The Cell The Basic Unit Quiz 3B
advertisement

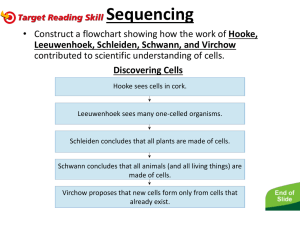
The Cell The Basic Unit Quiz 3B cytology: the study of cells Robert Hooke Anton van Leeuvenhoek Matthias Schleiden Theodor Schwann Rudolf Virchow Robert Hooke Cytology can be traced back over 300 years to the English scientist Robert Hooke. Robert Hooke In 1665 he published Micrographia - a report of his use of simple compound microscopes capable of magnifying approximately 30 times to observe cork. Robert Hooke The neat rows of little boxes reminded him of rows in a prison or a monastery he therefore named the "cells." (“coined”) Robert Hooke In 1665 Robert Hooke was the first to use the term cell. He saw only the dead, empty cell walls of cells. Anton van Leeuwenhoek Around the same time as Robert Hooke, Anton van Leeuwenhoek also began to observe tiny objects with microscopes. Anton van Leeuwenhoek He looked at drops of lake water, scrapings from teeth and gums, and water from rain gutters. Anton van Leeuwenhoek He saw tiny moving organisms which he called “animalcules,” meaning “little animals.” Matthias Schleiden A German botanist In 1838 said, "All plants are composed of cells." Theodor Schwann A German zoologist In 1839 said, "All animals are composed of cells." Rudolf Virchow A German doctor who is referred to as the "Father of Pathology," In 1855 he proposed that new cells are formed only from cells that already exist. The three basic principles of the cell theory All cells come from preexisting cells. All living things are made of cells and of the products of cells. The functions of living things are performed by the cells they are made of. Cellular functions Use energy Manufacture materials Respond to environment Reproduce If the new cells are produced faster than the old cells die, the organism will grow. Some cells, such as certain human brain cells, lose their ability to divide when they become mature.