University of Texas at Brownsville College of Education
advertisement

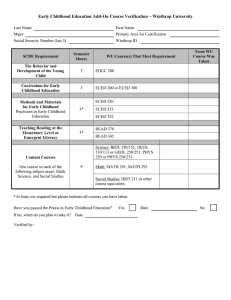
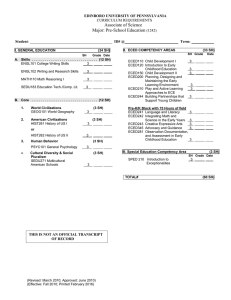
University of Texas at Brownsville College of Education ECED 6302 Curriculum in Early Childhood: Fall 2013 Dr. Georgianna Duarte Phone: O: 882-5710 H: 943-6503 Email: georgianna.duarte@utb.edu COURSE SCHEDULE Course No./Section ECED 4389 ECED 6302 ECED 6307 EDCI 8380.4 Course Name Environments in ECE Curriculum in ECE Emergent Literacy Dissertation II Time 4:25-7:05 4:25-7:05 7:15-10:00 6:00-9:00 Day(s) T W T M Room OFFICE HOURS Monday Tuesday Wednesday 3-5 2-4 2-5 Thursday Friday Course Description: This course will include the major principles of curriculum planning, organization, scope and sequence of a constructivist model. Special emphasis will be given to research on developmentally appropriate early childhood education environments and materials. A major portion of this course will include community based experiences. Please be sure to visit the utb.edu website, explore and examine the graduate school links for news and information through out your academic program: Required Texts: Hendrick, J. & Weissman, P. (2010) Total Learning: Developmental Curriculum for the Young Child, 8th Edition, Merrill Prenctice Hall, Columbus, Ohio Optional Text: Annual Editions , 2013-2014 McGraw Hill Contemporary Learning Series Dubuque, Iowa Kostelnik, M.J. & Sodrman, A. & Whiren, A. (2010) Developmentally Appropriate Curriculum: Practices in Early Childhood Education, Merrill Prentice Hall, Columbus, Ohio Required Readings: There will be a variety of assigned readings throughout the course. Please be sure to carefully organize and save these readings for research, and the comprehensive exam. Also, I will be emailing a variety of web sites regarding constructivism, and providing extensive materials on BB. 1 TBA Course Objectives: The student should be able to: 1. Identify major theorists (past and present) and describe their research and contributions to the field of early childhood education. 2. 3. 4. 5. Identify and describe the Standards for Developmentally Appropriate Curriculum as defined by NAEYC, and the state of Texas. Articulate through seminar the early learning standards, and the NCATE standards for quality curriculum Analyze and critique various curriculum models. Compare and contrast different curriculum models and their theoretical foundations COURSE OBJECTIVES Objectives of Course Standard One Promoting Child development And learning Standard Two: Building Family and Community Relations Standard Three Observing, Documentin g and Assessing Standard Four Using Developmentally Appropriate Approaches Identify major theorists X Identify and describe the Standards of NCATE Articulate the early learning standards and the NCATE standards Analyze and critique various curriculum models Compare and contrast different curriculum models and their theoretical foundations X X X X X X X X X X X X X Standard Five: Using Content Knowledge to Build Meaningful Curriculum X X X X X Standard Six: Becoming A Professional Standard Seven Early Childhood Field Experience s X X X X X X X COE Conceptual Development and Knowledge Base The conceptual framework contains four core concepts, which are themes through which we organize and deliver our programs; hence they are central to our vision of professional educators and scholars. These include: Inter-culturalism Interrelatedness Inquiry Pedagogical Leadership College of Education (COE) Mission Statement To prepare highly skilled professionals to assume roles and positions in teaching, research, educational leadership, and human development. To provide undergraduate and graduate programs based on proven best practice, knowledge acquisition, reflective inquiry, critical thinking, and respect for the cultural and linguistically diverse learner. To continuously develop a dynamic local, state, national, and international, dimension that promotes innovations and contributes to scientific educational, economic, and social change. 2 College of Education (COE) Vision Statement The vision of the College of Education is to be consistently recognized as fully-accredited and as a nationally and internationally respected college in the areas of science, mathematics, educational technology and intercultural dimension (language, literacy, culture and interdisciplinary studies in regard to preparing teachers, counselors, administrators, educational researchers, and professional at all levels, not only for the school system but for other economical and service areas which require training, human resources, development and life-long learning. Teacher preparation programs of the College of Education will be central to the mission of the University and will have national prominence. It will be at the forefront in programs for English Language Learners and, through teacher preparation, P-16 and life-long education initiatives will be a model for helping to close the student achievement gap. All of these will require the COE to be noted for the quality of its graduates, the scholarship of its faculty, and the leadership and service they provide to the local, regional, and national educational communities in the previously mentioned areas. Note: Be advised that the College of Education conducts ongoing research regarding the effectiveness of the programs. You will receive one survey in the final semester prior to graduation regarding the operations of the unit during your time here. A second survey will occur within one year following graduation from or completion of a program, and will be sent to your employer. This survey will focus on the preparation received at UTB/TSC. Please remember that your response to these surveys is critical to UTB/TSC excellence. Description: 3 Emphasis is on a curricular framework that included providing the environment, materials, methods and practices that are developmentally appropriate for young children. Assessment, classroom management, and lesson planning will be addressed. Field based activities will be integrated within the framework of the course (birth through grade three).The UTB website is an important resource of information, and I strongly encourage you to explore, use, and revisit for updates on information, news, and opportunities. Required Texts: Required Websites for EDEC 6302 Please take the time and examine each website carefully for research, advocacy, and service articles. 