Major Minerals
advertisement

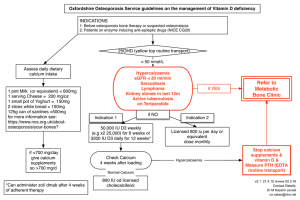
Major Minerals Objectives • After reading Chapter 7 and class discussion, you will be able to: – Define major minerals • Inorganic elements • Micronutrients • Macrominerals • Stability, Indestructible • Calcium, Phosphorous, Potassium, Sodium, Sulfur, Magnesium, Objectives • Define bioavailability (p.226) • Identify recommendations, upper limits for – Calcium, Potassium, Sodium • Describe the functions of – Calcium, Potassium, Sodium • Identify content of foods for – Calcium, Potassium, Sodium • Identify sodium content of salt • Describe how to reduce sodium intake The Minerals • Major minerals –Calcium –Chloride –Magnesium –Phosphorus –Potassium –Sodium –Sulfur • Trace Minerals – Chromium – Copper – Fluoride – Iodine – Iron – Manganese – Molybdenum – Selenium – Zinc The Minerals An Overview Major Minerals • Inorganic elements – Stable; especially in preparation • The body’s handling of minerals – Some are like water soluble vitamins • Potassium-easily absorbed and excreted – Some are like fat soluble vitamins • Calcium-need carriers to be absorbed & excreted; excess stored; toxicity Major Minerals • Concert effect/interaction • Functions varied; primarily – fluid balance and body structure • Variable bioavailability –Binders •Phytates-legumes, grains •Oxalates-spinach, rhubarb Sodium • Hypertension –Salt sensitivity •Fm Hx, Age, DM •Ethnicity; Obesity • Osteoporosis – h NaCl in c h Ca out • Foods Sodium: In Summary • Adequate Intake: – 1500 mg/day (19-50 yr old) [5.5%] – 1300 mg/day (51-70 yr old) – 1200 mg/day (>70 yr old) – 500 mg/day minimum requirement • Upper Limit: 2300 mg/day [18.8%] • Chief functions in the body – Maintains normal fluid and electrolyte balance – Assists in nerve impulse transmission and muscle contraction Sodium: In Summary • Deficiency symptoms – Muscle cramps, mental apathy, loss of appetite • Toxicity symptoms – Edema, acute hypertension • Significant source – Table salt, soy sauce(1t NaCl=2 gNa) – Moderate amounts in meats, milks, breads, and vegetables – Large amounts in processed foods Ubiquitous Sodium •Sodium Everywhere!! •Sodium in the soil. •All foods grown in soil has sodium. •All foods which eat products from the soil contain sodium Where does dietary sodium come from? • 75% salt from manufacturers • 15% from salt added in cooking or at the table • 10% comes from natural content Sodium Decreasing Sodium Intake • Use • Use • Use • Use fresh, whole, unprocessed foods little or no salt in cooking little or no salt at the table other sodium-free spices: – Basil, bay leaves, curry, cumin, garlic, ginger, mint, oregano, pepper, paprika, rosemary, thyme; lemon, vinegar, wine • Use low-salt or salt-free commercial products • READ Labels! Decreasing Sodium •Foods prepared in brine CAUTION •Pickles, olives, sauerkraut •Smoked, processed meats •Bologna, corned/chipped beef, bacon, ham, lunch meat, frankfurters, sausage, salt pork •Smoked/processed fish •Anchovies, caviar, salted/dried cod, herring, sardines, smoked salmon Decreasing Sodium CAUTION • Snack foods • Potato chips, pretzels, salted nuts, crackers • Condiments • Bouillon, MSG, soy, teriyaki, horseradish, catsup, mustard, Worcestershire, barbeque • Cheeses: esp. processed • Canned/instant soup READ the Label • Where’s the sodium in this Appedix A breakfast? – ½ c. orange juice – 1 c. bran flakes – ½ c. skim milk – 1 scrambled egg – 1 slice bacon p. 532, #334 p. 540, #479 p. 520, #121 p. 522, #149 p. 558, #759 Where does the