Imperfect: Part I as completed.
advertisement
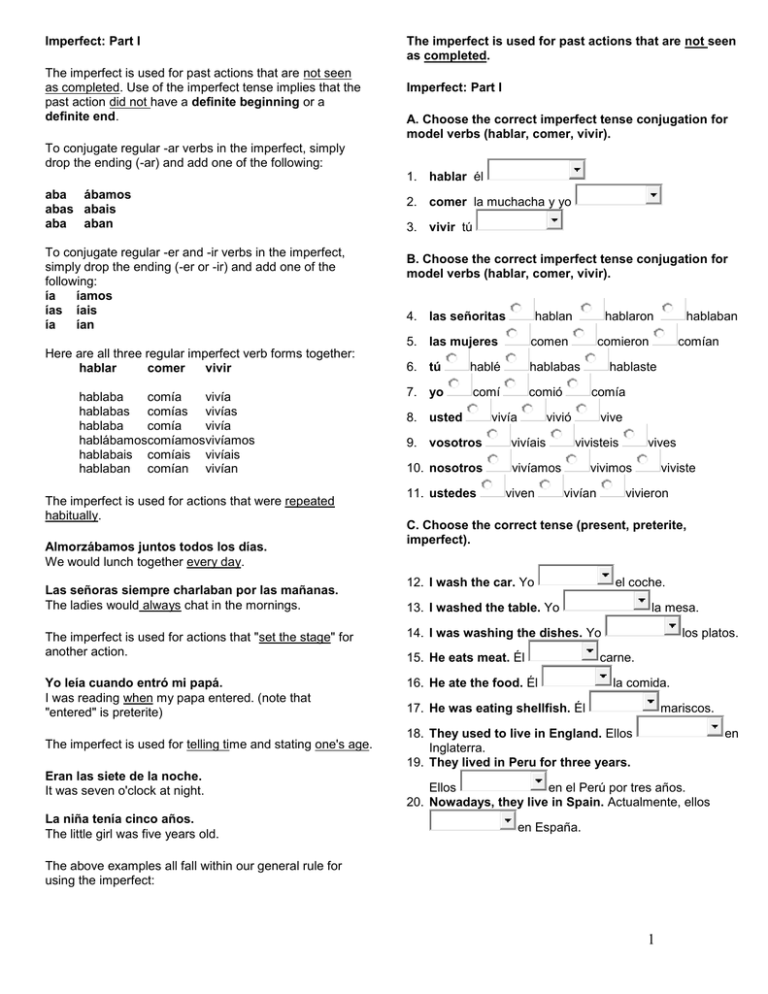
Imperfect: Part I The imperfect is used for past actions that are not seen as completed. Use of the imperfect tense implies that the past action did not have a definite beginning or a definite end. The imperfect is used for past actions that are not seen as completed. Imperfect: Part I A. Choose the correct imperfect tense conjugation for model verbs (hablar, comer, vivir). To conjugate regular -ar verbs in the imperfect, simply drop the ending (-ar) and add one of the following: 1. hablar él aba ábamos abas abais aba aban To conjugate regular -er and -ir verbs in the imperfect, simply drop the ending (-er or -ir) and add one of the following: ía íamos ías íais ía ían Here are all three regular imperfect verb forms together: hablar comer vivir hablaba comía vivía hablabas comías vivías hablaba comía vivía hablábamoscomíamosvivíamos hablabais comíais vivíais hablaban comían vivían The imperfect is used for actions that were repeated habitually. Almorzábamos juntos todos los días. We would lunch together every day. Las señoras siempre charlaban por las mañanas. The ladies would always chat in the mornings. 2. comer la muchacha y yo 3. vivir tú B. Choose the correct imperfect tense conjugation for model verbs (hablar, comer, vivir). 4. las señoritas hablan hablaron 5. las mujeres comen 6. tú hablé hablabas 7. yo comí comió 8. usted vivía vivíais 10. nosotros vivíamos 11. ustedes comieron viven comía vive vivisteis vivían C. Choose the correct tense (present, preterite, imperfect). 12. I wash the car. Yo el coche. 13. I washed the table. Yo la mesa. Yo leía cuando entró mi papá. I was reading when my papa entered. (note that "entered" is preterite) 16. He ate the food. Él La niña tenía cinco años. The little girl was five years old. viviste vivieron 14. I was washing the dishes. Yo Eran las siete de la noche. It was seven o'clock at night. vives vivimos The imperfect is used for actions that "set the stage" for another action. The imperfect is used for telling time and stating one's age. comían hablaste vivió 9. vosotros hablaban 15. He eats meat. Él los platos. carne. la comida. 17. He was eating shellfish. Él mariscos. 18. They used to live in England. Ellos Inglaterra. 19. They lived in Peru for three years. en Ellos en el Perú por tres años. 20. Nowadays, they live in Spain. Actualmente, ellos en España. The above examples all fall within our general rule for using the imperfect: 1 Imperfect: Part II 10. Juan y yo Remember, the imperfect is used for past actions that are not seen as completed. The imperfect tense implies that the past action did not have a definite beginning or a definite end. The imperfect tells when -- in general, an action occurred. Good news! There are only three irregular verbs in the imperfect. You must simply memorize them. 11. las mujeres 12. tú viste vamos íbamos ven veían ves iban vieron veías D. Choose the correct tense (present, preterite, imperfect). 13. I was a carpenter for three years. Yo carpintero por tres años. 14. I was once a carpenter. ser ir ver era eras era éramos erais eran iba ibas iba íbamos ibais iban veía veías veía veíamos veíais veían Una vez yo carpintero. 15. Carmen goes to the beach. Carmen a la playa. 16. Carmen went to the beach last summer. Carmen a la playa el verano pasado. 17. Carmen went to the beach every afternoon. To review some of the rules for using the imperfect: Carmen a la playa cada tarde. The imperfect is used for actions that were repeated habitually. 