Contents • Description of Theory Preconventional
advertisement

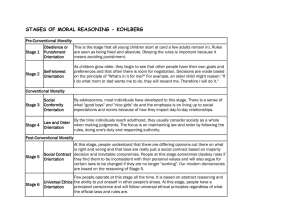
Contents • • • • • • • Description of Theory Preconventional Conventional Postconventional Which Level Are You? (Heinz Dilemma) Practice Lesson Assessment Lawrence Kohlberg (1927-1987) Morality is the system one uses to decide what is right and wrong; how one’s conscience affects choices. Lawrence Kohlberg, a psychologist, explored what motivates individuals to act the way they do. He then devised a theory about how people change their views of what’s right and wrong as they grow. Back to Contents Stages of Moral Development He creates six stages of moral development divided into three levels. Level 1: Preconventional What Is Good for Self Reward & Punishment Usually young children, Very selfish Stage I: Reward/Punishment • Acts to avoid pain or punishment • Wants to not get spanked or get a “time out” Stage II: Reciprocity • Acts to get a reward • Wants to get a hug or a piece of candy or back scratch Back to Contents Level 2: Conventional What Is Good for Others Majority of adults; Conform to expectations and are usually loyal Stage III: Conformity • Acts to gain approval; conforms • Wants to be a “good girl/boy”; wants others to see as nice Stage IV: Law & Order • Acts because of belief in the law and order • Wants society to be orderly and understands duty/respect for authority Back to Contents Level 3: Postconventional What Is Universally Good Minority of adults; Define moral values on own values (do not rely on authority’s definition) Stage V: Principles of Justice • Acts for the welfare of others • Wants other people to be safe and happy; willing to change law if necessary Stage VI: Morality of Christian Love/Agape • Acts because of her/his own conscience/set of beliefs • Wants all human beings to be respected for their dignity, believes in justice and equality; will disregard law if necessary Back to Contents Which level are you? Read the Heinz dilemma to find out… Heinz’ wife was near death. There was one drug on the planet that could save her, and it was only sold in Heinz’ hometown. The druggist who was selling it, however, was charging ten times what it cost to make the drug. Heinz couldn’t afford the drug. He tried borrowing money from his friends and family, and could only come up with half of the cost of the drug. He explained his problem to the druggist, but the druggist refused to sell him the drug for less money, and he also refused to let Heinz pay the second half later. Heinz decided that he had to steal the drug. Should Heinz have stolen the drug? A. YES B. NO Because… A. he would get in trouble from his family members for not getting help B. he can risk his life if he thinks he can get away with it C. no one will respect him if he lets her die D. it’s his duty to his wife, he should pay later and accept the law’s penalty E. the law wasn’t meant to violate life, the law should be reinterpreted if he is caught F. if he didn’t steal it, he’d be putting another value above that of life; respect for property should not be above the respect for life; there shouldn’t be private property; it is everyone’s duty to help the dying Because… A. he would go to jail B. it’s more risk than it’s worth C. everyone will think he’s a criminal D. because even though his natural duty is to obey the law, it would create violence/crime if every store owner were charging excessive prices You are… Stage I: Reward/Punishment • Acts to avoid pain or punishment • Wants to not get spanked or get a “time out” On to Practice You are… Stage II: Reciprocity • Acts to get a reward • Wants to get a hug or a piece of candy or back scratch On to Practice You are… Stage III: Conformity • Acts to gain approval • Conforms • Wants to be a “good girl/boy” • Wants others to see as nice On to Practice You are… Stage IV:Law & Order • Acts because of belief in the law and order • Wants society to be orderly and understands duty/respect for authority On to Practice You are… Stage V: Principles of Justice • Acts for the welfare of others • Wants other people to be safe and happy; willing to change law if necessary On to Practice You are… Stage VI: Morality of Christian Love/Agape • Acts because of her/his own conscience/set of beliefs • Wants all human beings to be respected for their dignity, believes in justice and equality; will disregard law if necessary On to Practice Practice Directions: Choose the correct level of moral reasoning for each example. Example #1 If I make my neighbor a present and give it to her, she’ll be very happy. A. B. C. D. E. F. Stage 1: Reward/Punishment Stage 2: Reciprocity Stage 3: Conformity Stage 4: Law and Order Stage 5: Principles of Justice Stage 6: Morality of Christian Love/Agape Example #2 If I leave my bicycle in the middle of the front yard, I will be punished. A. B. C. D. E. F. Stage 1: Reward/Punishment Stage 2: Reciprocity Stage 3: Conformity Stage 4: Law and Order Stage 5: Principles of Justice Stage 6: Morality of Christian Love/Agape Example #3 In order to stay true to my personal code of morals, I need to protest the dictatorship of the government. A. B. C. D. E. F. Stage 1: Reward/Punishment Stage 2: Reciprocity Stage 3: Conformity Stage 4: Law and Order Stage 5: Principles of Justice Stage 6: Morality of Christian Love/Agape Example #4 If I obey the speed limit, the roads will be safer for everyone. A. B. C. D. E. F. Stage 1: Reward/Punishment Stage 2: Reciprocity Stage 3: Conformity Stage 4: Law and Order Stage 5: Principles of Justice Stage 6: Morality of Christian Love/Agape Example #5 If I want to protest a government policy or action, the Bill of Rights guarantees my freedom to do so. A. B. C. D. E. F. Stage 1: Reward/Punishment Stage 2: Reciprocity Stage 3: Conformity Stage 4: Law and Order Stage 5: Principles of Justice Stage 6: Morality of Christian Love/Agape Example #6 If I do the dishes for my father, he will take me to the baseball game. A. B. C. D. E. F. Stage 1: Reward/Punishment Stage 2: Reciprocity Stage 3: Conformity Stage 4: Law and Order Stage 5: Principles of Justice Stage 6: Morality of Christian Love/Agape Back to Contents You are correct! Great Job On to example 1 2 3 4 5 6 OR On to lesson assessment Oops! That answer is incorrect. Try Again. Back to example 1 2 3 4 5 6 OR On to lesson assessment Lesson Assessment • Click on the link below. Type answers, print, and hand in. It's a Dilemma.doc Back to Contents