EXAM 4. BIOLOGY 1406 NAME __________________________
advertisement

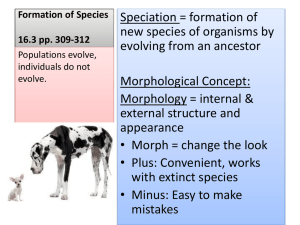
EXAM 4. BIOLOGY 1406 1. The ability of organisms to pass on to their offspring physical changes that the parents developed during their own lifetimes is known as _______. a. genetic drift b. natural selection c. artificial selection d. adaptive radiation e. inheritance of acquired characteristics 2) The incorrect theory that "organisms can modify their bodies through use or disuse of parts, and that these modifications can be passed on to their offspring" was formulated by A) Hutton. B) Darwin. C) Aristotle. D) Lamarck. E) Lyell. 3. Structures that may differ in function but that have similar anatomy, presumably because of descent from common ancestors, are called ______. a. analogous structures b. homologous structures c. vestigial structures 4) Which of these statements indicates a problem with the theory of catastrophism? A) Not all species have been recovered. B) Many species have become extinct. C) There are millions of undescribed species in the world. D) There are no humans in early fossil records. NAME __________________________ E) The Earth is billions of years old. 5. Structures that serve no apparent purpose but are homologous to functional structures in related organisms are called _______. a. analogous structures b. homologous structures c. vestigial structures 6) The author of On the Origin of Species by Means of Natural Selection is A) Mendel. B) Malthus. C) Galvani. D) Darwin. E) Lamarck 7. Which of the following lines of evidence support(s) the idea of evolution ? a. the fossil record b. genetic and biochemical analyses c. comparative anatomy and embryology d. artificial selection e. all of the above 8) Darwin and Wallace both realized that most species produce many more offspring than is necessary to maintain a constant population. What is the fate of the excess individuals? A) They have evolved so that they cannot survive in their environment. B) Some less favorable individuals do not survive to reproduce. C) They evolve to take advantage of natural resources. D) Some individuals die arbitrarily. E) They mutate and then are able to adapt to new environments. 9. Which of the following is a mechanism or cause of evolution? a. mutation b. gene flow c. genetic drift d. natural selection e. all of the above 13) Natural selection on a trait can only occur if the trait is ________. A) inheritable B) behavioral C) favorable D) morphological E) a new mutation 10) The theory of natural selection states that A) all individuals live to reproduce in each generation. B) only the largest and strongest survive. C) random assortment of genes results in better characteristics in the following generations. D) the best adapted individuals survive and reproduce, contributing the most genes to the next generation. E) individuals that mutate in response to their environment will survive. 14) Which of the following is NOT an example of natural selection? A) Plants with thorns are less likely to be eaten by herbivores than other members of the same species that lack thorns. B) Bacterial populations in hospitals develop resistance to drugs used to combat infection by them. C) Scientists breed cows that give greater amounts of milk than their ancestors. D) Fruit fly larvae with an enzyme to break down alcohol are better able to feed on fermenting fruit than those that lack the enzyme. E) Female fish that produce more eggs leave more offspring than those that produce fewer eggs. 11. Selection against individuals at both ends of a phenotypic distribution for a character, favoring those in the middle or average of the distribution, is an example of __________. a. kin selection b. sexual selection c. directional selection d. disruptive selection e. stabilizing selection 12. What is a gene pool? a. a region of DNA found at a specific position on a chromosome b. the number of copies of an allele for a specific gene in a population c. the total number of all the genes in a population d. none of the above 15. Evolution is best defined as a change in __________. a. number of species b. physical traits c. DNA sequence d. allele frequencies 16. Individuals with two identical copies of a given allele are called ____________________ for that allele. a. heterozygous b. twins c. compatible d. homozygous 17) Specific inheritable mutations, which may allow a population to evolve, are : A) produced by chance. B) produced as a response to environmental change. C) produced as a response to selection pressure. D) produced by other species in the environment. E) produced by artificial selection. 18) A change in the genetic makeup of a population is A) natural selection. B) uniformitarianism. C) artificial selection. D) evolution. E) genetic drift. 