ARACEAE

ARACEAE
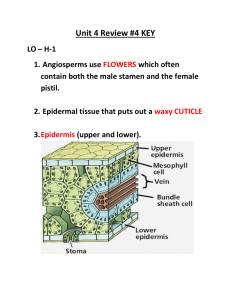
monocots
Current
Angiosperm
Phylogeny
Group Tree for Flowering
Plants
CHARACTERS DIAGNOSTIC
OF MONOCOTS:
• herbaceous
• branching sympodial
• vascular bundles in stem scattered, closed [no interfascicular cambium developing]
• tertiary veins without free endings
• leaf base sheathing
• pollen monosulcate
• gynoecium three-parted
• cotyledon 1
• primary root present but unbranched, not persisting
• expanded here covered in Araceae
CHARACTERS DIAGNOSTIC
OF MONOCOTS:
• branching sympodial
CHARACTERS
DIAGNOSTIC OF
MONOCOTS:
• vascular bundles in stem scattered, closed
[no interfascicular cambium developing]
ARACEAE
Key Characters net venation, no dead-end veins spathe (inflorescence bract) spadix (thick spike) monocot numbers in flowers
Colocasia esculenta --
TARO
Colocasia affinis
Zantedischia "cally lily"
Amorphophallus titanica
dicot-like secondary and tertiary veins in
Anthurium , Araceae textbook monocot veins
dicot
Acorus (sweetflag) – currently the most primitive monocot
taro ( Colocasia esculenta) calcium oxalate raphides
500x: photo by Tina Weatherby
Carvalho
monosulcate pollen
- Monstera
No monosulcate pollen in descendants of this ancestor.
Mostly monosulcate pollen in early flowers and gymnosperms.
Monstera - hemiepiphyte with holes in leaves
Philodendron - juvenile stem ascending trunk of a balsa tree
Monstera inflorescences as fruit in the market
Montrichardia monopodial , coastal swamp forests, looks like a treelet.
Pistia and Lemna – floating aquatics in the Araceae, but separate origins
Lemna
monocots
Current
Angiosperm
Phylogeny
Group Tree for Flowering
Plants