1. www.aera.org 2. www.ericdigests.org/2001-2/curriculum.html 3. http://www.casel.org/home/index.php 4. www.acei.org 5. www.teachingstrategies.com 6. www.naeyc.org 7. www.nectac.org/ Special Needs Americans with Disabilities Act: Students with disabilities may request assistance through Disability Services , an office of the Counseling Center. Students who need help with registration should contact the office several days before registration. Those who need special services throughout the semester should inform Disability Services several weeks before the semester. Some of the services available include volunteer note takers, taped notebooks, memos to faculty, special test conditions, sign language interpreting and registration assistance. An Adaptive Technology Lab and Testing Service is available for student use. To request services, students must register with the Counselor/Coordinator of Disability Services. All services are elective and must be requested each semester as needed. Permits for parking spaces designated for the handicapped may be obtained at Campus Police, located at Cavalry Hall. Proof of disability is required. TDD users who wish to contact the University by phone may call through Relay Texas at 1-800-735-298. For more information, Contact Disability Services. (956-544-8292) Emergency Academic Continuity Program In compliance with the Emergency UTB/TSC Academic Continuity Program, academic courses, partially or entirely, will be made available on the MyUTBTSC Blackboard course management system. This allows faculty members and students to continue their teaching and learning via MyUTBTSC Blackboard http://myutbtsc.blackboard.com, in case the university shuts down as a result of a hurricane or any other natural disaster. The university will use Blackboard to post announcements notifying faculty members and students of their responsibilities as a hurricane approaches our region. If the 4 university is forced to shut down, faculty will notify their students using Blackboard on how to proceed with their course(s). To receive credit for a course, it is the student’s responsibility to complete all the requirements for that course. Failure to access course materials once reasonably possible can result in a reduction of your overall grade in the class. To facilitate the completion of classes, most or all of the communication between students and the institution, the instructor, and fellow classmates will take place using the features in your MyUTBTSC Blackboard and UTB email system. Therefore, all students must use Scorpion Online to provide a current email address. Students may update their email address by following the link titled “Validate your e-Mail Account” in MyUTBTSC Blackboard Portal. In the event of a disaster that disrupts normal operations, all students and faculty must make every effort to access an internet-enabled computer as often as possible to continue the learning process. Academic Honesty Students are expected to be above reproach in all scholastic activities. Students who engage in scholastic dishonesty are subject to disciplinary penalties, including the possibility of failure in the course and dismissal from the university. "Scholastic dishonesty includes but is not limited to cheating, plagiarism, collusion, the submission for credit of any work or materials that are attributable in whole or in part to another person, taking an examination for another person, any act designed to give unfair advantage to a student or the attempt to commit such acts." Regents' Rules and Regulations, Series 50101, Section 2.2. Since scholastic dishonesty harms the individual, all students, and the integrity of the university, policies on scholastic dishonesty will be strictly enforced. (refer to Student Handbook for more information) UTB/TSC monitors academic progress every fall and spring semester to identify those students who are experiencing difficulty with their courses. Satisfactory Academic Progress (SAP) is based upon two components: GPA of 2.0 or higher and successful course completion of at least 70% of course work attempted. Students remain in good standing with the university and Financial Aid when both criteria are met. Students who do not maintain these required minimum standards will be placed on probation or suspension as appropriate. The complete Satisfactory Academic Progress policy and the Undergraduate Satisfactory Academic Progress for Financial Aid policy can be found in the current Undergraduate Catalog. Class Participation Outstanding Contributor: Contributions in class reflect thorough preparation. Ideas offered are usually substantive, provide one or more major insights as well as direction for the class. Arguments, when offered, are well supported and persuasively presented. If this person were not a member of the class, the quality of the discussion would be diminished significantly. Good Contributor: Contributions in class reflect thorough preparation. Ideas offered are usually substantive, provide good insights and sometimes direction for the rest of the class. Arguments, when presented, are well supportive and are often persuasive. If this person were not a member of the class, the quality of the discussion would be diminished considerably. Adequate Contributor: Contributions in class reflect satisfactory preparation. Ideas offered are sometimes substantive, provide generally useful insights. Arguments are sometimes presented, and are fairly well supported. 