18. We see the boat. Nosotros 19. We saw the boat yesterday. The imperfect is used for actions that "set the stage" for another action. Nosotros el barco ayer. 20. We would see the boat every morning. The imperfect is used for telling time and stating one's age. Nosotros el barco. el barco cada mañana. Imperfect: Part II Imperfect: Part III A. Choose the correct imperfect tense conjugation for the three irregular verbs (ser, ir, ver). One way to determine if a verb is actually the imperfect is to try substituting one of the following: 1. ser el perro was/were ...ing used to ... would (meaning used to) ... 2. ir tú The following examples show how to use this substitution test for the imperfect: 3. ver Juan y María B. Choose between present and imperfect. 4. It's five o'clock. Son las cinco. 5. It was two o'clock. Son las dos. 6. It was one o'clock. Es la una. I worked in the agency during the day. I was working in the agency during the day. Eran las cinco. Eran las dos. Era la una. I visited my grandmother every day. I used to visit my grandmother every day. Every afternoon I took a nap. Every afternoon I would take a nap. C. Choose the correct imperfect tense conjugation for irregular verbs (ser, ir, ver). 7. él fue 8. tú eran 9. las señoritas es One does not normally think of a general mental state or physical sensations as having a definite beginning or end, and so they are usually expressed in the imperfect. era eras fueron fuiste iban van Ramón tenía miedo de hablar en público. Ramón was afraid to speak in public. 2 7. Pablo read the paper last night. Yo creía que Juan podía hacerlo. I thought that Juan could do it. leyó Me gustaba el coche. I liked the car. (The car was pleasing to me.) The imperfect is used to describe how things were or what things were like. Use the imperfect when describing the characteristics of people, things or conditions. Era un muchacho muy inteligente. He was a very intelligent boy. Era una señorita muy guapa. She was a beautiful young lady. Las ventanas estaban abiertas. The windows were open. leía B. Choose the correct tense for the following general mental states and physical sensations. 8. I waited in the rain for the taxi. 9. She loved the boy. amó 10. Their feet hurt. dolieron esperé amaba dolían 11. They were very tired. estuvieron 12. The ladies liked her church dress. gusto estaban gustaba La casa era blanca. The house was white. 13. I knew that. Imperfect: Part III 14. They wanted more food. quisieron 15. You-all couldn't change the tire. A. Try substituting "was/were ...ing" "used to ..." or "would ..." (meaning "used to ...") for the verb in order to determine whether the tense should be imperfect or preterite. esperaba supe no pudisteis sabía querían no podíais 16. He thought about the day they met. 1. Every day I visited my aunt. (used to visit) pensó visité visitaba 2. He wore a white shirt to the party. llevó llevaba 3. He wore a white shirt every day. (used to wear) llevó llevaba pensaba C. The following sentences all describe how things were, or what things were like. Which is appropriate, imperfect or preterite? 17. The house was white. fue era 18. The sky was cloudy. estuvo estaba 19. The bag was heavy. estuvo estaba 20. The store was full of candy. estuvo 4. Carmen prepared dinner when the doorbell rang. (was preparing) prepare preparaba 5. Juan ran ten miles. corrió corría 6. Juan ran most mornings. (used to run) corrió corría 3 estaba