Bible Sacred Scripture Testament
advertisement

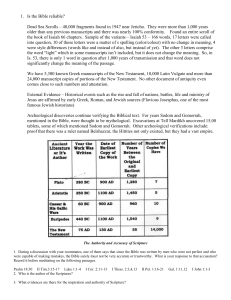
Topic: The Bible Notes Bible = book Sacred Scripture = Holy Writings Testament = Covenant Written by humans, inspired by God. God is the source of the Bible’s power. Passed down throughout the generations via oral tradition. Originally written in Greek (not English). Text appears in many literary forms; for example: Poetry, allegory, short story, historical novel, parables and speeches. Created in a 5 step process: Community's experience of God; Oral Tradition; Written, Edited, Chosen for significance and included as official Canon. Perceived from 3 basic approaches: historical, theological and inspirational. Hebrew and Christian Scriptures = Old and New Testaments are the 2 parts of the Bible. Hebrew Scripture = 46 books, divided into four sections. Begins with the book of Genesis and ends with Malachi. Teaches about the relationship between God and God's people, the Hebrews. Section I: The Pentateuch (5 books) Genesis through Deuteronomy Also known as the Torah or “Law”, are the central stories of the Hebrews. Contain the stories of Creation, Noah and the Great flood and the Exodus. II: The Historical Books Joshua through 2Maccabees Tells of Israel’s kings and the continued evolution of Judaism after the Exile. Contain the stories of Kings David and Solomon. III: The Wisdom Books Job through Ecclesiasticus, including the Psalms Uses human experience to help understand and solve life’s problems. Teaches how to be fair and just in our everyday existence. Contains the Psalms (150 songs) which express a very wide range of human emotion and sentiment. IV: The Prophetic Books Isaiah through Malachi Expresses judgments of human moral conduct, personal responsibility and passionately speaks out against idolatry. Christian Scripture = 27 books, divided into four sections. Begins with the book of Matthew and ends with Revelation Teaches about Jesus of Nazareth as Lord and Savior to the People of God. The New Testament speaks about Jesus as the fulfillment of the prophecies proclaimed in the Hebrew Scripture. Section I: The Gospels Matthew, Mark, Luke and John Stories of the life, death and Resurrection of Jesus Each written for a particular audience II: The Acts of the Apostles (The Gospel of the Holy Spirit) The continuation of Luke’s Gospel, tells of the development of the church after the resurrection of Jesus III: The Epistles (letters) Romans through Jude 21 letters written to various communities, authored by Paul, James, Peter, John and Jude. Designed to teach and encourage the early believers IV: Revelation (The Apocalypse) Calls Christians to be faithful and trust that God will always be victorious. Gave hope to early Christians being persecuted by the Romans Full of symbolic meanings and images, not to be read literally