5 Non-participant: This person has said little or nothing in the class. Hence, there is no adequate basis for evaluation. Unsatisfactory Contributor: Contribution in class reflects inadequate preparation. Ideas offered are seldom substantive; provide few if any insights, and rarely a constructive direction for the rest of the class. Availability: I check my voice mail and email frequently. Please be sure to leave your complete name, the purpose of your call, and the date of the call. Cell Phones and Pagers: Out of consideration for others, please turn your cell phone and pagers to the silent mode. If you do not have a silent or vibrate mode, please turn them off. Email: It is critical that you check you email account daily, and ensure that the address is accurate, and your mailbox is ready to receive mail. Course Requirements and Method of Evaluation: Assignments: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 8. Chapter Quizzes Three Lesson Plans Reflection Journal on Curriculum Models Unit Plan Observed Lessons Final Exam 140-130 129-119 118-108 107-97 96- 30 30 20 30 30 10 A B C D F Plagiarism: It is plagiarism to go to the internet, find an article, copy it to the clipboard and then drop it into your work processor. Listing the article as reference on the last page will not cover this issue. This is also plagiarism. There are a couple of things you can do that will help prevent yourself from being charged with academic dishonesty. Note the following: 1. Any time that you use the words or ideas of another person without giving credit, it is considered plagiarism. 2. Differences between direct and indirect quotes. A. Direct quotes: include the exact wording from the source. B. Indirect quotes: Summarizes or paraphrases the content from the source. 3. APA in-text requirements: A. Direct Quote: Author's last name, publication date, and page number B. Indirect quote: Author's last name, publication date. 4. Punctuation requirements: Al word for word quotations must be placed in quotation marks. 6 5. Exception to the rule: Common Knowledge-if the same information can be found in three or more sources and those sources don't cite an earlier source the information is considered common knowledge. Also, commonly known facts (e.g., Washington D.C. is the Capital of the U.S.) Do not need a citation even if you had to look them up. When in doubt, CITE *****SECURE & MAINTAIN A CALENDAR & CHECK EMAIL DAILY How to Evaluate Journal Articles [Detailed version of How to Evaluate Journal Articles] To evaluate a journal article look for: Purpose of Article: Why was the article written? To: persuade the reader to do something? inform the reader? prove something? Type of Journal: For college-level term papers, information should be obtained mostly from scholarly journals. See also Evaluation Clues for Articles Taken from the Web Organization and Content: Is the material organized and focused? Is the argument or presentation understandable? Is this original research, a review of previous research, or an informative piece? Bias (of the publisher) Date of Article Bibliography Usefulness: Is the article relevant to the current research project? Authority/author: Is the author an expert in this field? Where is the author employed? What else has he/she written? Has he/she won awards or honors? Coverage: Does the article cover the topic comprehensively, partially, or is it an overview? Audience: For what type of reader is the author writing? Illustrations: Are charts, graphs, maps, photographs, etc. used to illustrate concepts? Are the illustrations relevant? Are they clear and professional-looking? “Service is the rent we pay for being. It is the very purpose of life, and not something you do in your spare time.” Marian Wright Edelman Unit development plan For this assessment you will be asked to create a unit for implementation in the classroom. The unit will be designed for a particular age or grade level. The unit will be multidisciplinary as you will plan activities for all of the content areas. In addition, the unit plan needs a description of how the needs of diverse learners will be met including, special education students, linguistic 7 differences, cultural differences, socioeconomics and gender. The unit should plan activities for a week of instruction. Instructions for the Unit development plan Each student will create a week long unit for a particular setting. Students may use their current setting as the site of instruction. Students will prepare a binder which describes a detailed description of The setting The age group Contextual factors which are significant (gender, special education students, language of the students etc.) For each day of the week the student will prepare lesson plans which will include a description of The content covered The method of instruction The set up of the environment The grouping of the students The inclusion of technology The assessment of the instruction The unit plan addresses standard 1 in that students will need to understand children’s development and the influences on students learning in order to prepare and appropriate unit. For examples what age group are they preparing for and what linguistic background do they have? The unit plan addresses standard 2 in that in order to create