals to at least 5. e) Recall all pairs of numbers for totals to at least 5. f) Work out the corresponding subtraction facts. 3) Use the vocabulary related to addition and subtraction and symbols to describe and record addition and subtraction number sentences. a) Use the vocabulary related to addition. b) Use the vocabulary related to subtraction. c) Use symbols to describe and record addition and subtraction number sentences. 4) Visualise and name common 2D shapes and 3D solids and describe their features. a) Visualise and name common 2D shapes. b) Describe features of common 2D shapes. c) Visualise and name common 3D solids. d) Describe features of 3D solids Autumn Spring Summer Comment 5) Estimate, measure, weigh and compare objects, choosing and using suitable uniform non-standard or standard units and measuring instruments (e.g. a lever balance, metre stick or measuring jug). a) Estimate, measure and compare length of objects. b) Estimate, measure and compare weight of objects. c) Estimate, measure and compare capacity of containers. d) Choose and use suitable uniform non-standard or standard units. e) Choose and use suitable measuring instruments. 6) Answer a question by recording information in lists and tables; present outcomes using practical resources, pictures, block graphs or pictograms. a) Answer a question by recording information in lists and tables. b) Present outcomes using practical resources or pictures. c) Present outcomes using block graphs or pictograms. Name: Date of birth: Year 2 – END of YEAR OBJECTIVES 1) Count up to 100 objects by grouping them and counting in tens, fives or twos; explain what each digit in a two-digit number represents, including numbers where 0 is a place holder; partition 2-digit numbers in different ways, including into multiples of 10 and 1. a) Count objects by grouping and counting in twos. b) Count objects by grouping and counting in fives. c) Count up to 100 objects by grouping and counting in tens. d) Explain what each digit in a 2-digit number represents. e) Partition 2-digit numbers into multiples of 10 and 1. f) Partition 2-digit numbers in different ways. 2) Derive and recall all addition and subtraction facts for each number to at least 10, all pairs with totals to 20 and all pairs of multiples of 10 with totals up to 100. a) Derive and recall all addition and subtraction facts for each number to at least 10. b) Derive and recall addition and subtraction facts for all pairs with totals to 20. c) Derive and recall addition and subtraction facts for all pairs of multiples of 10 with totals up to 100. 3) Add or subtract mentally a one-digit number or a multiple of 10 to or from any 2-digit number; use practical and informal written methods to add and subtract 2-digit numbers. a) Add or subtract mentally a one-digit number to or from any 2digit number. b) Add or subtract mentally a multiple of 10 to or from any 2-digit number. c) Use practical and informal written methods to add 2-digit numbers. d) Use practical and informal written methods to subtract 2-digit numbers. 4) Use the symbols + - x ÷ and = to record and interpret number sentences involving all four operations: calculate the value of an unknown in a number sentence (e.g. ÷ 2 = 6, 30 - = 24). a) Use the symbols +, - and = to record and interpret number sentences. b) Use the symbols x, ÷ and = to record and interpret number sentences. c) Calculate the value of an unknown in addition and subtraction number sentences (e.g. 30 - = 24). d) Calculate the value of an unknown in multiplication and division number sentences (e.g. ÷ 2 = 6). 5) Visualise common 2D shapes and identify them from pictures in different positions. 6) Visualise common 3D solids and identify them from pictures in different positions and orientations. Autumn Spring Summer Comment 7) Sort, make and describe shapes, referring to their properties. 