sodium we consume come from? Natural Added Processed Foods Potassium: In Summary • Adequate Intake (AI) for adults: 4700 mg/day; No UL • Chief functions in the body – Maintains normal fluid and electrolyte balance – Facilitates many reactions – Supports cell integrity – Assists in nerve impulse transmission and muscle contractions Potassium: In Summary • Deficiency symptoms – Muscular weakness, arrhythmias – Increased blood pressure – Glucose intolerance – Confusion • Toxicity symptoms – Muscular weakness – Vomiting – If given into a vein, can stop the heart Potassium: In Summary • Significant sources – All whole foods, fresh foods – Meats, milks, fruits, vegetables, grains, legumes Calcium Calcium: In Summary • Chief functions in the body –Mineralization of bones and teeth –Involved in muscle contraction and relaxation, nerve functioning, blood clotting –Blood pressure, immune defenses Calcium: In Summary • 1997 adequate intake (AI) –Adolescents: 1300 mg/day –Adults 19-50 yrs: 1000 mg/day –Adults 51 & older: 1200 mg/day –Elderly women: 1500 mg/day • Upper level for adults: 2500 mg/day Calcium: Controversy • Women’s Health Initiative – Links calcium supplementation to • Vascular calcification, kidney stones • h risk of cardiovascular events – http://www.nhlb.nih.gov/whi/cad.htm • IOM: upper level for women >50: 2000 mg/day • British Medical Journal-61,000 – Fractures only in those with intake CAUTION below 750mg/day – Warensjo, et al, BMJ, 2011:342:d1473 Calcium: In Summary • Deficiency symptoms –Stunted growth in children –Bone loss (osteoporosis) in adults Calcium: In Summary • Toxicity symptoms –Constipation –Increased risk of urinary stone formation and kidney dysfunction –Interference with absorption of other minerals Sources of Calcium Milk and milk products; Small fish with bones; Tofu (bean curds); Greens (broccoli, chard); Legumes Copyright 2005 Wadsworth Group, a division of Thomson Learning Calcium CAUTION • Bioavailability –The degree to which a nutrient is absorbed and available to be used by the body. Osteoporosis And Calcium • Bone development and disintegration – Bone density Healthy vs. osteoporotic trabecular bone Osteoporosis And Calcium • Age and bone calcium • Maximizing bone mass Osteoporosis And Calcium Fig H12-3, p.431 Osteoporosis And Calcium • Physical activity and body weight • Smoking and alcohol Osteoporosis And Calcium • Dietary calcium is the key to prevention • Other nutrients in supporting role – Vitamin D – Magnesium – Sodium – Phosphorus Osteoporosis And Calcium Osteoporosis And Calcium Osteoporosis And Calcium • A perspective on supplements –Antacids –Bone meal –Oyster shell –Dolomite (limestone) Calcium Supplements • Administration: several times/day • Dose at 500mg (or less) • Supplements –Calcium carbonates=40% –Calcium citrate=21% –Calcium lactate=13% –Calcium gluconate=9% Calcium Dissolvability • Drop calcium tablet into 6 oz glass of vinegar • Stir occasionally • Calcium tablet should dissolve in 30 minutes Objectives • After reading Chapter 7 and class discussion, you will be able to: – Define major minerals • Inorganic elements • Micronutrients • Macrominerals • Stability, Indestructible • Calcium, Phosphorous, Potassium, Sodium, Sulfur, Magnesium, Objectives • Define bioavailability • Identify recommendations, upper limits for – Calcium, Potassium, Sodium • Describe the functions of – Calcium, Potassium, Sodium • Identify content of foods for – Calcium, Potassium, Sodium • Identify sodium content of salt • Describe how to reduce sodium intake