Final Exam Study Guide Directions:
advertisement

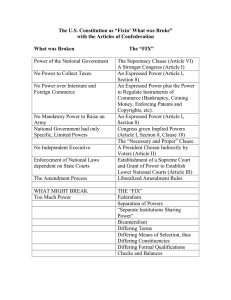
U.S. Government Mr. Partin Final Exam Study Guide Directions: To earn extra credit, you must explain each term or concept below. Use Cornell format, number the concepts as below, and complete all of them in order. If you do not follow all directions, there will be no credit given. 1. Characteristics of a state 2. Social Contract Theory 3. Unitary Government 4. Federal Government 5. Confederate Government 6. Ideas in the Declaration of Independence 7. Virginia Plan 8. New Jersey Plan 9. Connecticut Compromise 10. Three-Fifth’s Compromise 11. Purpose of the Federalist Papers 12. The Anti-Federalist position 13. Bill of Rights 14. Examples of Check and Balance 15. Definition of Separation of Powers 16. Formal Methods of changing the Constitution 17. Definition of Federalism 18. Expressed Powers 19. Implied Powers 20. Inherent Powers 21. Legislative power 22. Reapportionment 23. Redistricting 24. Reynolds v. Sims 25. Necessary and Proper Clause 26. Commerce Power 27. Implied Powers Doctrine 28. McCulloch v. Maryland 29. Gibbons v. Ogden 30. Heart of Atlanta Motel v. United States 31. Filibuster 32. Cloture 33. Provisions of 22nd Amendment 34. Provisions of 25th Amendment 35. Presidential Succession Act 36. Criticisms of the Electoral College 37. Plans for reforming Electoral College 38. President’s military powers 39. President’s legislative powers 40. Actions President may take on a bill U.S. Government Mr. Partin 41. Largest source of federal revenue from taxes 42. U.S. Foreign Policy before World War I 43. U.S. Foreign Policy during the Cold War 44. Structure of the Federal Court System 45. Purpose of the Federal Courts of Appeals 46. Marbury v. Madison 47. How judges are selected for federal courts 48. Writ of certiorari 49. Majority Opinions 50. Dissenting Opinions 51. Civil Rights 52. Civil Liberties 53. Free exercise clause 54. Due Process Clause 55. When laws against seditious speech have been upheld by the Courts 56. In what ways has the government encouraged religion in the U.S.? 57. Writ of Habeas Corpus 58. Exclusionary Rule 59. Substantive Due Process 60. Procedural Due Process 61. 5th Amendment Rights 62. 6th Amendment Rights 63. Historical equality of minority groups 64. Equal Protection Clause 65. Affirmative Action 66. Definition of citizenship 67. De Facto Segregation 68. De Jure Segregation 69. Civil Rights Act of 1964 70. Naturalization process