an appropriate unit students will need to have knowledge of the children’s family and culture in order to create an appropriate lesson. For example, children from a rural community may have specialized knowledge about farming activities. This might influence how a unit is put together. The unit plan addresses standard 3 in that the candidate will need to know appropriate methods of assessment in order to evaluate the success of the unit. For example paper and pencil tasks may be appropriate assessments for second graders but would not be appropriate in all cases for preschoolers. Standard 4 will be assessed using the unit plan in that the student will have to describe how instruction is being delivered and why. For example, if they are using computers as part of the instruction then they must describe how it is being done age appropriately. Standard 5 will be assess using the unit plan in that students will be required to explain how content is delivered and what content is covered. For example, how does the student integrate content areas such as literacy and math during the school day? Field Experience Description of Assessment 8 Field experience will consist of two placements. The first field placement will occur in ECED 6302 Early Childhood Curriculum. Students are required to be in the field for 10 hours. The second placement will occur in ECED 6308. The field experience in this course is an internship that will consist of a field placement in the candidates’ own classroom. The internship will take place over one semester in which the candidate will complete 40 hours per week for 8 weeks. The two placements will differ in type of classroom setting (preschool, Head Start and public school) and in the age of the children (infant toddler, preschool, school age). In Field Placement #1 (ECED 6302) students will: - Observe to get a general understanding of the classroom environment - Teach three lessons from the unit that was developed in ECED 6302 - Reflect on teaching NAEYC Standards Assessed Standard 1 Advanced Early Childhood Educators are able to use, (1a) Understanding of young children’s characteristics and needs, (1b) Multiple influences on development and learning, (1c) Using developmental knowledge to create learning environments. Standard 2 Advanced Early Childhood Educators are able to use, (2a) Family and community characteristics, (2b) Supportive family relationships, and (2c) Demonstrating cultural competence and effective collaboration. Standard 3 Advanced Early Childhood Educators are able to use, (3a) Assessment goals, benefits and uses, (3b) Using appropriate assessments, (3c) Practicing responsible assessment, (3d) Developing assessment partnerships with families and colleagues Standard 4 Advanced Early Childhood Educators are able to use, (4a) Understanding positive relationships and interactions with young children, (4b) Knowing and understanding effective strategies and tools including technology (4c) Using a broad repertoire of approaches with a high level of cultural competence (4d) Reflecting on practice to promote positive outcomes. Standard 5 Advanced Early Childhood Educators are able to use, (5a) Understanding content knowledge and resources, (5b) Knowing central concepts, inquiry tools and structures of content areas, (5c) Using knowledge to develop meaningful and challenging curriculum. Standard 7 Advanced Early Childhood Educators are able to use, (7a) Opportunities of observe in two of three early childhood age groups, (7b) Opportunities to observe and practice in at least two of three types of settings Lesson Planning ( NAEYC Standard 1 & 5) Needs Improvement 1 Still Developing Proficient 2 3 Understands content, knowledge and resources Understands how 9 Exceeds Expectations 4 the following areas of development relate to planning and organizing instruction: Pphysical, Affective, Cognitive Learning objectives are linked to standards and reflect an awareness of student’s prior experiences Objectives are developmentally and individually appropriate Considers students’ cultural background and interests when planning Plans a variety of effective teaching strategies that take into account the needs of diverse learners Materials and resources are developmentally appropriate, individually appropriate, and culturally appropriate Total Reflecting on Practice NAEYC Standard 4 & 6 Needs Improvement Still Developing Reflects on impact of instruction on student learning and makes adjustments 10 Proficient Exceeds Expectations accordingly Asks supervisor for feedback Utilizes constructive criticism Total Additional Comments: ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ 11 Assessment NAEYC Standard THREE Needs Still Developing Proficient Improvement Exceeds Expectations Understands the goals, benefits, and uses of assessments Uses assessment results to develop appropriate goals, curriculum and teaching strategies Reflects knowledge about and uses observation, documentation and other developmentally appropriate assessment tools and approaches Uses technology in documentation, assessment, and data collection Demonstrates the ability to collaborate effectively to build assessment partnerships with families and with professional colleagues to to build effective learning environments Total Learning Environment Design (NAEYC Standard ONE) Needs Improvement Still Developing Uses developmental knowledge to create supportive challenging learning environments for young children Provides and maintains an attractive and orderly learning 12 Proficient Exceeds Expectations environment Maintains classroom routines and procedures Develops an atmosphere which fosters self discipline Promotes positive interper. relations based upon mutual respect Total 13