19) Evidence which supports the theory of evolution is found in the studies of A) embryos. B) biochemistry. C) fossils. D) artificial selection. E) all of these 20) The fossil record indicates that over the last 50 million years the horse has evolved in all but which of the following ways? A) tooth structure B) leg anatomy C) overall size D) abundance of hair E) It has evolved in all these respects. 21) Structures which are homologous to important structures in other organisms but serve no purpose in the organism being considered are A) analogous. B) mutations. C) homozygous. D) convergent. E) vestigial 22) Which of the following structures is NOT homologous to the others? A) alligator forelimb B) bird wing C) human arm D) insect wing E) bat wing 23) Strong evidence for the close relatedness of vertebrates is A) they all have legs. B) their means of reproduction. C) the similarity of their embryological stages. D) they all evolved from fish. E) they all possess DNA. 24) The many different breeds of domestic dog were produced by A) natural selection. B) artificial selection. C) kin selection D) mutation. E) divergent evolution. 25) Most commercial pesticides are effective for only 2-3 years. This is because A) new pests invade the area. B) the chemicals induce mutations that convey immunity. C) the chemicals mutate. D) the pests learn to ignore the chemicals. E) those pests with advantageous mutations will survive and reproduce. 26) Anolis lizards are transplanted from an area with many large trees to islands with many small plants and few trees. You would predict them to A) undergo no evolutionary change. B) evolve shorter legs. C) evolve longer legs. D) evolve to be able to run away from predators more quickly. E) evolve to be able to maneuver less efficiently. 27) The Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium represents an idealized, evolutionfree population in which the allele frequencies and genotype frequencies will not change over time. In order for this to happen, five conditions must be met: 1) there must be no mutation; 2) there must be no gene flow between populations; 3) the populations must be very large; 4) all mating must be random; and 5) there must be no natural selection. If one of these five conditions was violated, genetic change, and thus evolution, would occur in the populations of subsequent generations. Suppose that only condition 3 were violated— that the population was very small. In this situation, the evolution would probably be due to _________. a. mutation b. migration c. genetic drift d. natural selection e. all of the above 28) Genetic drift, population bottlenecks, and founder populations all illustrate __________. a. decreasing population size has a greater effect on changing allele frequencies than increasing the population size b. that reducing population size will likely decrease genetic variability within the population c. the strong role played by very small isolated populations in the creation of new species d. all of the above 29) What type of natural selection favors individuals with rarely encountered traits over individuals with traits that are frequently encountered? a. disruptive selection b. stabilizing selection c. directional selection 30) Gene flow __________. a. cannot influence the evolution of a population b. prevents the spread of alleles through a species c. causes populations to diverge from each other d. makes populations more genetically similar 31) Why is the sickle cell allele found at a high frequency in African human populations? a. Individuals with sickle cell anemia are resistant to malaria, which has historically been prevalent in Africa. b. Heterozygote carriers of the allele are susceptible to malaria, which has historically been absent in Africa. c. Individuals with sickle cell anemia are susceptible to malaria, which has historically been absent in Africa. d. Heterozygote carriers of the allele are resistant to malaria, which has historically been prevalent in Africa. 32) Before the modern era of science, organisms were assigned to species categories on the basis of A) behavioral similarities. B) existence of fossils of previous forms. C) capability of interbreeding. D) similarities in appearance. E) geographic location. 33) What is: "all the populations of organisms that can potentially interbreed with one another under natural circumstances and are reproductively isolated from other populations"? A) genus B) species C) genotype D) community E) tribe 34) Fruit fly species all look more or less alike. If you have a male and female fruit fly how can you prove that they are the same species? A) Determine the base sequence of the DNA of their chromosomes. B) Examine them closely with a low power microscope comparing their physical characteristics to published species key lists of characteristics. C) If they mate when they are put together then they are the same species. D) If they mate successfully and their offspring can also mate successfully all are the same species. E) If they can both asexually reproduce and their offspring can also successfully asexually reproduce then they are all the same species. 