VSEPR: covalent structure The COVALENT BOND
advertisement

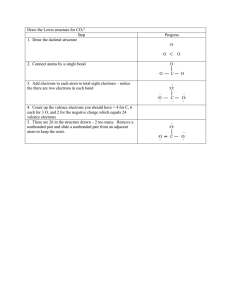
VSEPR: covalent structure The COVALENT BOND 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Electrons are NOT transferred. Electrons are shared between the nuclei of the two atoms in a bond A single covalent bond is a PAIR of shared electrons between two nuclei. A double covalent bond is 2 PAIR of shared valence electrons. Non-polar covalent bonds have an ionic character of 0.0. Ionic character of above 0.0 to about 0.4 are so weakly polar that their polarity is negligible. Compounds with an ionic character of 0.4 to 1.7 are polar, UNEQUAL sharing of the electron pairs. Covalent boding is the only type of bonding that creates molecules, these molecules have definite geometry. VSEPR: valence shell electron pair repulsion theory OBJECTIVES: -To Construct Lewis Dot Structures for Covalent Compounds AND ACCOUNT FOR EACH VALENCE ELECTRON IN THE STRUCTURE.. -To calculate molecular geometry -To assess symmetry of the molecules. • THE VSEPR METHOD AND PROCESS. • STEP ONE: CALCULATE THE VALENCE ELECTRONS – • STEP TWO; DRAW WITH SINGLE BONDS ONLY – – – • PLACE THE LEAST ELECTRONEGATIVE ATOM IN THE CENTER. H CANNOT BE IN THE CENTER EVEN IF LEAST ELECTRONEGATIVE. SINGLE BOND IT TO THE SURROUNDING ATOMS (LIGANDS) STEP THREE: – – • MULTIPLY EACH BOND BY 2 TO GET THE ELECTRONS THAT ARE INVOLVED IN BONDING. SUBTRACT THE BONDING ELECTRONS FROM THE VALENCE ELECTRONS. STEP FOUR-A: – • ADD THE GROUND STATE VALENCE ELECTRONS OF EACH ATOM IN THE SUBSTANCE. DRAW ELECTRONS AS DOTS TO COMPLETE THE OCTET OF EACH ATOM (EXCEPT H), SUBTRACT THOSE ELECTRONS FROM THE TOTAL THAT REMAIN IN STEP THREE. STEP FOUR-B: PLACE ANY REMAINIG ELECTRONS ON THE CENTRAL ATOM • • • • • Example one, ammonia, NH3 STEP ONE – ADD VALENCE ELECTRONS ( first use ionic character to verify covalent bonding). – N has 5 valence electrons ( 2-5) : 5 – Each of the 3 H atoms has one electron : 3 8 electrons total STEP TWO – DRAW, here N must be central as H cannot 2 bonding e- H H N H • • • • Example one, ammonia, NH3 STEP ONE – ADD VALENCE ELECTRONS. – N has 5 valence electrons ( 2-5) : 5 – Each of the 3 H atoms has one electron : 3 8 electrons total STEP TWO – DRAW, here N must be central as H cannot 4 bonding e- H H N H • • • • Example one, ammonia, NH3 STEP ONE – ADD VALENCE ELECTRONS. – N has 5 valence electrons ( 2-5) : 5 – Each of the 3 H has one electron : 3 8 electrons total STEP TWO – DRAW, here N must be central as H cannot 6 bonding e- H H N H • • • Example one, ammonia, NH3 STEP ONE – ADD VALENCE ELECTRONS. – N has 5 valence electrons ( 2-5) : 5 – Each of the 3 H has one electron : 3 8 electrons total STEP TWO – DRAW, here N must be central as H cannot ( 8 total electrons ) – ( 6 bonding e- ) = 2 remain, place on central atom (N) H H N H H N H H 1. The ammonia molecule has ONE UNBONDED PAIR of electrons and THREE COVALENT BONDS: one pair and three bonds. 2. This pattern indicates a TRIGONAL PYRAMIDAL GEOMETRY.