8) Use units of time (seconds, minutes, hours, days) and know the relationship between them; read time to the quarter hour; identify time intervals, including those that cross the hour. a) Use units of time (seconds, minutes, hours, days). b) Know the relationship between units of time (seconds, minutes, hours, days). c) Read the time to the quarter hour. d) Identify time intervals, including those that cross the hour. 9) Use lists, tables, and diagrams to sort objects; explain choices using appropriate language, including ‘not’ [in Carroll diagrams, e.g. magnetic : not magnetic]. a) Use lists, tables and diagrams to sort objects. b) Explain choices using appropriate language, including ‘not’. Name: Date of birth: Year 3 – END of YEAR OBJECTIVES 1) Partition three-digit numbers into multiples of 100, 10 and 1 in different ways. 2) Derive and recall all addition and subtraction facts for each number to 20, sums and differences of multiples of 10 and number pairs that total 100. a) Derive and recall all addition and subtraction facts for each number to 20. b) Derive and recall sums and differences of multiples of 10. c) Derive and recall number pairs that total 100. 3) Add and subtract mentally combinations of one-digit and two-digit numbers. a) Add mentally combinations of one-digit and two-digit numbers. b) Subtract mentally combinations of one-digit and two-digit numbers. 4) Draw and complete shapes with reflective symmetry; draw the reflection of a shape in a mirror line along one side. 5) Read, to the nearest division and half-division, scales that are numbered or partially numbered; use the information to measure and draw to a suitable degree of accuracy. a) Read, to the nearest division and half-division, scales that are numbered or partially numbered. b) Use the information to measure and draw to a suitable degree of accuracy. 6) Use Venn diagrams or Carroll diagrams to sort data and objects using more than one criterion. a) Use Venn diagrams to sort data and objects using more than one criterion. b) Use Carroll diagrams to sort data and objects using more than one criterion. Autumn Spring Summer Comment Name: Date of birth: Year 4 – END of YEAR OBJECTIVES 1) Use diagrams to identify equivalent fractions (e.g. 6/8 and ¾, or 70/100 and 7/10 ); interpret mixed numbers and position them on a number line (e.g. 3½) a) Use diagrams to identify equivalent fractions (e.g. 6/8 and ¾, or 70/100 and 7/10 ) b) Interpret mixed numbers and position them on a number line (e.g. 3½) 2) Derive and recall multiplication facts up to 10 x 10, the corresponding division facts and multiples of numbers to 10 up to the tenth multiple. a) Derive & re-call x facts and corresponding ÷ facts: x 2 b) Derive & re-call x facts and corresponding ÷ facts: x 3 c) Derive & re-call x facts and corresponding ÷ facts: x 4 d) Derive & re-call x facts and corresponding ÷ facts: x 5 e) Derive & re-call x facts and corresponding ÷ facts: x 6 f) Derive & re-call x facts and corresponding ÷ facts: x 7 g) Derive & re-call x facts and corresponding ÷ facts: x 8 h) Derive & re-call x facts and corresponding ÷ facts: x 9 i) Derive & re-call x facts and corresponding ÷ facts: x 10 3) Add or subtract mentally pairs of two-digit whole numbers (e.g. 47 + 58, 91 – 35) a) Add mentally pairs of two-digit numbers (e.g. 47 + 58) b) Subtract mentally pairs of two-digit numbers (e.g. 91 – 35) 4) Develop and use written methods to record, support and explain multiplication and division of two-digit numbers by a one-digit number, including division with remainders (e.g. 15 x 9, 98 ÷ 6) a) Develop and use written methods to record, support and explain multiplication of two-digit numbers by a one-digit number (e.g. 15 x 9) b) Develop and use written methods to record, support and explain division of two-digit numbers by a one-digit number, including with remainders (e.g. 98 ÷ 6) Autumn Spring Summer Comment 5) Know that angles are measured in degrees and that one whole turn is 360°; compare and order angles less than 180°. a) Know that angles are measured in degrees and that one whole turn is 360° b) Compare and order angles less than 180°. 6) Choose & use standard metric units & their abbreviations when estimating, measuring & recording length, weight & capacity; know the meaning of 'kilo', 'centi' and 'milli' and, where appropriate, use decimal notation to record measurements (e.g. 1.3 m or 0.6 kg) a) Choose & use standard metric units & their abbreviations when estimating, measuring and recording length. b) Choose & use standard metric units & their abbreviations when estimating, measuring and recording weight. c) Choose & use standard metric units & their abbreviations when estimating, measuring and recording capacity. d) Know the meaning of 'kilo', 'centi' and 'milli' and, where appropriate, use decimal notation to record measurements (e.g. 1.3 m or 0.6 kg). 