35) Populations once considered to be separate species are now sometimes assigned to the same species because A) it was discovered that they can produce viable and fertile hybrid offspring. B) they have evolved to look different. C) they are no longer capable of interbreeding. D) they have evolved to look the same. E) they have been found to be genetically similar. 36) If there is no gene flow into a population, it is said to be A) allopatric. B) sympatric. C) a founder population. D) isolated. E) in a bottleneck. 37) Two species of squirrels live on either side of the Grand Canyon. They are an example of A) temporal isolation. B) behavioral isolation. C) mechanical isolation. D) hybrid inviability. E) allopatric speciation. 38) The Kaibab squirrel lives on the north side of the Grand Canyon and the Abert squirrel lives on the south side. Even though these two populations are only miles apart, their gene pools are kept isolated by A) mechanical incompatibility. B) hybrid infertility C) geographic isolation D) ecological isolation. E) temporal isolation. 39) The flies that show a preference for either hawthorn or apple trees, and are no longer interbreeding populations because of this, illustrate what type of speciation? A) allopatric B) specialization C) polyploidy D) founder effect E) sympatric 40) All members of the golden hamster species known today are descendants of a single litter collected in Syria in 1939. Its diploid chromosome number is 44. Two other species of hamster, each with a diploid number of 22 overlap in Syria. The golden hamster is thought to be a new species following the mating of a male and female of the two other hamster species. What mechanism might explain this recent event of speciation? A) adaptive radiation B) formation of fertile hybrid and halving of the chromosome number of this hybrid C) polyploidy D) temporal isolation E) disruptive selection 41) The organisms most likely to undergo sympatric speciation by polyploidy are A) mammals. B) insects. C) plants. D) protists. E) birds. 42) When a species invades a new habitat and evolves rapidly into several new species to better exploit new resources what has occurred? A) phyletic speciation B) divergent speciation C) stabilizing selection D) polyploidy E) adaptive radiation 43) Two different species of pine release their pollen at different times. This is an example of A) geographical isolation. B) ecological isolation. C) behavioral incompatibility. D) temporal isolation. E) mechanical isolation. 44) Blue-footed boobies of the Galapagos will only mate after a very specific courtship display on the part of the male. He high steps to advertise his bright blue feet. What isolating mechanism discourages mating outside the species? A) ecological isolation B) temporal isolation C) behavioral isolation D) mechanical isolation E) gametic incompatibility 45) In many species of fireflies males flash to attract females. Each species has a different flashing pattern. This is an example of A) allopatric speciation. B) geographical isolation. C) temporal isolation. D) natural selection. E) behavioral isolation. 46) One method of protecting the genetic identity of a population is the inability of sperm to fertilize eggs of a different species. This is called A) ecological isolation. B) temporal isolation. C) behavioral isolation. D) hybrid inviability. E) gametic incompatibility. 47) The great dane and the chihuahua are both domestic dogs (the same species), but mating between them is limited by A) hybrid infertility. B) hybrid inviability. C) mechanical incompatibility. D) behavioral isolation. E) heterozygote disadvantage. 48) A horse has 2N=64 and a donkey has 2N=62. The hybrid of these two species, mules have 63 chromosomes and are sterile. Why are mules sterile? A) They cannot physically mate with each other. B) They cannot physically mate with horses and donkeys. C) Some chromosomes lack homologs and cannot undergo meiosis. D) Their zygotes cannot complete the first mitotic division to form the two cell stage. E) Only autoploid interspecies hybrids are able to form new species. 49) If a hybrid is unable to produce sperm because meiosis does not proceed correctly, gene flow between the populations is restricted by A) hybrid viability. B) hybrid infertility. C) gametic isolation. D) ecological isolation. E) temporal isolation. 50) The greatest cause of extinctions is A) asteroid impacts. B) interactions with other species. C) overspecialization. D) habitat destruction.. E) limited species range.