PROGRESSIVE ERA 1889-1920
advertisement

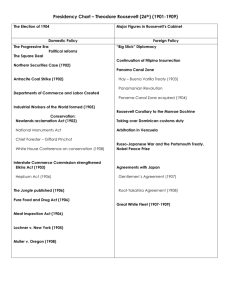
PROGRESSIVE ERA 1889-1920 Muckrakers •Name applied in 1906 by Pres. Theodore Roosevelt to a group of journalists who exposed the abuses of power and corruption in American political and business life. •They were largely responsible for mobilizing public opinion in favor of the progressive reform of the period. Upton Sinclair - The Jungle IDA TARBELL - HISTORY OF THE STANDARD OIL CO. FRANK NORRIS - THE OCTOPUS Lincoln Steffens - The Shame of the Cities Jacob Riis - How the Other Half Lives Ida B Wells Barnett - The Color Line Goals of Progressivism 1. Protecting Social Welfare a. Worked to soften some of the harsh conditions of industrialization b. Social gospel – preached salvation through service to the poor c. Settlement house movement – community centers in slum neighborhoods that provided assistance to people in the area 1. Health care 2. Education 3. Jobs 4. Language classes 5. Etc. 2. Promoting Moral Improvement: • Wanted people to uplift themselves by improving their personal behaviors • Ex. Prohibition Movement (ban alcoholic beverages) • 1872 WCTU – spearheaded the movement • By 1911 - 245,000 members • Group did much more than fight for prohibition: a. Worked for suffrage b. Visited prisoners and asylums c. Opened Kindergartens for immigrants 3. Creating Economic Reform •Big business often received favorable treatment from government officials and could use its economic power to limit competition. 4. Fostering Efficiency • • Put their faith into experts and scientific principles to make society and the workplace more efficient. • Ex. Muller v Oregon Justice Brandeis used data produced by social scientists to show how working long hours affected women and thus cost society. •Scientific management - time and motion studies to improve efficiency by breaking manufacturing tasks into simple parts “Taylorism” Reforms for Children, Workers, and Voters 1. Movement for Social Justice a. Settlement House Movement - located in immigrant neighborhoods • Provided services to those in the community • Taught English • Arts • Music • Children’s activities • Health care • Help with finding jobs • Etc. • Jane Adams – 1889 – Hull House - Chicago Jane Adams Hull House Lillian Wald Henry Street Library b. Child labor laws by 1914 every state had laws “on the books” • 1916 – Keating Owen Act – prohibited the shipment of products made with child labor, Ruled unconstitutional in 1918. • 1924 – child labor amendment was approved by Congress but was not ratified by the required three-fourths states • 1938 – Fair Labor Standards Act - abolished child labor in interstate industries. 2. Movement to Regulate Business and Labor A. Lochner v. New York (1905) A New York state law ruled that bakery workers could not work more than 60 hours a week including overtime. Court declared the law illegal – denied businesses due process. B. Muller v. Oregon (1908) An Oregon law prevented women from working more than 10 hours a day. Court declared the law constitutional. Used scientific studies for first time to help make decision. 3. Reforms in the Election Process a. Initiative b. Referendum c. Recall d. Primaries e. Secret Ballot Many of these reforms were the results of the Populists platform. Wisconsin became known as the “Progressive State” and Governor Robert LaFollette was known as the “father of Progressivism”. President Theodore Roosevelt (1901-1909) Roosevelt was a conservative, but did not hesitate to use the power of the presidency to deal directly with social and economic problems. Saw his job as one of stewardship - responsible for the welfare of all. Domestic policy became know as the “Square Deal” Reforms fell into three categories: 1. Regulating Business: A. Reputation as a “trust buster” Broke up over 40 trusts during his administration. Saw a difference in a “good trust” and a “bad trust” Felt that size did not immediately make a business bad. B. Northern Securities v. U.S. Northern Securities was a holding company – controlled the railroad system of the Pacific Northwest in 1904. Supreme Court ruled that the holding company had to be dissolved because it was in restraint of trade. C. Coal Strike: • Roosevelt called labor members and owners to a meeting to settle the strike D. Court cases • Lochner v. New York - 1905 • Muller v. Oregon – 1908 E. Legislation • • Elkins Act – 1903 - barred rebates Hepburn Act – 1906 – gave Interstate Commerce Commission power to nullify unreasonable railroad rates. •Commerce Dept. founded – 1903 2. Protecting the Consumer • • Meat Inspection Act – 1906 - est. health and sanitary conditions in the meatpacking industry. Pure Food and Drug Act – 1906 - banned harmful additives in food and misleading advertisement. 3. Conserving Natural Resources • Newlands Reclamation Act – 1902 – provided that money from the sale of desert land in the West be used to finance irrigation projects. •Forest Homestead Act – 1906 – opened up certain forest lands for agricultural use. •Inland Waterways Act – 1907 – provided for the appointment of a commission to study the use of the nation’s major rivers •National Park System - established with Gifford Pinchot as the head. •Antiquities Act – 1906 – Provided that sites of historic and/or scientific interest be placed under national protection •1907 – barred the cutting of trees on 150million acres •Of government timberland