7)Answer a question by identifying what data to collect; organise, present, analyse & interpret the data in tables, diagrams, tally charts, pictograms & bar charts, using ICT where appropriate. Name: Date of birth: Year 5 – END of YEAR OBJECTIVES 1) Explain what each digit represents in whole numbers and decimals with up to two places and partition, round and order these numbers. 2) Use knowledge of place value and addition and subtraction of two-digit numbers to derive sums and differences and doubles and halves of decimals (e.g 6.5 ± 2.7, half of 5.6, double 0.34). a) Derive sums and differences of decimals (e.g. 6.5 ± 2.7) b) Derive doubles and halves of decimals (e.g. half of 5.6, double 0.34) 3) Use efficient written methods to add and subtract whole numbers and decimals with up to two places. a) Use efficient written methods to add whole numbers and decimals with up to two places. b) Use efficient written methods to subtract whole numbers and decimals with up to two places. 4) Read and plot co-ordinates in the first quadrant; recognise parallel and perpendicular lines in grids and shapes; use a set-square and ruler to draw shapes with perpendicular or parallel sides a) Read and plot co-ordinates in the first quadrant b) Recognise parallel & perpendicular lines in grids & shapes c) Use a set-square and ruler to draw shapes with perpendicular or parallel sides 5) Draw and measure lines to the nearest millimetre; measure and calculate the perimeter of regular and irregular polygons; use the formula for the area of a rectangle to calculate the rectangle's area a) Draw and measure lines to the nearest millimetre b) Measure and calculate the perimeter of regular and irregular polygons c) Use the formula for the area of a rectangle 6) Construct frequency tables, pictograms and bar and line graphs to represent the frequencies of events and changes over time Autumn Spring Summer Comment Name: Date of birth: Year 6 – END of YEAR OBJECTIVES 1) Express one quantity as a percentage of another (e.g. express £400 as a percentage of £1000); find equivalent percentages, decimals and fractions a) Express one quantity as a percentage of another (e.g. express £400 as a percentage of £1000) b) Find equivalent percentages, decimals and fractions 2) Use knowledge of place value and multiplication facts to 10 × 10 to derive related multiplication and division facts involving decimals (e.g. 0.8 × 7, 4.8 ÷ 6) 3) Use efficient written methods to add and subtract integers and decimals, to multiply and divide integers and decimals by a one-digit integer, and to multiply two-digit and three-digit integers by a two-digit integer a) Use efficient written methods to add integers and decimals b) Use efficient written methods to subtract integers and decimals C) Use efficient written methods to multiply integers and decimals by a one-digit integer d) Use efficient written methods to divide integers and decimals by a one-digit integer e) Use efficient written methods to multiply two-digit and three-digit integers by a two-digit integer 4) Visualise and draw on grids of different types where a shape will be after reflection, after translations, or after rotation through 90° or 180° about its centre or one of its vertices a) Visualise and draw on grids of different types where a shape will be after reflection b) Visualise and draw on grids of different types where a shape will be after translations c) Visualise and draw on grids of different types where a shape will be after rotation through 90° or 180° about its centre or one of its vertices 5) Select and use standard metric units of measure and convert between units using decimals to two places (e.g. change 2.75 litres to 2750 ml, or vice versa) a) Select and use standard metric units of measure b) Convert between units using decimals to two places (e.g. change 2.75 litres to 2750 ml, or vice versa) 6) Solve problems by collecting, selecting, processing, presenting and interpreting data, using ICT where appropriate; draw conclusions and identify further questions to ask Autumn Spring Summer Comments